SJ #14 “Lesson 12 Notes: Solubility”
advertisement
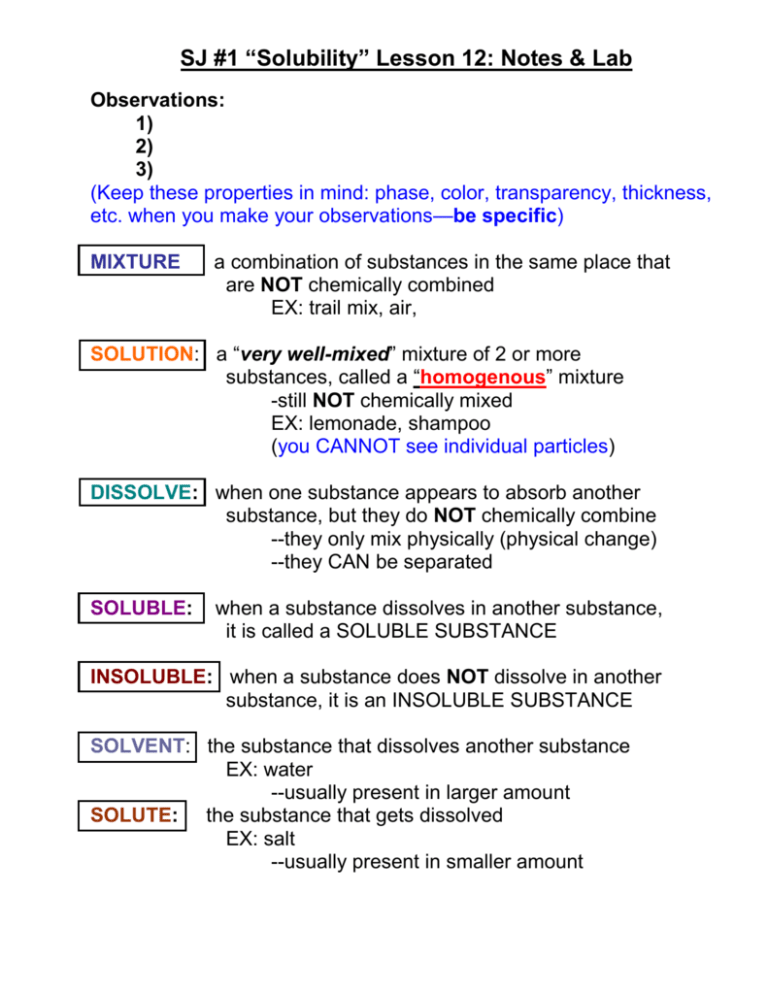
SJ #1 “Solubility” Lesson 12: Notes & Lab Observations: 1) 2) 3) (Keep these properties in mind: phase, color, transparency, thickness, etc. when you make your observations—be specific) MIXTURE a combination of substances in the same place that are NOT chemically combined EX: trail mix, air, SOLUTION: a “very well-mixed” mixture of 2 or more substances, called a “homogenous” mixture -still NOT chemically mixed EX: lemonade, shampoo (you CANNOT see individual particles) DISSOLVE: when one substance appears to absorb another substance, but they do NOT chemically combine --they only mix physically (physical change) --they CAN be separated SOLUBLE: when a substance dissolves in another substance, it is called a SOLUBLE SUBSTANCE INSOLUBLE: when a substance does NOT dissolve in another substance, it is an INSOLUBLE SUBSTANCE SOLVENT: the substance that dissolves another substance EX: water --usually present in larger amount SOLUTE: the substance that gets dissolved EX: salt --usually present in smaller amount ***Solvents and solutes can be ANY PHASE EX: --salt (S) in water (L) (most common) --oxygen (G) in water (L) --metal (S) with metal (S) alloys (melted together first) --air: gasses (G) dissolved in nitrogen (G) ELECTROLYTES: solutions that conduct electricity; salts NON-ELECTROLYTES: cannot conduct electricity; non-salts AQUEOUS SOLUTION: when water is the solvent POLAR MOLECULE: a molecule that has electrically charged parts, but is electrically neutral as a whole EX: water = H2O 2 hydrogens & 1 oxygen + H H O --“LIKE dissolves LIKE” --polar dissolves polar --nonpolar dissolves nonpolar --polar and nonpolar do NOT mix well = “IMMISCIBLE” (water + oil) SOLUBILITY: the amount of solute that can dissolve in a given amount of solvent, measured in (g/L) *Solubility changes with temperature. **At room temperature, a solvent can dissolve only a certain amount of solute *As temperature of a liquid increases, the solubility of a solid solute increases. EX: salt in water more salt dissolves in warmer water than in colder water DILUTE SOLUTION: a weak solution with not very much solute CONCENTRATED SOLUTION: a strong solution with a lot of solute SATURATED SOLUTION: when a solvent cannot dissolve any more solute UNSATURATED SOLUTION: when a solvent can still dissolve more solute SJ #1 Solubility LAB Problem: What happens to the solid when mixed with water? Materials: *test tube rack *paper towel *GOGGLES *chemicals in cups *copper sulfate *zinc oxide *powdered sugar *5 test tubes (A-E) *100 mL graduated cylinder *water *lab scoops *sodium chloride *corn starch Procedure: 1) Get materials and find an open space to work with your group. 2) Place ONE SCOOP of each chemical into the corresponding test tube (A-E). 3) Add 20 mL of water to each test tube. 4) Hold the test tube with your thumb and paper towel to shake the MIXTURE up and down 20 times. Place the test tube back in the rack so the particles can settle. 5) Repeat steps 3-4 for each chemical. 6) Once particles have settled, write at least 3 observations for each chemical in the data table under “Appearance”. 7) Based on your observations and results, discuss SOLUBILITY with your group and fill in the third column of your data table. 8) Clean the test tubes thoroughly with water and a test tube brush. All materials can be washed down the sink. 9) Put all lab materials back where they belong and clean up your work area. SJ #1 Solubility LAB Data Table 1. Write your observations in the table. Name of Substance Added to Water Appearance After Being Shaken 20 Times A Copper sulfate CuSO4 1. 2. 3. B Sodium chloride NaCl 1. 2. 3. C Zinc oxide ZnO 1. 2. 3. D Corn starch C6H10O5 1. 2. 3. E Powdered sugar C12H22O11 1. 2. 3. Does it Dissolve? Y or N 1. Which substances are soluble in water? (Write out the names!) 2. What evidence is there that a substance dissolves in water? List at least 2 observations from the lab. 3. Why were you asked to shake the test tube “vigorously”, instead of just gently swirling the mixture around? 2. Write your observations of what happens when water is added to the following: Substance Obs Before a) beach sand SiO2 1. 2. b) pink sand SiO2 1. 2. c) potassium permanganate KMnO4 1. 2. Trimethylhydroxysilane C3H10OSi Prediction w/ water Obs After








