Urinary tract infections (UTI guideline)
advertisement

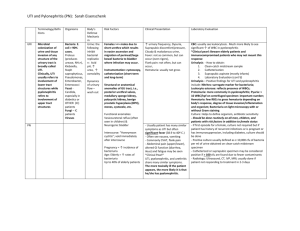
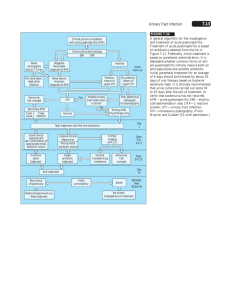
Urinary tract infections (UTI guideline) Anatomic Lower: urethritis, cystitis (superficial infection of bladder), prostatitis Upper: pyelonephritis (inflammatory process of the renal parenchyma), renal abscess Clinical Uncomplicated: cystitis in nonpregnant women without underlying structural or neurological disease Complicated: upper tract infection or any UTI in men or pregnant women or UTI with underlying structural or neurological disease (obstruction, reflux, azotemia, transplant, catheter-related) Microbiology Uncomplicated UTI: E.coli(80%), Proteus, Klebsiella, enterococci Complicated UTI: E,coli(30%), enterococci(20%), Pseudomonas(20%) , S.epidermidis(15%), other GNR Catheter-associated UTI: yeast(30%) , E.coli(25%), other GNR, enterococci, S.epidermidis Urethritis: Chlamydia trachomatis, Neisseria gonorrhoeae Clinical Manifestations Cystitis: dysuria, urgency, ↑frequency, △ in urine color/odor, suprapubic pain; fever generally absent Urethritis: may be identical to cystitis except for urethral discharge Pyelonephritis: fever, shaking chills, flank or back pain, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea Renal abscess( intrarenal or perinephric): identical to pyelonephritis except persistent fever despite appropriate antibiotics Diagnostic studies Urinalysis: pyuria+ bacteriuria +/-hematuria Significant bacterial counts: > 105 CFU/ ml in asymptomatic women, > 103 CFU/ml in men, > 102 CFU/ml in symptomatic or catheterized patients Sterile pyuria urethritis, renal tuberculosis, foreign body Urine gram stain and culture ( from clean-catch midstream or straight-catheterized specimen) in pregnant women and in patients undergoing urologic surgery-screen for symptomatic bacteriuria blood cultures: consider in complicated UTIs First-void and midstream urine specimens Abdominal CT to rule-out abscess in patients with pyelonephritis who fail to defervesce after 72h Urologic workup (KUB, renal U/S, abdominal CT, voiding cystography) Treatment of UTIs Clinical scenario Cystitis Urethritis Pyelonephritis Renal abcess Clinical scenario TMP-SMX or FQ x 3d or x 10-14 d(complicated) Asymptomatic bacteriuria in pregnant women or Treat for both Neisseria and Chlamydia Neisseria: ceftriaxone 125 mg IM x1 or ofloxacin 400 mg POx1 Outpatient: FQ or amoxicillin/clavulanate or 1st gen.ceph.PO x 14d Inpatient: [ampicillin IV+gentamicin] or ampicillin/sulbactam or FQ or P Ceph 3 or AP Pen X 14 d(△IVPO when patient improved Drainage + antibiotics as for pyelonephritis Reference: 1.Harrison’s Principles of Internal Medicine,15ed, P1620-1626 2.The Washington Manual of Medical Therapeutics 30 ed, P310-312 3.The Massachusetts General Hospital Handbook of Internal Medicine P6-3 4.The Stanford Guide To Antimicrobial Therapy,2004,P23