USS BIO
advertisement
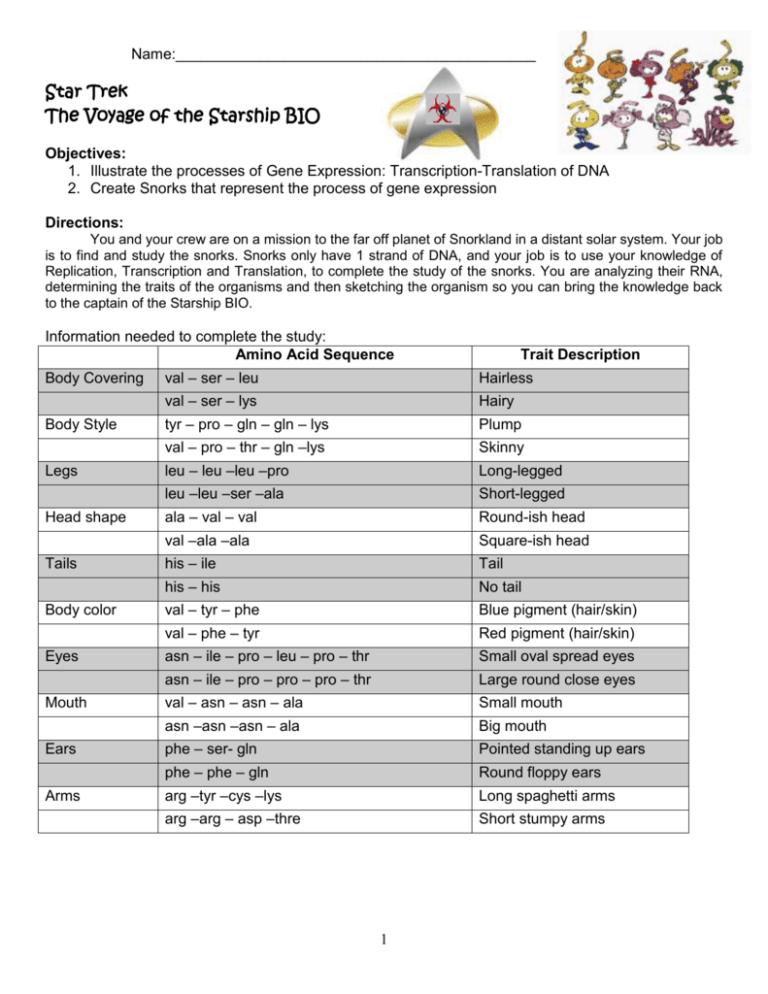
Name:___________________________________________ Star Trek The Voyage of the Starship BIO Objectives: 1. Illustrate the processes of Gene Expression: Transcription-Translation of DNA 2. Create Snorks that represent the process of gene expression Directions: You and your crew are on a mission to the far off planet of Snorkland in a distant solar system. Your job is to find and study the snorks. Snorks only have 1 strand of DNA, and your job is to use your knowledge of Replication, Transcription and Translation, to complete the study of the snorks. You are analyzing their RNA, determining the traits of the organisms and then sketching the organism so you can bring the knowledge back to the captain of the Starship BIO. Information needed to complete the study: Amino Acid Sequence Body Covering Body Style Legs Head shape Tails Body color Eyes Mouth Ears Arms Trait Description val – ser – leu Hairless val – ser – lys Hairy tyr – pro – gln – gln – lys Plump val – pro – thr – gln –lys Skinny leu – leu –leu –pro Long-legged leu –leu –ser –ala Short-legged ala – val – val Round-ish head val –ala –ala Square-ish head his – ile Tail his – his No tail val – tyr – phe Blue pigment (hair/skin) val – phe – tyr Red pigment (hair/skin) asn – ile – pro – leu – pro – thr Small oval spread eyes asn – ile – pro – pro – pro – thr Large round close eyes val – asn – asn – ala Small mouth asn –asn –asn – ala Big mouth phe – ser- gln Pointed standing up ears phe – phe – gln Round floppy ears arg –tyr –cys –lys Long spaghetti arms arg –arg – asp –thre Short stumpy arms 1 Prelab: Complete the sequence. 1. Fill in the lines for the following sequences. Complement: ____________________________________________________________________ Gene: ____________________________________________________________________ mRNA: AUG - tRNA: _____________________________________________________________ AA: _____________________________________________________________ Complement: ATG - _____ - _____ - _____ - _____ - _____ - _____ - _____ - _____ Gene: TAC mRNA: ____ - _____ - tRNA: ____ - AA: ____ - _____ - _____ - _____ - ACU - AGC - UGG - GGG - UAU - UAC - UUU - UAG - _____ - _____ - _____ - _____ - ATG CUC - _____ - _____ - _____ UGU - GAU - _____ - _____ - _____ - _____ - _____ - _____ - _____ - _____ - _____ - UUG - _____ - AUU ala 2 - _____ - _____ - pro - _____ Each of the below DNA samples was taken from volunteer snorks. Your job is now to analyze each RNA sample and determine what the snork looks like based on their DNA sequence. Remember that AUG is always the start codon, and it signifies the beginning of each translation. UAA is a stop codon and signifies the end of translation. You are to make the complementary strand of DNA, then the DNA strand and lastly translate the information into amino acid sequences. /25pts DNA (the gene) Sequences Complementary DNA mRNA AUG | GUC AGC AAA | UAC CCC CAA CAG AAA | CUC UUA AGU GCG |GCU GUU GUG | CAU CAU | GUU UUU UAC | AAU AUC CCA CUG CCC ACC | AAU AAC AAU GCC | UUU UCU CAG | CGC CGA GAC ACA | UAA Amino Acids 3 Picture /25pts DNA (the gene) Sequences Picture Complementary DNA mRNA AUG | GUA UCU AAA | GUU CCU ACU CAA AAG | CUU CUC CUC CCC | GUU GCG GCU | CAU CAC | GUA UAU UUU | AAU AUU CCC CCU CCC ACA | AAC AAC AAU GCA | UUC UCG CAG | CGC UAC UGC AAA | UAA Amino Acids Student Reflection (4pts per question) Answer the following questions completely and honestly about the work you completed. 1. What is the central dogma of biology? Explain the process of gene expression in the appropriate steps. 2. Describe the process of transcription. 3. How did this activity have you perform transcription? 4. Describe the process of translation. 5. How did you perform translation in this activity? 6. Describe precisely how you know where a gene starts and stops (give the sequences of DNA). 4 7. You were given mRNA sequences instead of DNA sequences. Which two pieces of information (boxes, basically) can you get directly from the RNA? 8. Which of the boxes were nearly identical (the difference being the T U substitution)? 9. Are there any genes found that had the same trait but different codon sequences for the two organisms? (Yes) List the DNA, mRNA, and amino acid sequences for each organism below. DNA sequences mRNA sequences Amino acid sequences 10. Why did different DNA/codon sequences give the same amino acid sequence, and therefore trait? 5









