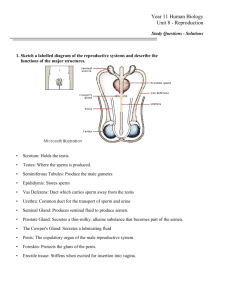
concept map
advertisement
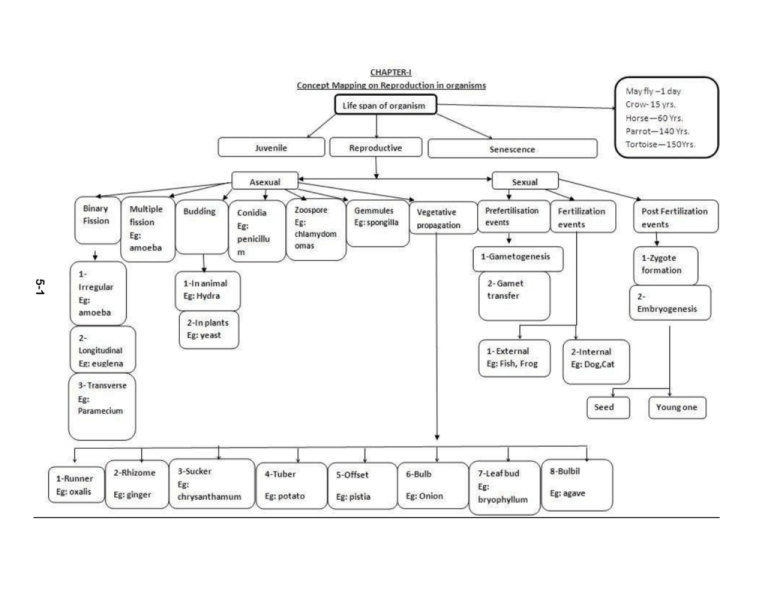
5-1 CHAPTER- 2 Sexual reproduction in flowering plants 8-1 (CHAPTER-3): HUMAN REPRODUCTION REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM PARTS EVENTS OF REPRODUCTION FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM ACCESSORY GLANDS PARTS GAMETOGENESIS MENSTRUAL CYCLE ACCESSORY GLANDS FERTILISATION Proliferative Phase PARTURITION EMBRYONIC DEVELOPMENT Testis Cowper’s Gland Ovary Lobules (Follicular) CLEAVAGE Scrotum Prostrate Gland Oviduct Alveoli Luteal Phase MORULA Seminiferous Seminal Vesicle Uterus Tubules (Secretory phase) BLASTULATION Tubules Cervix Mammary Ducts Menstrual Phase GASTRULATION Vasa Efferentia Vagina Ampulla (Degenerative Phase) ORGANOGENESIS Epididymis External Lactiferous Ducts Vas Deferens Genitalia Ejaculatory duct Penis SPERMATOGENESIS HORMONAL REGULATION 12-1 HYPOTHALAMUS GnRH PROCESS SPERMATOGONIAL CELLS (2N) FSH Puber ty SPERMATID (N) SPERMIOGENESIS INHIBIN TESTOSTERONE SPERMATOZOA (N) INHIBITS SPERM PRODUCTION STIMULATES SPERMATOGENESIS Release of Sperm (SPERMIATION) GnRH Meiosis I completed ANTERIOR PITUITARY Unequal Division (N) First Polar Body Spermiogenesis ANDROGEN HYPOTHALAMUS PRIMARY OOCYTE (2N) SECONDARY SPERMATOCYTE (N) SERTOLI CELLS HORMONAL REGULATION OOGONIAL CELLS (2N) Meiosis I Meiosis II LEYDIG CELLS PROCESS PRIMARY SPERMATOCYTE (2N) ANTERIOR PITUITARY LH OOGENESIS LH SECONDARY OOCYTE(N) (Small) GRANULOSA CELLS FSH CORPUS LUTEUM ESTROGEN (Large) Mature (Metaphase of Meiosis II) Second Polar Body(Small) ESTROGEN ESTROGEN PROGESTERONE OVUM (N) Release of Ovum (N) (OVULATION) -ve feedback High level INHIBITS GnRH SECRETION HUMAN REPRODUCTION MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM TESTIS SCROTUM contains SEMINIFEROUS PENIS ACCESSORY DUCTS Testes within Testes Urination & Vasa Efferentia organ for transfer Transfer Sperm Tubules Epididymis Produces maintains low temp. for Spermatogenesis Site for Spermatogenesis COWPER’S GLAND (Bulbo-urethral gland) 12-2 Produces lubricating fluid to Penis OVARY Located in Lower abdomen Produces ovum Leads to vas deferens Urethra Stores Sperm Stores & till maturation PROSTATE GLAND Vas Deferens Leads to of Sperm Sperm ACCESSORY GLANDS accomodates TUBULES Densely coiled tubules Seminiferous FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM transport Sperm SEMINAL VESICLE Provides alkaline fluid for protection Secretes seminal plasma of sperm from vaginal acidic media Contains Fructose, Calcium & Enzymes Supply nutrient for sperm maturation FALLOPIAN TUBE UTERUS Connecting tube from ovary consists of CERVIX Pear shaped wall Consists of VAGINA Small canal Birth canal Connects uterus Remain closed by Peri-, Myo- & Endometrium to vagina EXTERNAL GENITALIA Consists of Labia Minora Labia Majora Mons Pubis ACCESSORY GLANDS (Mammary Gland) Clitoris membranous Hymen Receives Sperm INFUNDIBULUM Possess finger like Projections Ovulation Collect ovum AMPULLA Transport Mature Sperm ISTHMUS Transfer Fertilized ovum LOBES Contain Alveolar cells Site of development of Embryo Endometrium allows impregnation