CH 19 Reactions
advertisement

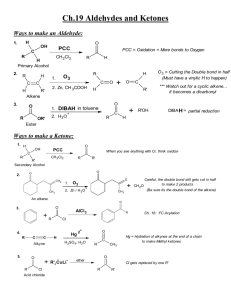
CH 19 Reactions CHM 2211 Preparation of Aldehydes H PCC OH Mild oxidizing agent, PCC will oxidize primary alcohols to aldehydes but will not oxidize alkenes O CH2Cl2 O O3 O using cyclic alkenes a dicarbonyl cmpd results H Zn, CH3 CO2 H O O3 O H Zn, CH3CO2H H O O O3 H Zn, CH3 CO2 H O + H using alkenes with at least 1 vinylic hydrogen, oxidative cleavage results in aldehydes O H DIBAH toluene O -78 C H3 O+ H DIBAH = Al Preparation of Ketones OH O PCC Several oxidizing agents can be used (see CH 17) to produce ketones from secondary alcohols CH2Cl2 O3 H 2C O + Zn, H3O+ O ozonolysis produces ketones if one of the unsaturated carbon atoms is disubstituted O O + AlCl3 Cl Friedel Craft's Acylation heat H3O+ methyl ketones are produced by hydration of terminal alkynes HgSO4 O Cl O (CH3)2CuLi ether O 1 Oxidation of Aldehydes and Ketones Oxidation of an aldehyde to a carboxylic acid can be accomplished by several reagents Jones reagent = CrO3, H3O+, acetone, 0C Tollens reagent = Ag2O, NH4OH, H2O Oxidations of ketones are much more difficult to accomplish Oxidative Cleavage with KMnO4, H2O, NaOH, H3O+ Nucleophilic Addition Reactions Nucleophile can be negatively charged HO-, H-, R3C-, RO-, NCNucleophile can be neutral H2O, ROH, NH3, RNH2 Base catalyzed hydration of aldehyde/ketone O NaOH OH H2O + NaOH + NaOH OH O NaOH H H2O OH H OH Acid catalyzed hydration of aldehyde/ketone 2 OH H3O+ O + H2O OH OH H3O+ O H2O H H3O+ H + H3O+ OH Addition of H-Y to C=O Y = electronegative Y + Y = -OCH3, -OH, -Br, -Cl, HSO4- H-Y OH O Cyanohydrin Formation CN + HCN OH O Aldehydes and unhindered ketones Cyanohydrin reactions CN OH CN LiAlH4 THF H2O H3O+ heat OH CH2NH2 forms a primary amine OH COOH forms carboxylic acids OH Addition of Grignard Reagents 3 CH2CH3 CH3CH2MgX ether O H3O+ OH aldehyde or ketone Hydride Addition LiAlH4 or NaBH4 O + ethanol H3O+ H2O OH aldehyde or ketone Addition of Amines (Imine and Enamine formation) Add. Of primary amines leads to imines O N CH3CH2CH2NH2 H3O+ H CH2CH2CH3 H + H3O+ + H3O+ aldehyde or ketone Add. Of secondary amines leads to enamines O H H3C (CH3)2NH H3O+ H N CH3 aldehyde or ketone Addition of Hydrazine: W-K reaction 4 H2NNH2 O H3O+ + KOH -OH yields an alkane aldehyde or ketone Addition of Alcohols (acetal formation) O 2 CH3CH2OH HCl OCH2CH3 + H2O OCH2CH3 aldehyde or ketone Addition of Phosphorus Ylides: Wittig Reaction O (CH3)2C-P+(Ph)3 THF + O=P(Ph)3 aldehyde or ketone Cannizaro Reaction Addition to ,-unsaturated Aldehydes and Ketones 5 Conjugate Addition of Amines O CH3NH2 O NHCH3 H3O+ aldehyde or ketone Conjugate Addition of Alkyl groups: Organocopper Reactions O (CH3)2CuLi ether H3O+ O CH3 ketone only 6