outline31255
advertisement

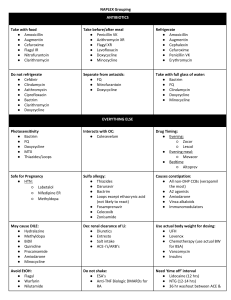
Oral Antibiotics Feel More Confident and Comfortable in One Hour Prescribing Oral Antibiotics for Your Patients 1-Hour Course Outline Greg Caldwell, OD, FAAO I. II. III. IV. Disclosures a. Greg A. Caldwell, OD, FAAO will mention many products, instruments and companies during our discussion; I don’t have any financial interest in any of these products, instruments or companies. No financial interests to disclose. b. All of these cases have entered/referred to my practice Rules During this Presentation a. There are no rules b. Have fun, enjoy and relax c. Ask questions at the time of the case Medical History a. Before we Rx any medications we take a thorough medical history which includes: i. Adverse/Allergic Reaction to Systemic Medication ii. Hypersensitivity- fever, rash, photosensitivity or ANAPHYLAXIS iii. Renal Impairment- Identify patients on hemodialysis 1. Adjustment made by patient’s creatinine clearance (CrCl)…ml/min 2. Work with patient’s PCP/Internist b. FDA Pregnancy Categories i. Category A- studies in pregnant women, no risk ii. Category B- animal studies no risk but human not adequate…or…animal toxicity but human studies no risk…safe iii. Category C- animal studies show toxicity human studies inadequate but benefit of use may exceed risk…avoid iv. Category D- evidence of human risk but benefits may outweigh risks…avoid v. Category X- fetal abnormalities, risk>benefits…avoid 42 year old woman, OD red, painful and stuck shut in the AM a. Slit Lamp Evaluation further reveals. i. New Diagnosis? 1. Recurrent bacterial conjunctivitis secondary to dacryocystitis 2. Dacryocystitis b. Treatment discussion? i. Topical antibiotics ii. Oral antibiotics c. Remember to check for? i. Patient is allergic to Penicillin and Keflex ii. Which antibiotic would you use? d. Oral antibiotic Paradigm i. Cross Reaction ii. Augmentin 1. Amoxicillin and potassium clavulanate 2. Kills everything, good for everyone a. 12 weeks old and older 3. Safe in pregnancy…category B 4. Watch for PCN allergies 5. Adults: 250, 500 and 875 mg iii. iv. v. vi. vii. 6. 125 mg of potassium clavulanate 7. Children <100 pounds: oral suspension 25-45 mg/kg divided into 2 doses 8. Covers Staph, Strep and Haemophilus influenzae Zithromax (azithromycin) 1. Macrolide antibiotic (erythromycin) 2. Drug of choice in PCN sensitive patients 3. All age groups and pregnancy category B 4. No renal adjustment 5. Adult: a. 250 mg bid (day1), 250 mg qd (day 2-5), 6 pack b. 500 mg qd x 3 days, tri-pack 6. Children<16: 10 mg/kg (day1), 5 mg/kg (day 2-5) 7. Covers Staph, Strep and Haemophilus influenzae 8. Better tolerated than erythromycin, little GI upset 9. Chlamydia…1 g qd-“The Vegas Drug” Keflex (cephalexin) 1. Cross reaction with PCN sensitive patients 2. 1st generation, moderately affective against PCN-ase 3. Good for Gram +, not good for Haemophilus (-) 4. Available in 250 and 500 mg 5. Category B 6. Adult: typically, 500 mg bid x 1 week a. Maximum 4 g in 24 hrs 7. FYI...Drug of choice for blow out fractures Ceftin (cefuroxime) 1. Minimal cross reaction with PCN sensitive patients 2. 2nd generation 3. Better for Haemophilus (-) 4. Children: 3 months to 12 years old, oral suspension 15 mg/kg divided into 2 doses x 10 days 5. Available in 125, 250 and 500 mg 6. FYI: adults typically 250 mg bid x 10 days 7. Category B Cipro (ciprofloxacin) Levaquin (levofloxacin) 1. In my opinion, an end of the line, antibiotic to use…allergic to PCN, cephlosporins, macrolides… 2. Really effective 3. Would avoid if pregnant…category C 4. Only use 18 years or older (oral) 5. Cipro and Levaquin available in 250, 500 and 750 mg 6. Cipro 750 mg for only severe infections a. 500 mg bid x 1 week-Cipro b. 500 mg qd x 1 week-Levoquin 7. Levaquin-tendon ruptures Sulfa Drugs 1. Limited use…last line of defense 2. Contraindicated in pregnancy and sickle cell disease 3. Category C 4. 