Record of Pupil`s Progress Level 1 -Exceptional
advertisement

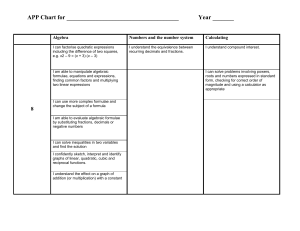
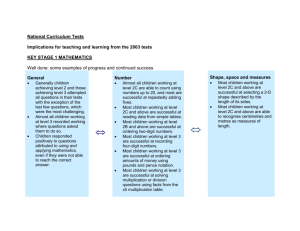
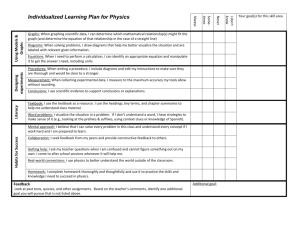
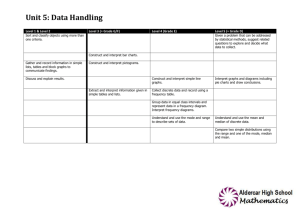
Record of Pupil’s Progress in Mathematics (Level 1 – Exceptional Performance) Pupil’s name ________________ Year 6 Year 7 Year 8 Year 9 Level 1 S k i l l s - Use mathematics as an integral part of classroom activities - Use everyday language to compare and to describe positions - Use everyday language to compare and to describe properties of regular shapes - Represent their work with objects or pictures and discuss it - Recognise repeating patterns - Use repeating patterns - Make repeating patterns - Sort and classify objects, demonstrating the criterion used - Measure and order objects using direct comparison - Order events Level 2 - Choose the appropriate operation when solving addition problems - Choose the appropriate operation when solving subtraction problems - Talk about the work using familiar mathematical language - Represent the work using symbols and simple diagrams. - Sort objects and classify them using more than one criterion - Gather information and record the results in simple lists - Gather information and record the results in tables - Gather information and record the results in simple diagrams - Gather information and record the results in block graphs Level 3 - Organise the work - Check results - Try different approaches - Talk about and explain their work - Use and interpret mathematical symbols - Use and interpret mathematical diagrams - Find particular examples that satisfy a general statement. - Classify shapes in various ways - Extract and interpret information presented in simple tables and list - Construct and interpret bar charts - Construct and interpret pictograms Level 1 R a n g e - Count when solving problems involving up to 10 objects - Order numbers when solving problems involving up to 10 objects - Add numbers when solving problems involving up to 10 objects - Subtract numbers when solving problems involving up to 10 objects - Read numbers up to 10 Write numbers up to 10 - Count on in steps of different sizes and from different numbers - Count back in steps of different sizes and from different numbers - Aware of the value of different coins - Use everyday language to compare and to describe positions -Use everyday language to compare and to describe properties of regular shapes - Sort and classify objects, demonstrating the criterion used - Measure and order objects using direct comparison - Order events Level 2 - Count sets of objects reliably - Recall number facts to 10 to add larger numbers - Recall number facts to 10 to subtract larger numbers - Order numbers up to 100 - Identify and use halves and quarters in practical situations - Recognise sequences of numbers. - Use mental calculation strategies to solve number problems - Use mental calculation strategies to solve money problems - Use mental calculation strategies to solve measure problems - Use everyday non-standard units to measure length - Use everyday non-standard units to measure mass - Use standard units to measure length - Use standard units to measure mass - Distinguish between straight and turning movements - Recognise half-turns - Recognise quarter-turns - Recognise right angles in turns. Gather information and record the results in tables - Gather information and record the results in simple lists - Gather information and record the results in simple diagrams - Gather information and record the results in block graphs Level 3 - Use place value in numbers up to 1000 to make approximations - Use decimal notation in recording money - Recognise negative numbers in the context of temperature - Develop further mental strategies for adding numbers with at least two digits - Develop further mental strategies for subtracting numbers with at least two digits - Use mental recall of the 2, 3, 4, 5, & 10 multiplication tables in solving whole-number problems involving multiplication - Use mental recall of the 2, 3, 4, 5, & 10 multiplication tables in solving whole-number problems involving division, including those giving rise to remainders - Use standard units of length - Use standard units of capacity - Use standard units of mass. - Use standard units of time - Classify shapes in various ways. - Extract and interpret information presented in simple tables and list - Construct and interpret bar charts - Construct and interpret pictograms