Chemistry 1A - Cherry Hill High School
advertisement

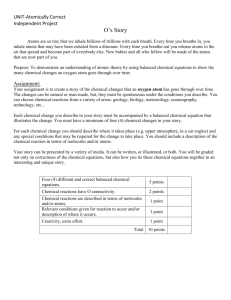
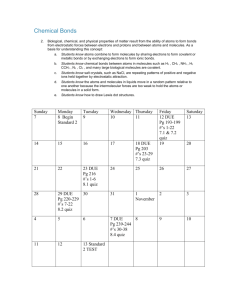
CURRICULUM MAP – Chemistry 1A Skills Content Essential Questions September CCCS Page 1 of 2 October What information is provided What information can be by a chemical formula? obtained from a chemical equation? How is nomenclature used to identify compounds? How can the products of chemical reactions be How can the composition of predicted? substance be used to determine its chemical formula? Nomenclature Empirical & Molecular Formulas Use chemical symbols and formulae to represent atoms and molecules Recognize, name, and write formulas for diatomic, polyatomic, multivalent, and covalent compounds, including acids and bases Determine the empirical and molecular formulas of compounds 5.1, 5.2, 5.3, 5.4, 5.6 Chemical Reactions Symbolically represent chemical equations Use balanced chemical equations to represent actual chemical reactions Know that chemical reactions depend on collisions between the reacting particles to form new combinations of atoms Accurately predict the activity and products of chemical reactions 5.1, 5.2, 5.6 November How are chemical reactions quantified? Stoichiometry Examine the quantitative relationships between the components of a chemical reaction Discover how physical properties can be explained by the arrangement and motion of atoms and molecules Know that the forming or breaking of chemical bonds requires a net input or release of energy resulting in a more stable state Recognize that chemical reactions depend on collisions between the reacting particles to form new combinations of atoms 5.1, 5.3, 5.6 December January What is the relationship What laws describe the between energy flow and the behavior of gases? states of matter? How does kinetic molecular theory describe the behavior of matter? In what direction does heat flow? What is enthalpy and how is it determined? On what two factors does heat capacity depend? How is heat involved in chemical reactions? States of Matter Thermochemistry (cont’d) Thermochemistry Gas Laws Understand how energy is transformed Explain how specific heat is determined and used Measure enthalpy using a calorimeter Create thermochemical equations Describe how heat is involved in changes of state 5.1, 5.6, 5.7 Use the gas law equations to calculate volume, pressure, temperature, mass, density, and number of molecules Understand the qualitative and quantitative behavior of gases Use the gas law equations to calculate volume, pressure, temperature, mass, density, and number of molecules Understand the qualitative and quantitative behavior of gases 5.1, 5.3, 5.6 CURRICULUM MAP – Chemistry 1A Skills Content Essential Questions February CCCS Page 2 of 2 March April What are the relationships What information about atoms What are the unique properties between and element’s can be determined from an of aqueous solutions? atomic structure and its understanding of What factors determine solubility position on the periodic table? electromagnetic radiation? and the rate at which a What is the basis of the substance dissolves? periodic table? What conditions determine the How do different types of amount of solute that will bonds affect the properties of dissolve in a given solvent? molecules? How does molecular geometry affect chemical properties? Gas Laws (cont’d) Electrons Periodic Law Recognize that the arrangement of electrons describes how atoms interact with other atoms Organize elements based on chemical and physical properties into a Periodic Table Discover that the properties of the elements depend on the structure of the atom and vary with the atomic number in a systematic way 5.1,5.3, 5.6 Periodic Law (cont’d) Ionic/Metallic Bonding Explain the nature of electromagnetic radiation and compare the components of the electromagnetic spectrum Demonstrate that the forming or breaking chemical bonds requires or releases energy resulting in a more stable state Explain that atoms form bonds by transferring or sharing electrons Draw and interpret Lewis diagrams of molecules 5.1, 5.3, 5.6 Covalent Bonding Water & Solutions Predict molecular geometry and polarity based on VSEPR theory Understand the importance of the unique properties of water Describe the properties of homogenous and heterogeneous aqueous systems Understand the properties and uses of electrolytes Describe the properties of colloids, emulsions, and suspensions and how they are different from solutions Explain how a solution is formed Describe solubility and factors that affect it Understand the difference between molarity and molality Explain and manipulate the colligative properties of solutions 5.1, 5.3, 5.6 May June How is the rate of chemical How can concepts learned change expressed? throughout the year be used to solve a complex problem? What four factors influence the rate of a chemical reaction? How is equilibrium achieved/ manipulated? What are the properties of acids and bases? How did Arrhenius define an acid and base? What distinguishes an acid from a base in the BronstedLowry theory? How did Lewis define an acid and a base? Final Exam Preparation Reaction Rates/Equilibrium Performance Assessment Acids, Bases, & Salts Understand that reaction rates Demonstrate ability to identify are affected by such factors and manipulate laboratory as concentration, pressure, equipment temperature, or the presence Solve a problem using of a catalyst laboratory skills obtained Recognize the properties of throughout the year acids and bases Synthesize a response to an Differentiate between the open-ended question using theories of acids and bases critical thinking skills Calculate pH, pOH, and ion concentrations 5.1, 5.3, 5.6 5.1, 5.3, 5.6 Last Revised: 5/2007