Genetics
advertisement

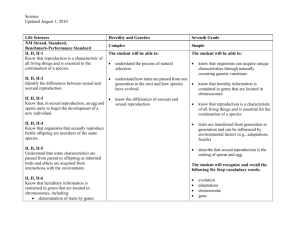
The Unit Organizer Last Unit: Cells Unit Standards: Reproduction is a characteristic of all organisms and is essential for the continuation of a species. Hereditary information is contained in genes which are inherited through asexual or sexual reproduction Name _____________________________ Big Idea / Overarching Question Why are organisms different from each other? Current Unit: Genetics & Heredity Unit Map: Is about… How inherited traits that are passed from parent to offspring Priority Standards 7.4.3.1.1: Cells contain genes and that each gene contains information that determines inherited traits of organisms. 7.4.3.2.3: Variation exists in every population and can help or hinder an organism’s ability to survive. Regular Standards 7.4.1.2.2: Recognize that cells repeatedly divide to make more cells for growth and repair. 7.4.3.1.2: Genes come from a single parent in asexual reproduction and half the genes come from each parent in sexual reproduction. 7.4.3.1.3: Distinguish between characteristics of organisms that are inherited and those acquired through environmental influences. 7.4.4.1.1: Describe examples where selective breeding has resulted in new varieties of cultivated plants and particular traits in domesticated animals. Next Unit: Classification & Change Over Time Time Frame: 4 weeks Create Are coded in Genetic Diversity & Variation DNA Can be predicted using Punnett Squares Unit Guiding Questions: 1. How are traits inherited through genes? 2. Why does a child look like its parents? 3. How does using a Punnett square help predict what an organism will look like? 4. How are traits passed on through reproduction? 5. What is the difference between sexual and asexual reproduction? 6. How does cell division help organisms heal? Are passed through Reproduction & Cell Division Unit Relationships: Calculating Probability Comparing & Contrasting Analyzing Similarities & Differences Predicting The Unit Organizer 7.4.1.2.2 Recognize that cells repeatedly divide to make more cells for growth and repair. Item Specifications Items may require students to understand how cells are replaced in an organism and how an organism gets larger Items will NOT require understanding the specific processes of mitosis and meiosis, although the term mitosis may be used Additional vocabulary may include terms such as cell division Items assessing this benchmark may also assess benchmarks 7.4.1.2.1 or 7.4.1.2.3 7.4.3.1.1 Recognize that cells contain genes and that each gene carries a single unit of information that either alone, or with other genes, determines the inherited traits of an organism. Item Specifications Items will NOT use the terms chromosome, phenotype, genotype, dominant or recessive Items will NOT require students to understand or use a Punnett square 7.4.3.1.2 Recognize that in asexually reproducing organisms all the genes come from a single parent, and that in sexually reproducing organisms about half of the genes come from each parent. Item Specifications Items will NOT require students to understand the process of meiosis Items may require students to know that sex cells contain half the total genetic information Items will NOT use the term chromosome Name _____________________________ 7.4.3.1.3 Distinguish between characteristics of organisms that are inherited and those acquired through environmental influences. Item Specifications Items will provide relevant background information Items may address how some inherited traits can also be affected by the environment. For example mutations caused by pollution, organism height, leaf number, leaf color Additional vocabulary may include terms such as instinctive, behavioral and learned characteristics 7.4.4.1.1 Describe examples where selective breeding has resulted in new varieties of cultivated plants and particular traits in domesticated animals. Item Specifications Items will provide relevant background information on traits found in the plants and animals 7.4.3.2.3 Recognize that variation exists in every population and describe how a variation can help or hinder an organism’s ability to survive. Item Specifications Additional vocabulary may include terms such as adaptation, genetic diversity