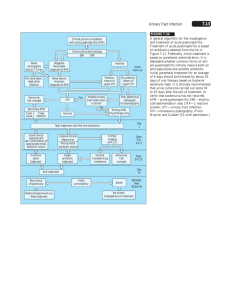
ACUTE PYELONEPHRITIS Zainab Aliyu 1904B Acute pyelonephritis is a bacterial infection of the renal pelvis and the renal parenchyma with fever, flank pain and bacteriuria. Symptoms include; flank pain, flank tenderness and/or fever. Ascending infection is the most common cause for acute pyelonephritis. It is more common in women than in men. Vesicourethral reflux (VUR) leads to refluxing urine, which becomes infected. Pyelonephritis in VUR tends to causes renal scarring, since intrarenal reflux is common. The incidence of bacteriuria in pregnancy is 4–7%, comparable to the rate of bacteriuria without pregnancy. PATHOLOGY Enlarged kidney with inflammatory edema Small subcapsular abscesses with hemorrhagic rim Pus-filled tubules The urothelium of the renal pelvis is thick and covered with exudate SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS Sudden fever and chills, malaise and weakness Constant flank pain. Children often complain about abdominal pain. Flank tenderness Frequency, dysuria, (micro)-hematuria Possible symptoms: nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal tenderness, decreased bowel sounds. Tachycardia, hypotension and further symptoms of urosepsis COMPLICATIONS OF ACUTE PYELONEPHRITIS Renal scarring, especially in children, with the development of chronic pyelonephritis Renal abscess Urosepsis with septic shock Emphysematous pyelonephritis in diabetes mellitus (high mortality) The diagnosis is mainly based on the triad of fever, flank pain and symptoms of bacterial cystitis. Radiological signs are discreet and ambiguous, they are found only in every fourth patient. DIAGNOSIS OF PYELONEPHRITIS Blood tests Leukocytosis Elevated ESR, elevated CRP Blood culture: pathogen can be detected in severe disease (high fever, signs of urosepsis) Appropriate antibiotics are fluoroquinolones, aminopenicillin in combination with beta-lactamase inhibitor and cephalosporins. In children, cephalosporins are preferred. Because of high resistance rates up to 40%, ampicillin or cotrimoxazole alone are inadequate. Duration of treatment: 7–14 days depending on severity and improvement Nephrectomy should be kept in mind, if urosepsis cannot be stabilized with the help of intensive medical care. SYMPTOMATIC TREATMENT OF PYELONEPHRITIS: Bed rest Analgesics with antipyretic effect, e.g. metamizol, for children paracetamol Increased fluid intake.