of Embryo by Placenta Endometrium degenerates resulting Menstruation ALVEOLI secretes Milk TUBULES MAMMARY DUCTS Tubes from alveoli Transport milk to duct AMPULLA Transport milk to Transport milk to ampulla Lactiferous duct LACTIFEROUS DUCTS Stores milk CONCEPT MAP (C3) GAMETOGENESIS HORMONAL REGULATION SPERMATOGENESIS (Process of production of male gamete i.e. sperm) OOGENESIS HYPOTHALAMUS SPERMATOGONIAL CELLS (2n) (Process of production of female gamete i.e. ovum) GnRH secretion increased (Undifferentiated diploid cells within Spermatogenesis Seminiferous tubules) LH OOGONIAL CELLS (2n) ANTERIOR PITUITARY ACTIVATION Activates FSH LH Oogenesis Activates (Undifferentiated diploid cells within Ovary) FSH Mitosis Embryonic stage till Birth (2n) Differentiates & Multiplies (2n) LEYDIG CELLS PRIMARY SPERMATOCYTE (2n) Stimulates SERTOLI CELLS Stimulates -ve feedback GRANULOSA CELLS CORPUS LUTEUM ESTROGEN synthesise 12-3 Meiosis I ANDROGEN SECONDARY SPERMATOCYTE (n) PRIMARY OOCYTE (Remain temporarily arrested till Puberty) SPERMIOGENESIS INHIBIN ESTROGEN PROGESTERONE Produces TESTOSTERONE Prophase I (Meiosis I) synthesise Synthesis of Meiosis II Initiates Differentiation during ESTROGEN Puberty Meiosis I completed Unequal Division (n) INHIBITS SPERM PRODUCTION -ve feed back High level First Polar Body(Small) SECONDARY OOCYTE(Large) (n) SPERMATID (n) STIMULATES SPERMATOGENESIS INHIBITS GnRH SECRETION Mature (Metaphase of Meiosis II) Spermiogenesis SPERMATOZOA (n) Release of Sperm (n) (SPERMIATION) Second Polar Body(Small) OVUM (n) Release of Ovum (n) (OVULATION) CONCEPT MAP (C4) PHASES OF MENS TRUAL CYCLE (Occurs in female at puberty) MENSTRUATION PHASE(3-5 days) FOLLICULAR/PROLIFERATIVE PHASE(6-12 days) (In absence of fertilization of ova ) (Reduced concentration of Gonadotropin) Rupture of endometrium lining of uterus Stimulates Hypothalamous Release of blood, serous fluid, (Begins after ovulation) Secretion of LH release of GnRH mucosa, unfertilized ova LUTEAL/SECRETORY PHASE(12-14 days) Inhibits Corpus Luteum formed ANTERIOR PITUITARY(Activated) secretes Gonadotropin produced LH Inhibin FSH Estrogen (less secretion) Ovarian follicle enlarges 12-4 (Stimulated by LH) Bind with Granulosa cells Synthesize Estrogen High level of LH Inhibin (less secretion) Thickening of Endometrium In absence of fertilisation Uterine wall ready for Implantation Regression of Corpus Luteum Synthesize CORPUS ALBICANS Estrogen & Progesterone Maturation of secondary oocyte OVULATION (More secretion) Corpus Luteum Increased secretion Release of Ovum Progesterone Endometrial wall breaks leading to MENSTRUATION Endometrium prepares for implantation Inhibits contraction of uterus Rupture of Graafian Follicle EMBRYONIC DEVELOPMENT CONCEPT MAP(C5) MALE GAMETE FEMALE GAMETE Fusion Penetration of Sperm FERTILIZATION Activation of Ovum ZYGOTE Fusion of sperm & egg nucleus CLEAVAGE (Holoblastic,Equal) (Repeated division by Furrowing ) BLASTOMERE Outer Cell Mass TROPHOBLAST MORULA (Develops into Placenta) Inner Cell Mass BLASTULATION 12-5 IMPLANTATION IN UTERINE WALL BLASTODERMIC VESICLE / BLASTOCYST TROPHOBLAST / TROPHOECTODERM (consists