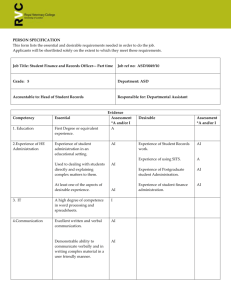
Summary comparison of traits of autism and mercury poisoning
advertisement

BodyTune Health Unlocking Human Potential Summary comparison of traits of autism and mercury poisoning Social deficits, shyness, social withdrawal Repetitive, perseverative, stereotypic behaviours; obsessive-compulsive tendencies Depression/depressive traits, mood swings, flat Psychiatric disturbances affect; impaired face recognition Anxiety; schizoid tendencies; irrational fears Irritability, aggression, temper-tantrums Lacks eye contact; impaired visual fixation (HgP)/problems in joint attention (ASD) Loss of speech, delayed language, failure to develop speech Speech and language deficits Dysarthria; articulation problems Speech comprehension deficits Verbalizing and word retrieval problems (HgP); echolalia, word use and pragmatic errors (ASD) Abnormal sensation in mouth and extremities Sensory abnormalities Sound sensitivity; mild to profound hearing loss Abnormal touch sensations; touch aversion Over-sensitivity to light; blurred vision Flapping, myoclonal jerks, choreiform movements, circling, rocking, toe walking, unusual postures Motor disorders Deficits in eye-hand coordination; limb apraxia; intention tremors (HgP)/problems with intentional movement or imitation (ASD) Abnormal gait and posture, clumsiness and incoordination; difficulties sitting, lying, crawling and walking; problem on one side of body Borderline intelligence, mental retardation – some cases reversible Poor concentration, attention, response inhibition (HgP)/shifting attention (ASD) Uneven performance on IQ subtests; verbal IQ higher than performance IQ Cognitive impairments Poor short term, verbal and auditory memory Poor visual and perceptual motor skills; impairment in simple reaction time (HgP)/lower performance on timed tests (ASD) Deficits in understanding abstract ideas & symbolism; degeneration of higher mental powers (HgP)/sequencing, planning & organizing (ASD); difficulty carrying out complex commands Self injurious behaviour, e.g. head banging ADHD traits Unusual behaviours Agitation, unprovoked crying, grimacing, staring spells Sleep difficulties Hyper or hypotonia; abnormal reflexes; decreased muscle strength, especially upper body; incontinence; problems chewing; swallowing Rashes, dermatitis, eczema, itching Physical disturbances Diarrhea; abdominal pain/discomfort, constipation, colitis Anorexia; nausea (HgP)/vomiting (ASD); poor appetite (HgP)/restricted diet (ASD) Lesions of ileum and colon; increased gut permeability Mercury exposure Autism Biochemistry Biochemistry Binds SH groups; blocks sulphate Low sulphate levels transporter in intestines, kidneys Low levels of glutathione; decreased ability Reduces glutathione availability, inhibits of liver to detoxify xenobiotics; abnormal enzymes of glutathione metabolism; glutathione peroxidase activity in glutathione needed in neurons, cells and erythrocytes liver to detoxify heavy metals; reduces Purine and pyrimidine metabolism errors glutathione peroxidase and reductase lead to autistic features Disrupts purine and pyrimidine metabolism Mitochondrial dysfunction, especially in Disrupts mitochondrial activities, especially brain in brain Immune System Immune System Sensitive individuals more likely to have More likely to have allergies and asthma; allergies, asthma, autoimmune-like familial presence of autoimmune diseases, symptoms, especially rheumatoid-like ones especially rheumatoid arthritis; IgA Can produce an immune response in CNS, deficiencies causes brain/MBP autoantibodies On-going immune response in CNS; Causes overproduction of Th2 subset; brain/MBP autoantibodies present kills/inhibits lymphocytes, T-cells and Skewed immune cell subset in the Th2 monocytes; decreases NK T-cell activity; direction; decreased response to T-cells induces or suppresses IGNg & IL-2 mitogens; reduced NK T-cell function; increased IFNg & IL-12 CNS structure CNS structure Selectively targets brain areas unable to Specific areas of brain pathology; many detoxify or reduce Hg induced oxidative functions spared (36) stress Pathology in amygdala, hippocampus, basal Accumulates in amygdala, hippocampus, ganglia, cerebral cortex; damage to Purkinje basal ganglia, cerebral cortex; damages and granule cells in cerebellum; brain stem Purkinje and granule cells in cerebellum; defects in some cases brain stem defects in some cases Neuronal disorganization; increased Causes abnormal neuronal cytoarchitecture; neuronal cell replication, increased glial disrupts neuronal migration, microtubules cells; depressed expression of NCAMs and cell division; reduces NCAMs Progressive microcephaly and Progressive microcephaly macrocephaly Neuro-chemistry Neuro-chemistry Prevents presynaptic serotonin release and Decreased serotonin syntheses in children; inhibits serotonin transport; causes calcium abnormal calcium metabolism disruptions Either high or low dopamine levels; positive Alters dopamine systems; peroxidine response to peroxidine, which lowers deficiency in rats resembles mercurialism in dopamine levels humans Elevated norepinephrine and epinephrine Elevates epinephrine and norepinephrine Elevated glutamate and asparate levels by blocking enzyme that degrades Cortical acetylcholine deficiency; reduced epinephrine muscarinic receptor binding in hippocampus Elevates glutamate Demyelination in brain Leads to cortical acetylcholine deficiency; increases muscarinic receptor density in hippocampus and cerebellum Causes demyelinating neuropathy Neurophysiology Neurophysiology Causes abnormal EEGs, epileptiform Abnormal EEGs, epileptiform activity, activity, variable patterns, e.g. subtle, low variable patterns, including subtle, low amplitude seizure activities amplitude seizure activities Causes abnormal vestibular nystagmus Abnormal vestibular nystagmus responses; responses; loss of sense of position in loss of sense of position in space space Autonomic disturbance: unusual sweating, Results in autonomic disturbance: poor circulation, elevated heart rate excessive sweating, poor circulation, elevated heart rate