How to Draw a Climate Graph
advertisement

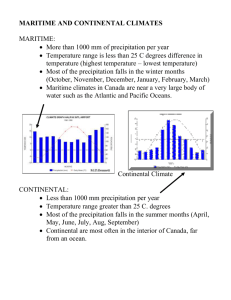
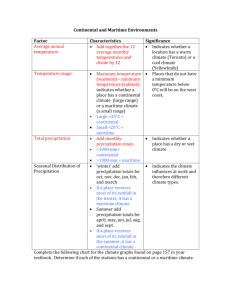
Climate Graphs Climate • overall weather pattern (temperature & precipitation) for an area over a long period of time Weather • the short term forecast for an area (temperature and precipitation) Climate Graph • is a graph that shows annual average temperature & total precipitation for a particular city How to Draw a Climate Graph Part 1: Temperature 1. Using a ruler, draw the horizontal and vertical axis on your graph paper 2. Label each month (i.e. J F M A, etc) across the horizontal axis. Label the entire horizontal axis ‘Months’. 3. Label the vertical line on the LEFT with appropriate numbers for temperature. Remember, that many places have averages below zero for some months, so put zero half way up the line and plot positive and negative numbers above and below. 4. Label the vertical axis ‘Temperature in Degrees Celsius’. 5. Using the data, plot each month. Do this by putting a dot in the middle of the box and then join all the dots with a RED pencil crayon. Part 2: Total Precipitation (plot on same graph) 6. Next, you are going to plot the Total Precipitation for each month at your station. 7. Draw a vertical line on the right hand side of your graph so it joins the horizontal axis 8. Label this line ‘Precipitation in mm’ 9. Next, determine what the number on your scale needs to be, by looking at the data. Label your axis with an appropriate scale. 10. You are going to use a bar graph to plot this data. All bars are coloured light BLUE. (Tip: It is helpful to cover up the temperature side so you are not tempted to use its scale) 11. Finally, make sure your climate graph has all of its essential features (i.e. title, name, date, etc) Part 3: Determine if your city has a continental or maritime climate • Continental climates are usually located in cities that have very cold winters and very hot summers and have very little precipitation. • Maritime climates are usually located in cities that have cool winters and warm summers and receive a lot of precipitation Using the Graph to Determine the Two Types of Climates 1. Temperature Range • subtract the highest and lowest average monthly temperatures (i.e.) If July’s temperature is 22 o C and January’s is -17 o C 22 – (-17) = 39 degree range RULE 2. Total Precipitation RULE 3. Season of Most Precipitation RULE 4. Average Annual Temperature • If your city has a range of less than 25 degrees Celsius, it has a maritime climate. If your city has a range that is over 25 degrees Celsius, it has a continental climate. • Add up the total precipitation for each month • If the amount is over 1000 mm, it has a maritime climate. If the total is under 1000 mm, it has a continental climate. • Calculate whether it precipitates more in winter months (Oct to Mar) or in the summer months (Apr to Sept) • If there is more precipitation in the winter, it has a maritime climate. If it has more in the summer, it has a continental climate. • Add up the average temperature for each month and divide by twelve (for the twelve months) Once you have done this, you can see if the city has a continental or maritime climate (or a mixture of both!)