of) BLASTOCOEL GASTRULATION (Movement of cells to form ) Primary Germinal Layer MORPHOGENETIC PLACENTA MOVEMENT YOLK SAC (Development of) AMNION (3 germinal layers) CHORION (Vacuolated space within Blastula) (Formation of) ALLANTOIS (Outer wall of Blastocyst) ENDODERM Enlargement of Blastodermic vesicle Proliferation of cells from inner cell mass of Embryonic disc MESODERM Proliferation of cells from caudal region ECTODERM Remaining cells of Embryonic disc of Embryonic disc Move out to form Mesodermal layer Arrange towards periphery to form Ectodermal layer Push out into Blastocoel to form Primitive Gut ORGANOGENESIS Formation of cap like Embryonic Disc ENDODERMAL DERIVATIVES MESODERMAL DERIVATIVES ECTODERMAL DERIVATIVES Tongue epithelium,Pharynx, Digestive tract,Middle ear, Trachea, Ligament, Tendon, Cartilage, Bone, all muscles, Skin epidermis,Cutaneous gland, Hair, Bronchi, Lung,Gall bladder, Liver, Pancreas, Urinary bladder, Teeth, Heart, Blood vessels,Spleen, Kidney, Ureter, Lining of Gut,Teeth enamel, External ear, Vagina, Prostrate. Urethra,G.I. glands,Adenohypophysis, Thymus, Sex organs,Eye,Adrenal cortex etc. Mammary gland,Hypothalamous,Neurohypophysis, Thyroid,Para-thyroid gland etc. Adrenal medulla,CNS,Nerves etc. ADDITIONAL SPECIAL NOTES: TYPES OF EGGS TYPES OF CLEAVAGE Alecithal: Without yolk TYPES OF BLASTULA Holoblastic :Complete division of zygote TYPES OF PLACENTA Stereoblastula : Solid mass Microlecithal:With small amount of yolk i) Equal:Cell size same after division Coeloblastula : With blastocoel Mesolecithal: With moderate amount of yolk ii) Unequal:Cell size differ after division Discoblastula : Disc shaped Macrolecithal: With large amount of yolk Meroblastic :Division restricted to animal pole at tip Periblastula : With central yolk Heterolecithal:With unevenly distributed amount of yolk BASED ON FOETAL MEMBRANE BASED ON BARRIERS BASED ON FATE OF UTERINE PLACENTA Yolk sac placenta :Derived from yolk sac & chorion Epitheliochorial: All attached membranes present Non deciduate :Uterine placenta not shed Chorioallantoic : Derived from chorion & allantois Syndesmochorial:Uterine epithelium absent Deciduate : Uterine placenta shed after birth Chorionic : Derived from mostly chorion Endotheliochorial: Uterine epithelium & connective tissue absent Centradeciduate : Whole placenta absorbed 12-6 Haemochorial: Uterine barrier absent Haemoendothelial: All barriers except foetal endothelial blood vessel absent CONCEPT MAP:Ref.CH-4(Page-1) REPRODUCTIVE HEALTH STRATEGIES BIRTH CONTROL MEDICAL TERMINATION AMNIOCENTESIS SEXUALLY TRANSMITTED OF PREGNANCY DISEASES INFERTILITY ASSISTED REPRODUCTIVE TECHNOLOGY (ART) NATURAL METHOD BARRIER METHOD INTRA-UTERINE DEVICE ORAL STERILISATION Sexually transmitted ADMINISTRATION Periodic Abstinence Condoms Lipples Loop Pills Withdrawl / Coitus Interruptus Diaphragm Copper releasing IUDS Lactational Amenorrhoea Cervical caps Hormone releasing IUDS Veneral Vasectomy Tubectomy Reproductive Tract infection Fem shield Vaults 25-1 IN-VITRO IN-VIVO FERTILISATION FERTILISATION (IVF) ZYGOTE INTRA GAMETE INTRAFALLOPIAN TRANSFER (GIFT) INTRA-UTERINE FALLOPIAN TRANSFER TRANSFER (ZIFT) (IUT) INTRA CYTOPLASMIC INTRA-UTERINE SPERM INJECTION INSEMINATION (ICSI) (IUI) ARTIFICIAL INSEMINATION (AI) CONCEPT MAP:Ref.CH-4(Page-2) REPRODUCTIVE HEALTH ASSOCIATED PROBLEMS AIM TO SOLVE PROBLEMS STRATAGIES Lack of awareness Create awareness Strict follow up of legal ban on Amniocentesis Sex related Myth & Misconception Sex education Follow up of child immunisation Common STDs Prevention of STDs Up-gradation of health care based on reproductive health, Population explosion Educate fertile couples Corrective measures of disorder & infertility Illegal abortion of foetus Provide medical facilities Legal right of MTP for due reasons Congenital & acquired infertility Manage reproductive disorder Enhance RCH Programme Reduce infertility problem (REPRODUCTIVE & CHILD HEALTH CARE) Creating reproduction related awareness Provide facilities for Sex education at Educate people for social consciousness about safe conception, child birth, to mankind by Govt. / NGOs reproductively healthy society school level Pre/ Post natal child care, equal opportunities to male/ female child, 25-2 importance of population explosion. POPULATION EXPLOSION NEED OF STUDYING FACTORS DETERMINING CAUSES OF INCREASE IN CONSEQUENCES OF HUMAN POPULATION POPULATION GROWTH RATE POPULATION GROWTH OVER POPULATION Consequences of uncontrolled population growth Birth rate(Natality) & Death rate(Mortality) Decline in death rate Scarcity of space Advantages of small family Total fertility rate (TFR) Control of disease Shortage of food supply Population density & food availability Replacement rate (Zero growth rate) Reduced infant mortality rate Unemployment & price rise Life standard in accordance with overpopulation Count of active reproductive age Improved community health Pollution & energy crisis Control measure to avoid overpopulation Emigration & Imigration rate Improved agricultural practices Eco-degration Population Explosion CONTROL MEASURES Education about advantages of controlled child birth Incentive for sterilisation Legal norms for raising age of marriage Easy availability of contraceptive devices at cheaper rates Encouraging Family Planning & birth control CONCEPT MAP:Ref.CH-4(Page-3) NATURAL METHOD BIRTH CONTROL BARRIER METHOD (Avoiding chances of fusion of sperm & ova) (Mechanical device) CHEMICAL METHOD ORAL ADMINISTRATION (Chemicals/ Hormones) Periodic Abstenence : Avoiding coitus during ovulation period. Progestogen / Progestogen-Estrogen pills Spermicidal : tablets, jellies, cream introduced (Rhythm Period) Coitus Interruptus: Withdrawal of penis from vagina just before into vagina before coitus. Inhibits ovulation & implantation Implant : Hormones like Progesterone/ Progesterone- Alters cervical mucus to prevent ejaculation of sperm. (Withdrawal Method) Estrogen capsules inserted under skin of fore arm Lactational Amenorrhea : Identified as ‘No Risk Period’ as for long term contraception. 