Level 4 - Develop own strategies for solving problems. - Choose and use suitable units and instruments, reading with appropriate accuracy, numbers on a range of measuring instruments. - Present information and results S systematically. k - Search for a solution by trying out own ideas. i - Check that results are reasonable by l considering the context or the size of the l numbers. s - Recognise and describe number patterns and relationships. - Use simple formulae expressed in words. - Draw and interpret frequency diagrams. - Construct and interpret simple line graphs. Level 5 - Identify and obtain information to solve problems. - Make sensible estimates of a range of everyday measures. - Describe situations mathematically using symbols, words and diagrams. - Check whether results are sensible in the context of the problem - Draw own conclusions, explaining their reasoning. - Make general statements of their own, based on available evidence. - Appreciate that different outcomes may result from repeating an experiment. Level 6 - Solve complex problems by breaking them down into smaller tasks. - Interpret, discuss and synthesise information presented in a variety of mathematical forms. - Represent mappings expressed algebraically. - Find and describe in words the rule for the next term or nth term of a sequence where the rule is linear. - Give some mathematical justifications to support own methods, arguments or conclusions. - Interpret frequency diagrams, pie charts and scatter diagrams Level 4 R a n g e - Use the understanding of place value to multiply and divide whole numbers by 10 and 100. - Use a variety of mental and written methods for computation. - Recall multiplication facts up to 10 x 10. - Add decimals to two places. - Subtract decimals to two places. - Use simple fractions describe approximate parts of a whole. - Use percentages to describe approximate parts of a whole. - Use simple formulae expressed in words. - Choose and use suitable units and instruments, reading with appropriate accuracy, numbers on a range of measuring instruments. - Use my knowledge of shape to make 3-D mathematical models. - Draw common 2-D shapes in different orientations on grids. - Reflect simple shapes in a mirror line. - Find perimeters of shapes. - Find areas by counting squares. - Find volumes by counting cubes. - Use and interpret co-ordinates in the first quadrant. - Collect discrete data. - Group data where appropriate. - Draw and interpret frequency diagrams. - Construct and interpret simple line graphs. - Use the mode and median as characteristics of a set of data. - Understand and use simple vocabulary associated with probability. Level 5 - Use my understanding of place value to multiply and divide whole numbers and decimals. - Order, add and subtract negative numbers. - Check solutions by applying inverse operations. - Estimate by using approximations. - Calculate fractional parts of quantities and measurements. - Calculate percentage parts of quantities and measurements. - Construct and use simple formulae involving one or two operations. - Use coordinates in all 4 quadrants. - Measure angles to the nearest degree. - Draw angles to the nearest degree. - Recognise, identify and describe all the symmetries of 2-D shapes. - Convert one metric unit to another. - Know the rough metric equivalents of imperial units in daily use. - Find areas of rectangles and triangles. - Find volumes of cuboids. - Read scales on maps, plans and graphs. - Use the mean of discrete data and compare 2 simple distributions. - Interpret graphs and diagrams. - Interpret pie charts. - Use the probability scale from 0 to 1. - Appreciate that different outcomes may result from repeating an experiment. Level 6 - Formulate and solve a variety of simple linear equations. - Find and describe in words the rule for the next term or nth term of a sequence where the rule is linear. - Use trial-and-improvement methods involving approximating and ordering decimals. - Calculate one number as a fraction or percentage of another. - Use the equivalences between fractions, decimals and percentages and calculate using ratios in appropriate situations. - Use common 2-D representations of 3-D objects, and the properties of quadrilaterals to classify different types of quadrilateral. - Solve problems using angle and symmetry properties of polygons and properties of intersecting and parallel lines. - Use formulae for finding circumferences and areas of circles. - Use formulae for finding areas of plane