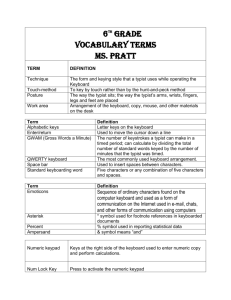
Alphabetic keys- Letter keys on the keyboard
advertisement

1. Technique- The form and keying style that a typist uses while operating the Keyboard 2. Touch-method- To key by touch rather than by the hunt-and-peck method 3. Posture- The way the typist sits; the way the typist’s arms, wrists, fingers, legs and feet are placed 4. Work area- Arrangement of the keyboard, copy, mouse, and other materials on the desk 5. Alphabetic keys- Letter keys on the keyboard 6. Enter/return- Used to move the cursor down a line 7. GWAM (Gross Words a Minute)- The number of keystrokes a typist can make in a timed period; can calculate by dividing the total number of standard words keyed by the number of minutes that the typist was timed 8. QWERTY keyboard- The most commonly used keyboard arrangement. 9. Space bar- Used to insert spaces between characters. 10. Standard keyboarding word- Five characters or any combination of five characters and spaces. 11. Emoticons- Sequence of ordinary characters found on the computer keyboard and used as a form of communication on the Internet used in email, chats, and other forms of communication using computers 12. Asterisk- * symbol used for footnote references in keyboarded documents 13. Percent- % symbol used in reporting statistical data 14. Ampersand- & symbol means “and” 15. Numeric Keypad- Keys at the right side of the keyboard used to enter numeric copy and perform calculation. 16. Num Lock Key- Press to activate the numeric keypad. 17. Application Software- Software designed to meet the user’s needs; performs a specific task. 18. CD-ROM- A compact disk that reads only memory. 19. Computer- An electronic device that receives, processes, stores, and outputs data. 20. CPU- Central Processing Unit; the brain of the computer. 21. Data- Text, numbers, sounds, and images entered into the computer to be processed. 22. Floppy Disk- A storage device; most common size is 3 1/2 and is sometimes called a diskette. 23. Dot-Matrix Printer- Uses dots to form words and images on paper. 24. File- A document stored on a disk. 25. Hard Copy- A printed copy of output. 26. Hard Disk/Hard Drive- A device that holds information such as software and files. 27. Hardware- The physical, touchable parts of a computer system. 28. Information Processing Cycle (IPOS)- The practice of handling data consisting of input, process, output, and storage. 29. Inkjet Printer- Sprays ink through small holes to form words and images on paper. 30. Input- The process of entering information (data) into a computer. 31. Keyboard- Contains letters, numbers, symbols, function keys; like a typewriter and a numeric keypad. 32. Laptop Computer- Designed to be small and light enough to be used on your lap. 33. Laser Printer- Uses light beams and toner to form words and images on paper. 34. Notebook Computer- Designed to be used on a desktop but still small enough to be portable. 35. Output- The results of processed data that is displayed in some form. 36. Peripheral Devices- Devices attached to a computer to expand its ability to perform more tasks. 37. Processing- Executes or carries out the instructions given to the computer. 38. RAM- Random Access Memory; temporary storage; is lost when computer is turned off. 39. ROM- Read Only Memory; permanent storage; user can not change. 40. Scanner- A device that sends data to a computer to make a hard copy. 41. Soft Copy- Output that is not in printed form; such as what is seen on a monitor 42. Software- Instructions for the computer; application and operating system. 43. Storage- A device that stores/saves data until needed. 44. System Software- Program that controls the operation of the computer. 45. Virus Protection Software- A program that protects a computer from computer viruses. _________________________________________________________________________ 46. Editing- The process of correcting or making changes to a document. 47. Error- Any keying or spacing mistake found in a document. 48. Grammar Check- The word processing feature that checks your document for grammatical errors. 49. Peer Editing- Allowing someone else to proofread a document before keying a final copy. 50. Proofreader Marks- Symbols that are used to mark corrections and changes to a document. 51. Proofreading- The process of comparing a copy on screen or paper to the original copy and marking errors to be corrected. 52. Punctuation Spacing- The distance on either side of a punctuation mark. 53. Spell Check- The word processing feature that checks your document for incorrectly spelled words. 54. Thesaurus- The word processing feature that identifies synonyms for the words in a document. 55. Alignment- The way multiple lines of text line up along the left, right, or both margins. 56. Bullets and Numbering- A word processing feature used to arrange items in a list with each item beginning with a bullet or number. 57. Center Align- The alignment of text between both margins, leaving a jagged left and right margin. 