Energy in our Atmosphere Study Guide
advertisement

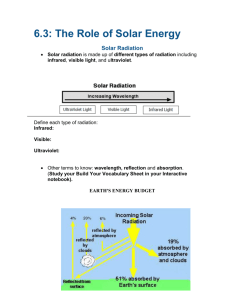
Name ___Answer Key_____________ Date __________________ Class Period ________ Energy in our Atmosphere Study Guide I. Matching. Write the correct word for each definition. Use: conduction, convection, radiation, convection currents 1) __Convection Currents__The process of warm air rising and cold air sinking in a repeated pattern. 2) 3) 4) Convection Conduction Radiation heat transferred though a liquid or a gas heat transferred directly from one solid to the next through direct contact. heat transferred through electromagnetic waves Matching. Write the correct word for each definition. Use: The Earth’s energy budget, wind, Greenhouse effect, The sun, greenhouse gases 5) Greenhouse effect The concept that certain gases trap heat in our atmosphere. 6) __The sun This is responsible for powering the atmosphere, oceans, causing weather, providing heat, light, energy, and causing life processes. 7) Wind The unequal heating and cooling of land and water that causes local winds. 8) Earth’s Energy Budget_ The concept that energy in our atmosphere is balanced by being absorbed and reflected. 9) Greenhouse gasses methane, water vapor, carbon dioxide 10. Complete the chart below: Convection How does it move? By moving molecules in a fluid (liquid or gas) What are some examples? Winds, heating in the atmosphere, boiling water, currents in the ocean Conduction By direct contact Hand warmers, holding a cup of tea, group hugs, laying on the warm ground. Radiation Through empty space on electromagnetic waves Sun through space, sunlight on your face, standing near a fire 11. Draw and label an illustration of warm air and cold air for each box. Beside each box tell 3 facts (think about what it does, it’s energy, it’s density). Cold Warm 1. Sinks 1. Rises 2. Molecules move slowly 2. Molecules move quickly 3. More dense 3. Less dense 12. Label the following on the electromagnetic spectrum diagram: infrared waves, radio waves, gamma rays, visible light, microwave, x-rays, ultraviolet light, MORE energy, LESS energy. Radio Waves Ultraviolet Microwaves Visible Light Infrared X-rays Gamma rays LESS Energy MORE Energy 13. Which part of the electromagnetic spectrum has more energy? Why does it have more energy? (Think about the wavelength and frequency) The side with gamma rays, it has more energy because it has a shorter wavelength and higher frequency. 14. Which part of the electromagnetic spectrum has less energy? Why does it have less energy? (Think about the wavelength and frequency) The side with radio waves, it has more energy because it has a shorter wavelength and higher frequency. True or False: If false, correct the sentence to make it true. 15. F Warm air sinks. Cold air sinks or Warm air rises 16. F Cold air rises. Cold air sinks or Warm air rises 17. T Heat is transferred through the atmosphere in convection currents. 18. F The sun does NOT cause the atmosphere to move, oceans to move, wind, and the water cycle. 19. T Gases that trap heat cause the Greenhouse effect. 20. F Radio waves, microwaves, and infrared waves Gamma Rays, UV, X-rays are dangerous to humans. 22. Explain the concept of the Earth’s Energy budget. The way Earth absorbs, reflects and uses solar energy. It should be 50% absorbed and used and 50% reflected to maintain an balanced energy budget. 23. What things reflect, absorb and scatter the Sun’s radiation Ground, Oceans/water source, Clouds, Dust, Water vapor, Gases in the atmosphere 24. About what percentage of the Sun’s energy is reflected and absorbed in a balanced energy budget? 50% 25. Use the chart below to answer the questions: Ms.Frizzle’s science class performed an experiment testing how different substances heat. Below are their observations: Item Starting Temperature (°C) Piece of clear glass Black piece of cloth White piece of paper Cup of sand piece of red plastic 17 19 17.5 19 17.5 Final Temperature (°C) after 30 minutes 28 35 19.5 27.5 33 A) Which object heated the least? Which heated the most? The white paper heated the least (19.5°C – 17.5°C = 2 °C). The black cloth heated the most (35°C - 19°C = 16°C) B) Which statement would be a correct conclusion based on the data? Circle your answer choice. The lighter objects increased their temperature more. OR The darker objects increased their temperatures more Convection Currents: Use the diagram to answer the questions below. 26. What do the arrows moving up represent? Warm air rising up 27. What do the arrows moving down represent? Cold air sinking down 28. Number the following steps in the order they occur in convection currents: _7_ The cycle repeats itself. 3_The ground heats the air above it through conduction. 6 Cold air sinks. 2_The sun’s radiation warms the ground. 4 Warm air rises through convection. 5 Air cools off high in the atmosphere. 1 The sun’s radiation moves through the atmosphere. 29. Why would the land be warmer then the water during the day? The land is warmer than water during the day because land heat up faster than water. 30. Why would the water be warmer then the land at night? The water is warmer than land at night because the water holds it’s heat longer than land. 31. Why do climates nearer to the ocean tend to be warmer in the winter then areas away from the ocean? Places near oceans stay warmer in the winter because the ocean stays warmer during the winter than just land would, so the areas near it are warmer. 32. Label the diagram below with the correct order of layers of the atmosphere-mesosphere, thermosphere, troposphere, stratosphere. 4) Thermosphere 3) Mesosphere 2) Stratosphere 1) Troposphere Read the following list of facts about the layers of atmosphere. Put a “T” next to troposphere facts, “M” next to mesosphere facts, “TH” next to thermosphere, and “S” next to stratosphere facts. 5) __T__ layer where weather occurs 6) _S__ location of ozone layer 7) __M_ meteors burn up here 8) _M__ coldest layer 9) __TH_ hottest layer 10) __T_ air is most dense here 11) _T__ we live here 12) __TH_ satellites orbit here