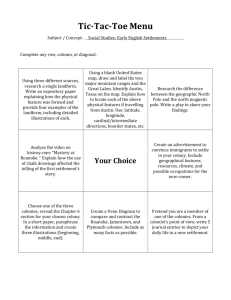
The primer pairs used for Dlk1 were
advertisement

Supplementary data for “Dlk1 in Normal and Abnormal Hematopoiesis” by Sakajiri S. et al. Real-time RT-PCR assay Total RNA was isolated from cell lines and clinical samples using Trizol reagent (Gibco, BRL) according to the standard protocol. Total RNA (1g) was processed directly to cDNA by reverse transcription with Superscript Ⅱ (Life Technologies, Inc.), according to the manufacture’s protocol in a total volume of 20 l. The primer pairs used for Dlk1 were 5’-AAG GAC TGC CAG AAA AAG GAC-3’(forward), 5’-GCA GAA ATT GCC TGA GAA GC-3’ (reverse). The probe for the Dlk1 was 5’- GCC TCC CAT GCC TCC TGC CT-3’. The primer pairs used for Integrin 3 were 5’-GCC TCT GGG CTC ACC TCG CTG -3’ (forward). The primer pairs used for 18S were 5’- AAA CGG CTA CCA CAT CCA AG-3’ (forward), 5’-CCT CCA ATG GAT CCT CGT TA-3’ (reverse). The probe for the 18S was 5’-AGC AGG CGC GCA AAT TAC CC-3’. Primers were purchased from Life Technologies, Inc., and probes were from Perkin-Elmer Applied Biosystems. For Dlk1 and 18S genes, amplification reactions contained 5 l of cDNA, 12.5 l of the Universal Taqman 2x PCR master mix (Applied Biosystems), and 2.5 l of each of the specific primers and probe. Primer and TaqMan probe concentrations in the final volume of 25 l were 500 nM and 100 nM, respectively. All reactions were performed in triplicate in an iCycler iQTM system (Biorad, Hercules, CA), and the thermal cycling conditions were as follows: 2 min at 50C, 10 min at 95C, followed by 45 cycles of 95C for 15 sec and 60C for 1 min. For Integrin 3, the cDNAs were subjected to PCR with SYBR GreenPCR Core Reagents (PE Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA) according to the manufacture’s protocol. Levels of mRNA for each gene were evaluated as a ratio to the level of ribosomal 18S RNA to standardize the quantity of cDNAs of each sample. Furthermore, levels of Dlk1 mRNA from the various samples were quantified as relative values to those present in K562 cells; the relative value of Dlk1 transcripts in K562 cells as measured by Real-time RT-PCR, was regarded as 100. Colony formation assays. For colony forming assays, we used 6-8 weeks old mice. Peripheral blood was obtained by heart puncture and bone marrow was flushed from isolated femurs with Alpha Minimum Essential Medium (-MEM) (Gibco BRL, Grand Island, New York, USA) including 10% FBS using a 26-gauge needle. Isolated spleens were injected with DMEM (Gibco BRL) plus 10% FCS, and crushed with forceps to release the cells. Mononuclear cells from both bone marrow and spleens were separated by Ficoll Hypaque density centrifugation (Amersham Pharmacia, Uppsala, Sweden). Resuspended mononuclear bone marrow cells and growth factors were added 1:10 to methylcellulose medium M3234 (Stem Cell Technologies Inc., Vancouver, Canada) to yield a final concentration of 1% methylcellulose, 30% FBS, 1% BSA, 10-4 M mercaptoethanol, and 2 mM L-glutamine. Colony formation was stimulated by multiple combinations of purified recombinant growth factors at the following final concentrations: murine GM-CSF at 10 ng/mL; murine G-CSF at 10 ng/mL; murine IL-3 at 10 ng/mL; human IL-7 at 10 ng/mL; and human Epo at 2 U /mL. mDlk1 protein was purified as previously described (16). Cells were cultured in six-well plates in a volume of 1 ml and incubated at 37C in a humidified atmosphere containing 5% CO2. Colonies were counted at various times. When using IL-3 and GM-CSF, colonies were enumerated after 8 days culture. When using either G-CSF or IL-7, colonies were counted after 12 days. Colonies (>50 cells) were enumerated with an inverted microscope. Colony type was established by morphology, and to ensure accurate determination, representative colonies were plucked from the plates, centrifuged onto slides, stained with Wright-Giemsa stain and examined by light microscopy. Myeloid and erythroid colony assays were performed by plating 2104 and 2105 bone marrow cells, respectively; CFU-E colonies (consisting of >8 cells) were counted after 3 days culture with EPO, and BFU-E colonies (consisting of >100 cells) were counted after 7 days culture with Epo and IL-3. The colony type was established by morphology; and to ensure accuracy, BFU-E colonies were stained with Benzidine. For the megakaryocyte colony-forming unit (CFU-Meg) assay, bone marrow cells (1105) were cultured with MegaCult-C media (StemCell Technologies, Vancouver, Canada) in the presence of 10 ng/ml recombinant murine IL-3 (Calbiochem, Darmstadt, Germany), 20 ng/ml recombinant human IL-6 (Calbiochem), and 50 ng/ml recombinant human TPO (Calbiochem). After culturing for 7 days, colonies were stained with acetylcholine esterase (AchE). CFU-Meg colonies were defined as at least 3 megakaryocytes in a cluster.