58. Clipboard- The temporary storage location for text or graphics that have been cut or copied. 59. Copy- The word processing feature that allows text or graphics to be copied to another location within a document. 60. Cursor- The on-screen blinking character that shows where the next character will appear. 61. Cut- The word processing feature that removes text or graphics from the current location in a document. 62. Double Space- When one blank line is left between lines of text; striking the enter key twice. 63. Editing- The process of updating a document to make changes, correct errors, and make it visually appealing. 64. Font- A specific design for a collection of letters, numbers, and symbols. 65. Footer- Allows you to type information below the bottom margin of each page of a document. 66. Formatting- The way text appears, for example: bold, underline, all caps, with color. 67. Function Keys- Allow you to quickly access frequently used functions. 68. Grammar check- The word processing feature that checks selected words in a document for grammatical errors. 69. Header- Allows you to type information above the top margin of each page of a document. 70. Horizontal Centering- When text is centered between the left and right margins, commonly used when creating invitations, announcements, and title pages. 71. Justified- The alignment of text along the left and right margin, leaving a no jagged edges. 72. Landscape- The page orientation in which the width of the page is greater than the height. 73. Left Align- The alignment of text along the left margin, leaving a jagged right margin. 74. Line Spacing- The spacing betweens lines of text within a document. 75. Margins- The blank space at the top, bottom, left, and right of a document where you cannot type. 76. Menu Bar- Provides you with a menu of options to use when creating a document. 77. Operational Keys- Allow you to operate the computer without a mouse. 78. Orientation- The direction in which you can print on a page (portrait or landscape). 79. Paste- The word processing feature that places text or graphics that have been cut or copied in a new location within a document. 80. Portrait- The page orientation in which the height of the page is greater than the width. 81. Quadruple Space- When three blank lines are left between lines of text; striking the enter key four times. 82. Right Align- The alignment of text along the right margin, leaving a jagged left margin. 83. Scroll Bars- Allow you to scroll throughout a document that is too long to fit on one screen. 84. Single Space- When no blank lines are left between lines of text; striking the enter key one time. 85. Spell Check- The word processing feature that checks your document for incorrectly spelled words, similar to an electronic dictionary. 86. Thesaurus- The word processing feature that allows you to find words with similar meanings (synonyms) for the text within a document. 87. Title Bar- Displays the filename of a document. 88. Tool Bars- Provide you with buttons that allow you to access frequently used commands. 89. Triple Space- When two blank lines are left between lines of text; striking the enter key three times. 90. Vertical Centering- When text is centered between the top and bottom margin, commonly used when creating invitations, announcements, and title pages. 91. Word Processing- Application software that is used to create text documents such as letters, memos, and reports. 92. Word Wrap- The automatic wrapping of text from the end of one line to the beginning of the next line without having to press the enter key. 93. Block Style- The paragraph format in which all lines of text are aligned with the left margin. 94. Hanging Indent- A temporary left margin that indents all lines but the first line of text. 95. Indented- The paragraph format in which the first line of the paragraph is indented. 96. Tab- The operational key of the keyboard that is used to indent paragraphs; moves the cursor 5 spaces in a line. 97. Attachment Notation- A special notation at the end of a memo or letter that indicates that an item is attached to the letter or memo. 98. Block Style- A keying style for a letter or memo in which all the text is aligned at the left margin. 99. Body- The main text of a personal letter, business letter, memo, email, or report. 100. Copy Notation- Use lowercase (c) by the name of the persons to receive a copy. 101. Double space- Pressing the Enter key twice leaving one blank line. 102. Email Heading- Includes the same information as the memo heading. 103. Entry- Information following the words in the memo heading. The tab key is used to align each entry. 104. Memorandum (Memo)- A written message used by employees within an organization to communicate with one another. 105. Single Space- Pressing the enter key one time leaving no blank lines. 106. Typists Initials- The lowercase initials of the keyboard operator and is keyed at the left margin a double space below the writer’s name.