25-3 Ovulation is disrupted during intense lactation period. Taken orally daily for 21 days sperm entry Eg.,Saheli(Non-steroidal) Emergency contraception : Progestogen-Estrogen combined/IUD applied within 72 hrs. of coitus, effective for treatment of Condom: Rubber/Latex sheath covering penis that obstruct semen ejaculation in vagina unprotected sex, sexual assault. Diaphragm: Tubular rubber sheath fitted into vagina for obstructing sperm entry Cervical cap:Rubber nipple fitted into cervix that prevent sperm entry in uterus Vault: Hemespheric rubber cap fitted over cervix to restrict sperm entry Fem shield:Polyurethene pouch covering external genetalia to restrict sperm entry INTRA-UTERINE DEVICES LIPPLES LOOP Increase phagocytosis of sperm within uterus SURGICAL METHOD COPPER RELEASING IUD eg., CuT, Cu7 Releases Cu ion that suppress sperm motility HORMONE RELEASING IUD eg.,Progestasert,Levonorgestrol(LNG-20) STERILISATION (Surgical intervention of blocking gamete transport permanently) Make uterus unsuitable for implantation & cervix hostile to sperm. INFERTILITY ASSISTED REPRODUCTIVE TECHNOLOGY (ART ) VASECTOMY TUBECTOMY In males,portion of Vas deferens blocked by cutting / ligation IVF (In vitro fertilisation): Fertilisation outside body in similar body condition ,followed by embryo transfer. GIFT(Gamete Intra Fallopian transfer): Transfer of sperm &harvested ovum into fallopian tube by Laparoscope ICSI (Intra Cytoplasmic sperm Injection) : Sperm directly injected into ovum in-vitro &zygote transferred to uterus. . AI (Artificial Insemination):Collected semen of donor(IUI)/ husband(AIH) introduced into uterus of female In females, portion of Fallopian tube bl ocked by cutting / ligation Involves transfer of zygote or embryo in fallopian tube/uterus ZIFT(Zygote intra fallopian transfer) At 8 blastomere stage IUT(Intra uterine transter) More than 8 blastomere stage CHAPTER- 5 Principles of inheritance and variation 37-1 CHAPTER- 6 Molecular basis of inheritance 46-1 CHAPTER- 7 CONCEPT MAP IN EVOLUTION 56-1 CHAPTER- 8 HUMAN HEALTH AND DISEASE 63-1 63-2 COMMON INFECTIOUS DISEASES Refer to fig. 8.1 stages in lifecycle of plasmodium page 147 and 148 NCERT 63-3 STRUCTURE OF ANTIBODY MOLECULE IMMUNITYOF LIFECYCLE PLASMIDIUM 63-4 Primary Lymphoid Organ 1. Bone Marrow 2.Thymus Lymphoid Organs Secondary Lymphoid Organ 1. Spleen 2. Lymph Nodes 3. Peyer’s Patch 4. Tonsils 5. Mucosal associated lymphoid tissue (MALT) TYPES OF ACQUIRED IMMUNITY ACTIVE IMMUNITY Function: Provide microenvironment For the development and Maturation of lymphocyte Function: 1. Spleen: Filter the microbes from blood 2. Lymph Nodes: Trap the microorganisms 3. Peyer’s Patch: Present in small intestine and help In the formation of effector celles 4. Tonsils: Trap microbes entering through Mouth 5. MALT: Traps Microbes - Antibody produced within own body - it is long lasting - Does not Cause allergy - Takes time to activate PASSIVE IMMUNITY - Antibodies transferred from another individual. - Not long lasting. - Sometimes cause allergy -Provides immediate relief. - Types of Immune Response: Types of Immune Response Primary Response - Exposure of body to pathogen for first time - Of Low Intensity Secondary Response - Subsequent exposure to same pathogen - Response of body is hieghtened 63-5 Vaccination and Immunization refers to the administration of vaccine. Immunization process