RSPT 1213 – Basic Respiratory Care Pharmacology Drug
advertisement

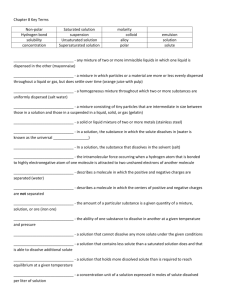
RSPT 1213 – Basic Respiratory Care Pharmacology Drug Calculations Lecture Notes/Handout I. Metric conversions – at times it will be required that conversions are performed. a. 1 mg = .001g b. 1g = 1000mg c. 1000 ml = 1L d. Perform the following: 2500 g 1.35 kg cc 35 mg 7.5 ml mg g .19L g cc II. Calculating with proportions a. Convert to consistent unit of measure b. Set up proportion Original dose Desired dose = per amount Per amount OR Original dose: per amount :desired dose: per amount EXAMPLE: 0.5g is needed of a drug that comes in 250 mg/tablet c. Drug in a solution EXAMPLE: 120 mg of Phenobarbital in 30 ml of Phenobarbital elixir. How many ml of elixir is required to deliver 15 mg? EXAMPLE: there is 0.2 mg/ml in glycopyrrolate. The order requires 1.5 mg, how many ml is required? d. Calculate with a dosing schedule – usually based on pt wt. Schedule = what should be given Prepared strength mixture (on hand) EXAMPLE: The dosing schedule for a patient receiving albuterol syrup is 0.1 mg/kg. The syrup comes 2 mg/5ml. How much syrup is required for a 20 kg child? EXAMPLE: a dose of surfactant calls for 5cc/kg; the infant weighs 1200g. How much surfactant will be delivered? III. Percentages a. Solution: composed of solute (med) dissolved in a solvent (liquid) b. Percentage strength solution: consists of active ingredient (solute) contained in 100 parts of total preparation. c. Types of % preparations Weight-Weight: g/100g ,mixture Weight-volume: g/100 ml mixture Volume-volume: ml/100ml mixture IV. Solutions by Ration (solute-to-solvent) a. Ratio is g/ml EXAMPLE: isoproterenol 1:200 solution EXAMPLE: Epinephrine 1:100 solution V. Ratio by Simple parts a. 1:8 is 1 part to 8 parts; or ¼ cc to 2cc b. Doesn’t state actual amounts or specific units; 1:8 is not precise c. Solution with pure active ingredient; (no dilution or 100% strength) Solute (g or cc) % strength = (in decimals) Total amount (solute & solvent) OR Amount solute Amount of solute = Total amount 100 parts (g or cc) EXAMPLE: How many mg of active ingredient are there in 2 cc of 1:200 isoproterenol? d. When active ingredient is already diluted (less than pure) Desired % (Dilute solute) x (% strength of solution) = strength Total amount of solution (in decimals) EXAMPLE: How much 20% mucomyst is needed to prepare 5cc of 10% mucomyst? EXAMPLE: How much 20% mucomyst is required to preare 5 cc of 5% mucomyst? ALTERNATIVE: solve for mg/ml EXAMPLE: Usual dose of albuterol sulfate is 0.5 ml of 0.5% strength solution. How many mg is this?