rectilinear figures and volumes of cuboids. - Enlarge shapes by a positive whole-number scale factor. - Collect and record continuous data. - Construct and interpret frequency diagrams. - Construct and interpret pie charts. - Construct and interpret scatter diagrams. - Use my own knowledge that the total probability of all the mutually exclusive outcomes of an experiment is 1, and find and justify probabilities. - Identify all the outcomes when dealing with a combination of two experiments. S k i l l s Level 7 - Consider alternative approaches, - Describe in symbols the next term or nth term of a sequence with a quadratic rule - Justify own generalisations, arguments or solutions. - Appreciate the difference between mathematical explanation and experimental evidence. - Specify and test hypotheses taking account of bias. Level 8 Exceptional Performance - Develop and follow alternative approaches, - Solve problems using intersections reflecting on their own lines of enquiry and and gradients of graphs, Pythagoras’ using a range of mathematical techniques theorem and trigonometric ratios - Convey mathematical or statistical - Solve problems in two and three understanding through precise and consistent dimensions using Pythagoras’ theorem use of symbols and trigonometric ratios - Examine and discuss generalisations or - Use mathematical language and solutions they have reached symbols effectively in presenting a - Interpret graphs of linear, quadratic, cubic convincing reasoned argument, and reciprocal functions, and graphs that including mathematical justification model real situations, cumulative frequency - Express general laws in symbolic tables and diagrams. form. - Compare distributions and make inferences - Give reasons for the choices made when investigating within mathematics. - Interpret graphs based on trigonometric functions and histograms. - Present a convincing reasoned argument, including mathematical justification Level 7 R a n g e - Examine critically and justify own choice of mathematical presentation. - Make estimates, round to one significant figure. - Multiply and divide mentally. - Understand the effects of multiplying and dividing by numbers between 0 and 1. - Calculate proportional changes. - Solve numerical problems with numbers of any size, using a calculator efficiently and appropriately. - Use algebraic and graphical methods to solve simultaneous linear equations in two variables and solve simple inequalities. - Use Pythagoras’ theorem in two dimensions. - Calculate lengths, areas and volumes in plane shapes and right prisms. - Enlarge shapes by a fractional scale factor. - Appreciate the imprecision of measurement and use compound measures such as speed. - Analyse data to determine modal class and estimate the mean. - Estimate the mean, median and range of sets of grouped data. - Use measures of average and range to compare distributions. - Draw a line of best fit on a scatter diagram by inspection. - Use relative frequency as an estimate of probability, and use this to compare outcomes of experiments. Level 8 - Solve problems involving calculating with the extended number system, including powers, roots and standard form. - Manipulate algebraic formulae, equations and expressions. - Solve inequalities in two variables. - Understand congruence and mathematical similarity. - Use sine, cosine and tangent in right-angled triangles. - Interpret and construct cumulative frequency tables and diagrams. - Solve problems using the probability of a compound event. - Interpret graphs of linear, quadratic, cubic and reciprocal functions, and graphs that model real situations, cumulative frequency tables and diagrams. - Compare distributions and inferences - Sketch and interpret graphs of linear, quadratic, cubic and reciprocal functions, and graphs that model real situations - Compare distributions and make inferences, using estimates of the median and interquartile range Exceptional Performance - Calculate lengths of circular arcs. - Calculate areas of sectors,. - Calculate surface areas of cylinders. - Calculate volumes of cones and spheres. - Use, generate and interpret graphs based on trigonometric functions. - Solve problems using intersections and gradients of graphs. - Understand how different sample sizes may affect the reliability of conclusions. - Solve problems in two and three dimensions using Pythagoras’ theorem and trigonometric ratios - Interpret and construct histograms - Recognise when and how to use conditional probability