5. V. VI. High incidence of Steven-Johnsons Cross reaction with: oral hypoglycemics, CAI’s, celebrex and thiazide diuretics…all sulfa based 6. Bactrim SS a. 400 mg sulfamethoxazole/ 80 mg trimethoprim, 1-2 tab PO bid 7. Bactrim DS (double strength) a. 800 mg sulfamethoxazole/ 160 mg trimethoprim, 1 tab PO bid viii. How About 1. PCN, Ampicillin and Amoxicillin 2. Dicloxacillin, 250mg qid x 1week e. Treatment i. Vigamox gtts TID ii. Zithromax iii. Disp: z-pak, Use as directed PO What group of antibiotics are we missing? a. Tetracycline 48 year old man, OU red, gritty, sandy and dry feeling a. Diagnosis- rosacea b. What findings support your diagnosis? i. Telangiectasias ii. Erythema of the cheeks, forehead and nose iii. Rhinophyma 1. Indicates chronic c. Let us get a closer look d. Rosacea Blepharitis-(Inflammatory Blepharitis, MGD) e. Treatment? i. In my opinion, most under treated condition ii. Warm compresses iii. Lid hygiene iv. Artificial tears v. Omega 3 fatty acid, flaxseed oil, fish oil 1. Flaxseed oil- short chains of Omega 3, thicken the lipid layer but decrease viscosity 2. Fish oil-long chains of Omega 3, suppresses inflammation vi. Dermatological consult (Acne Rosacea) vii. Oral antibiotics…??? 1. Which one and why?? 2. Minocycline / Doxycycline viii. Drug of choice for marginal inflammatory blepharitis (posterior blepharitis) 1. AB, anti-inflammatory and anti-collagenase 2. Inhibits lipase enzyme 3. No renal adjustment 4. 50-100 mg qd-bid 2-12 weeks (pulse) 5. 20 mg Periostat (Doxycycline) a. Helpful in those with stomach or GI sensitivity b. Excellent for those requiring long maintenance dose 6. My Paradigm for Minocycline / Doxycycline a. Status of MG i. Inspissated f. ii. Turbid iii. Clear b. Minocycline / Doxycycline Paradigm i. Maximum dosage for 2-12 weeks (pulse) 100 mg BID, QD ii. 50-100mg qd while turbid iii. 20 mg longer treatments 1. Periostat (Doxycycline) 2. 20 mg if maintenance dose needed c. Customize Treatment i. 50 mg Minocycline with pill cutter (25 mg) ii. Oracea- 40 mg of Doxycycline total 1. 30 mg immediate release 2. 10 mg sustained release iii. Alodox Kit 1. 20 mg Doxycycline 2. Ocusoft lid scrub iv. AzaSite (azithromycin opthalmic solution) 1.0% 1. Initiate early in treatment 2. Adjunctive when patient is already on Doxycycline 3. Alternative in states that do not have oral therapeutic licensure 7. Precautions With Oral Tetracycline Analogs a. Enhanced photosensitivity b. Avoid in children and pregnancy (Category D) c. Can enhance Coumadin d. Can enhance the action of digoxin e. ?Long term use with increase risk of breast cancer? i. 1 paper/study, not regarded as highly reliable study ii. Further investigation discredited the association f. Benign intracranial hypertension, reported cases i. 17 cases from 1978-2002 ii. Benign intracranial hypertension “It’s not rare if it’s in your chair” 8. Minocycline a. Less photosensitivity b. Less GI upset c. Less bacterial resistance ix. Successfully Treated 1. Warm Compresses 2. Lid Scrubs 3. Artificial Tears, Systane Balance 4. Mino 100 mg PO 6 weeks, 50 mg 3 months, 20 mg maintenance (Doxy) 5. Steroids, Tobradex qid (5 weeks with taper) 6. Moderately red and thickened lid margins 7. Marginal infiltrates x. Minocycline for Ulcers? 1. Are the anti-inflammatory benefits useful to help reduce the corneal degradation that occurs in sterile and infectious keratitis? What is an Inspissated MG? VII. VIII. i. I Can’t Believe It’s Not Butter!® Squeeze Questions? Thank-You and Hope You Enjoyed a. Greg Caldwell, OD, FAAO b. Grubod@gmail.com