base composite number cube number exponent exponential form
advertisement

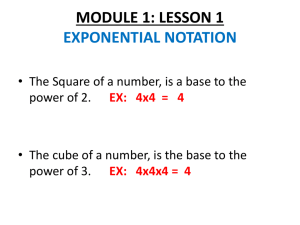
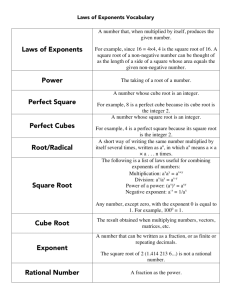
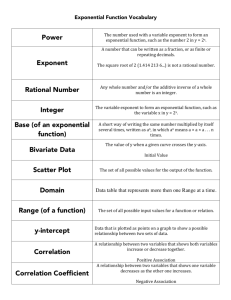
base composite number cube number exponent exponential form factor greatest common factor (GCF) lowest common multiple (LCM) multiple pattern perfect cube perfect square power prime number square number square root The factor repeated in a power. 4 Example: 3 is the base in the exponent 3 . A number with three or more factors. Example: 8 is a composite number because its factors are 1, 2, 4, and 8. A power with exponent 3. 3 Example: 8 is a cube number because 8 = 2 A number, shown in a smaller and raised (superscript), that tells how many times the number before it is used as a factor. 5 Example: 5 is the exponent in 2 A representation of a product in which a number called the base is multiplied by itself. The exponent is the number of times the base appears in the product. Example: 54 is in exponential form, where 5 is the base and 4 is the exponent. 54 means 5 x 5 x 5 x 5. Natural numbers that divide evenly into a given natural number. Example: The factors of 12 are 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, and 12, because all of these numbers divide evenly into 12. The largest factor that two or more numbers have in common. Example: The greatest common factor of 16 and 24 is 8. The lowest multiple that is the same for two numbers. Example: The lowest common multiple of 12 and 21 is 84. The product of a given number and a natural number. Example: Some multiples of 8 are 8, 16, 24, and 32. Any attribute that repeats. Examples: ◊ ◊ ◊ …, 25,50,75,100…, 1,4,9,16,25... A number that can be expressed as the product of three identical natural numbers. Example: 8 = 2 x 2 x 2; thus 8 is a perfect square. A number that can be expressed as the product of two identical natural numbers. Example: 9 = 3 x 3; thus 9 is a perfect square. A number written in exponential form; a shorter way of writing repeated multiplication. 3 Example: 4 x 4 x 4 can be expressed as 4 in exponential form. A whole number greater than 1 that has only two factors, itself and 1. Examples: 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 29, 31, and 43. The product of a number multiplied by itself. Example: 25 is the square of 5 because 5 x 5 = 25. A number which, when multiplied by itself, results in a given number. Example: 5 is a square root of 25, because 5 x 5 = 25.