by which the body produces antibodies in response to the vaccine to fight infections. Vaccine preparation of antigenic proteins of pathogens or inactivated/weakened pathogen. It is introduced into the body to generate antibodies which can neutralize the pathogens during actual infection. Vaccines also generate memory B & T cells that recognize the pathogens quickly. Vaccines that contain performed antibodies produce quick immune response and provide Passive Immunity e.g. vaccines against tetanus & snakebite. Other vaccines provide Active Immunity e.g. oral polio vaccine, BCG,cholera vaccine. Allergies The exaggerated response/hypersensitiveness of the immune system of a person to certain antigens coming in contact with or entering into the body. Auto-immunity Condition when structural & functional damage is caused due to the attack of the self cells of the body by its own immune cells . Examples : Rheumatoid arthritis, Insulin- dependent diabetes. 63-6 Refer Fig 8.6 replication of retrovirus page 155 NCERT 63-7 CHAPTER- 9 STRATEGIES FOR ENHANCEMENT OF FOOD PRODUCTION 65-1 CHAPTER- 10 Microbes in human welfare 68-1 CHAPTER- 12 Biotechnology and its application 98-1 CHAPTER- 13 Organisms and populations 102-1 CHAPTER- 14 Ecosystem 108-1 Steps of Decomposition Cycle 108-2 DECOMPOSITION: It is the breaking down of complex organic matter into simple organic substances by microorganism. See figure 14.1 page2 44 NCERT 108-3 Peacock ↑ Snake ↑ Frog ↑ Earthworm ↑ Detritus ENERGY FLOW THROUGH DIFFERENT TROPIC LEVELS 108-4 Energy flow is governed by law of thermodynamics. In each trophic level there is loss of 10 % energy (see 14.3figure page-247 NCERT) STANDING CROP Biomass present in atrophic level at a particular time. Biomass is the dry weight of organism. stratification- vertical distribution of different species in different strata. iii) trophic organization- Food relationship of producers and consumers. Ecological Pyramids Graphical Representation of food and energy relationship between organisms of different tropic level 108-5 Pyramid of Biomass Pyramid of Number Pyramid of Energy 108-6 (Xerarch Succession) (Hydrach Succession) SUCCESSION Gradual and fairly predictable changes in species composition of a given area . Types – i) primary succession – Succesion on bare land ex:- bare rocks ,newly created ponds etc. ii)Secondary succession – Occures in an area where there was vegetation earlier. Soil or sediment present that is why it is faster than primary succession . Two types ,based on nature of habitats. i) Hydrach succession – Succesion in water or wet areas Steps in hydrach - Phytoplanktons--- Floating angiosperms---Rooted hydrophytes---sedges---grasses---shrubs and trees (Pioneer) (climax) Xearch succession – succession on bare rock Stages or steps – Lichens---mosses---herbs---shrubs---trees (pioneer) (seral) (climax) 108-7 Carbon cycle Atmospheric input High. between Gaseous exchange organism and environment is high Phosphorus cycle 108-8 in put low. Gaseous exchange negligible Seefig 14.6 atmospheric See fig 14.7 CHAPTER- 15 Biodiversity and conservation 110-1 CHAPTER- 16: Environmental Issues 113-1 113-2