the reproductive system
advertisement

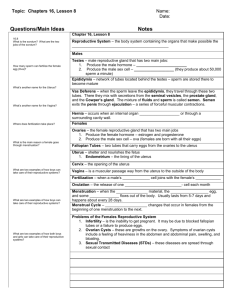
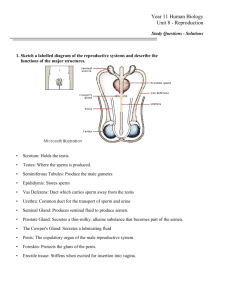
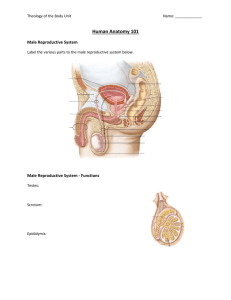
THE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM NOTE SHEET TERMS TO IDENTIFY: USE TEXT BOOKS OR DEVICES Circumcision Embryo Fetus Fertilization Hermaphrodite Mastectomy Menstruation Ovulation Papanicolaou Stain (Pap smear) Placenta Semen Sperm Cell Vasectomy PARTS OF THE FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM A. ___________ – primary reproductive organ of the female, found in upper part of pelvic cavity on each side of uterus, produce _______ and ______________________. B. ________________ – female sex cell. C. ______________________ – duct leading from point near ovaries to the uterus. The oviducts __________________ ova from the body cavity to the uterus. D. _______________ – fringe-like extensions from anterior end of oviducts. When an ovum is released from the ovary, the__________________ work like tentacles to draw the ovum into the _________________. E. _______________– organ for containing and __________ the embryo during ____________. F. ______________ – muscular tube connecting the uterus with the exterior part of the body. G._______________ – external parts of the female reproductive system. 1. ___________ - an elevation of adipose tissue covered by skin and coarse pubic hair. a. ________________: an area of _________ longitudinal folds extending inferiorly and posteriorly. b. ________________: the __________ longitudinal folds of the vulva. c. ________________: a small, cylindrical mass of ___________ and erectile tissue. d. ________________: the cleft between the labia minora H. _________________ – pelvic floor - commonly used to mean the area between the vagina opening and the_________. I. _________________ - actually modified sudoriferous (__________) glands. Each gland consists of 15 to 20 lobes or compartments separated by adipose tissue. The __________ is the dark, circular, pigmented area that encircles the nipple. The nipple is the raised area on the breast that an infant suckles to receive milk and stimulate____________ or the process of _______________, secretion, and ejection. PARTS OF THE MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM A. __________ – sac containing the ___________. B. ____________ – male organ of sexual intercourse. C. ____________ – male reproductive glands - produce ________________ and secrete male sex hormones. D. Epididymis – tube inside the testes in which sperm cells are collected and _________ until they mature. E. __________________ (vas deferens) – continuation of epididymis extending to juncture with the seminal vesicle. F. ________________ – tubes extending from the area back of the urinary bladder to the ductus deferens. Secretes mucoid substance which _________________________________________. G. _______________ - ejects sperm into the ______________________ just prior to ejaculation H. Prostate gland – gland surrounding the neck of the bladder and the ___________. The ________ produces fluid which helps sperm cells maintain their ________________. I. _______________ - serves as the passageway for__________ or spermatozoa to the external environment. J. Sperm cell – male____________ cell. MENSTRUAL CYCLE A. Changes in female hormone secretions occur in a ___________ cycle. B. _______________________ occurs at about the middle of each 28-day period. C. Uterine wall prepares for the ___________________ of _______________________ egg. D. If fertilization does not occur, the _________ of the uterine wall sloughs off, and is _________. E. This loss of uterine lining leaves some areas _________; thus, blood is also discharged from the uterine wall. F. After __________________, the uterus begins to prepare for ________________ again. G. Menstruation usually begins in females from ages ___________ and indicates production of ova. H._______________ is the state at which the menstrual cycle ceases, usually occurs between the ages of 45-50. I. The menstrual cycle is controlled by _________________. PREGNANCY A. Fertilization normally occurs when the ovum is about ___________ of the way down the ___________. The fertilized egg continues the passage down the tube until it reaches the _______. B. _______ to_____ days after fertilization, the ___________ becomes implanted in the uterine wall. C. The ____________ begins to form after implantation occurs. The placenta functions in the exchange of _______, _______, and ___________ between mother and baby. D. The placenta also serves as a ___________ against the passage of _________ from mother to baby. However, blood-borne diseases such as _________ and some viruses may be transmitted from mother to baby. Maternal _______________ are transmitted from mother to baby. E. The duration of pregnancy is about ______ days or _______ weeks. DISORDERS OF PREGNANCY A. ________________ – fertilized ovum is implanted at a site other than the uterus, as in a fallopian tube. B. __________ – loss of embryo of fetus during the first ________ weeks of pregnancy. 1. ______________________ – abortion that occurs without having been induced 2. _________________ – termination of pregnancy by artificial means a. Criminal abortion – abortions performed _________________ b. ____________________ – abortions performed by ___________ for a variety of reasons 3. ____________________ – loss of fetus between _______ and _____ weeks of pregnancy DISORDERS OF THE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM A.___________________ – absence of _______________________. B. ___________________ – failure of ________ to descend into the ________________. C. Dysmenorrheal – ____________ menstruation. D. ________________ – infectious venereal disease caused by ______________; characterized by a ______________________ discharge. E. _________________ – both male and female sex organs _______________________. There are no known cases in which a true hermaphrodite is___________, either as a male or female. F. _________________________ – genitalia of one sex is evident; secondary sex characteristics of opposite sex predominate. G. ________________________ – rupture in abdominal wall, in region of wall where_________ descend from abdominal cavity into __________. H.__________________ – vaginal discharge. I. __________________ – inflammation of testes due to ___________, mumps or other infection. J. _______________ – any condition resulting in __________________ of the prostate gland, with accompanying retention of __________ in the bladder. K. Salpingitis – inflammation of the _______________ L. ______________________ – inability to reproduce. M. __________________– infectious venereal disease characterized by _______________ which may involve any organ or tissue. N. Tumor – ________________ or enlargement. May occur in any part of the reproductive system, occurs commonly in the ___________. May be ____________ or ______________.