Chapter 18 Notes
advertisement

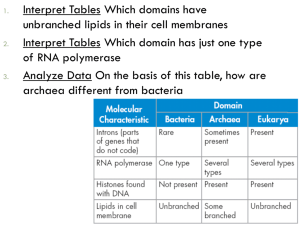
Chapter 18 Section 18-1 Classification: Used to name organisms and group them in a logical manner. Taxonomy: The science of classifying and assigning each organism a name Binomial Nomenclature: Each species is given a 2 part name (Latin) Developed by Carolus Linnaeus 1st Name= Genus (1st letter is CAPITALIZED) 2nd name= species Always written in italics Example: Ursus arctos= Grizzly Bear Ursus= Genus arctos= species Taxon: A group or level of Classification. 7 Levels of Classification Kingdom: Largest and most inclusive category Phylum: Made of different Classes Class: Made of different Orders Order: Made of different Families Family: Made of different Genus’ Genus: Made of Different Species Species: Smallest and most specific category Kingdom Phylum C l a s s O r d e r F a m i l y G e n u s Species “King Philip Could Order his Family to Go to School” 6 Kingdoms: 1. Plantae: Plants 2. Animalia: Animals 3. Fungi: Fungus, Mushrooms, Yeast 4. Protista: Amoeba, Paramecium 5. Archaebacteria: “Ancient Bacteria” 6. Eubacteria: E. Coli, Streptococcus bacteria (Strep Throat) Chapter 18-2 Evolutionary Classification http://www.ucmp.berkeley.edu/education/explorations/tours/T rex/index.html We classify based upon evolution, not just physical similarities Derived Characteristics: Characteristics that appear in organisms, but was not present in past, similar organisms. Example: Primates (Fur) Humans (Hair) Cladogram: A diagram that shows evolutionary relationships. Similar to a Family Tree Uses Derived Characteristics Roaches and Mantids are closely related Molecular Clock: By comparing DNA of 2 or more species, biologists can estimate how long the species have been separated. Uses mutations in DNA sequence Chapter 18-3 6 Kingdoms 3 Domains 1. Bacteria: Eubacteria Prokaryotes (No Nucleus) Cell walls WITH Peptidoglycan Examples: Strep throat, E. Coli 2. Archae: Archaebacteria Prokaryotes (No Nucleus) Cell walls WITHOUT Peptidoglycan Examples: Halophiles, Bacteria in your intestines 3. Eukarya: Eukaryotes (Has a Nucleus) Protista; Fungi; Plantae; Animalia