Physiological Homeostasis means …………
advertisement

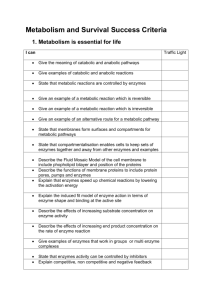
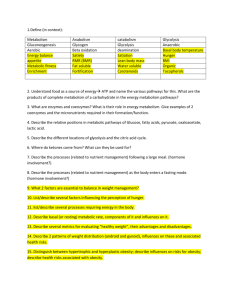
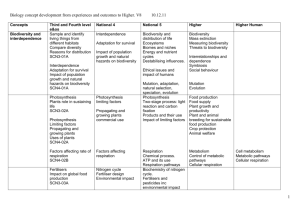
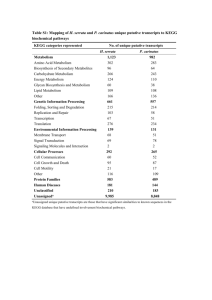
Metabolism & Survival Check List Higher Biology Section 1 – Metabolism and Survival Make sure you can ... State what is meant by catabolism and anabolism and given examples of each State that the metabolism is the total set of reactions in a cell Explain the importance of reversible and irreversible steps in pathways Explain the importance of alternative steps in metabolic pathways Explain why enzymes are necessary in cell reactions Describe how folding membranes and organelles can increase efficiency of pathways Describe how a phospholipid bilayer forms Describe the fluid mosaic model Give examples of functions of proteins in the fluid-mosaic Describe the activity of enzymes in terms of substrate and enzyme concentrations Describe how activation energy can be lowered by heat and enzymes. Explain enzyme function in terms of the induced-fit model of action Describe the effect of concentrations of substrates and products on pathways Explain enzyme induction using the lac operon in E.coli as an example Describe and explain the effect of competitive inhibitors on enzymes Describe and explain the effect of non-competitive inhibitors on enzymes Explain why feedback inhibition is needed in cells. Understand that the process of cellular respiration is common to all three domains of life Understand that cellular respiration is the core pathway in cells which delivers energy for cell metabolism Describe how glucose is broken down to ultimately deliver ATP Explain that ATP is used to transfer energy to carry out cell processes Explain the reversible nature of ATP production Describe how ATP is synthesised Describe glycolysis Describe the progression of respiration pathways, both in the presence and absence of oxygen Describe the citric acid cycle Understand that respiration is a series of enzyme mediated reactions © PJS@JOAT2014 Page 1 of 4 G A R Metabolism & Survival Check List Higher Biology Explain the importance of the products of the citric acid cycle Describe the electron transport chain as a membrane bound system Explain the role of dehydrogenase enzymes Understand the key role of NAD and FAD and their reduced forms Explain the role of oxygen in the electron transport chain and the consequences of its absence Describe how other substances can be used in place of glucose in cellular respiration Section 2 – Maintaining Metabolism Make sure you can ... State that metabolic rate can be measured by calculating the oxygen uptake, carbon dioxide production and the amount of heat produced State that high metabolic rates require efficient delivery of oxygen to cells Describe the physiology of the heart, circulation and lungs in amphibians, reptiles, mammals and birds Describe the heart and circulation in fish Explain how some organisms have adapted to survive in low oxygen areas, eg high altitude and under water Describe the graph showing how oxygen concentration changed over the geological timescale Compare the oxygen uptake in fit and unfit people and explain the reasons behind this Explain the term conformer and regulator in terms of metabolic rate Explain that the ability of an organism to maintain its metabolic rate is affected by abiotic factors State that conformers internal environment is dependent on the external environment Explain why conformers may have a narrow ecological niche Explain why regulators have an increased range of possible ecological niches State that regulators require energy for homeostasis Explain how thermoregulation takes place in mammals in terms of hypothalamus, nerves, effectors and skin State that organisms must have adaptations to survive environmental change Explain the meaning of dormancy and give an example of organisms who use this as a means of survival © PJS@JOAT2014 Page 2 of 4 G A R Metabolism & Survival Check List Higher Biology Explain the difference between predicted and consequential dormancy Give examples of hibernation in animals and aestivation in organisms and how these help their survival in adverse conditions Say what is meant by daily torpor and why it is important for some organisms State that some animals avoid adverse conditions by migration Understand why migration is important for some organisms Explain how innate and learned behaviour influences migratory behaviour Give the meaning of extremophiles and examples of where they will be found Give an adaptation of an extremophile to enable them to survive in their environment Section 3 – Metabolism in Microorganisms Make sure you can ... State that microorganisms include bacteria, archea (thermophiles) which are prokaryotes G State that some species of eukaryotes are also classed as microorganisms eg photosynthetic algae State that microorganisms can use a wide range of substrates for metabolism and produce a wide range of products in their metabolic pathways State that all microorganisms require an energy source (chemical/light) Say why simple chemical compounds are necessary in the growth media of microorganisms Explain why some growth media require more complex compounds Explain why sterile techniques are important when culturing microorganisms State that microorganisms require a suitable temperature, suitable oxygen concentration and an optimum pH for growth Say how to control the above conditions when culturing bacteria Draw a growth curve and note the lag, log/exponential, stationary and death phases on the graph Relate the phases of the growth curve to changes in the growth media State that some microorganisms can exhibit two types of metabolism – primary and secondary State when primary metabolism takes place and explain that it produces primary metabolites and energy State when secondary metabolism takes place and the secondary metabolites can confer an ecological advantage Give examples of how the secondary metabolites can confer an ecological advantage to the microorganism and how some can be beneficial to humans Explain how metabolism can be manipulated using induction, inhibition and end product inhibition Describe how lactose can be an inducer molecule in the formation of galactosidase in © PJS@JOAT2014 Page 3 of 4 A R Metabolism & Survival Check List Higher Biology E.coli State that wild strains of bacteria can be improved by mutagenesis, selective breeding, or recombinant DNA State what mutagenesis is and how this can be induced in microorganisms State how recombinant DNA technology can improve the strain of bacteria Explain how sexual reproduction between microorganisms eg fungi can produce desirable characteristics in the daughter cells Explain how some bacteria can transfer plasmids or chromosomal DNA to each other Describe the process of alteration of the DNA in a bacterial cell by recombination of a gene(genes) from another organism to include the terms endonucleases ,ligase, restriction site, vectors Know that the purpose of an artificial chromosome allows a much longer sequence of DNA to be carried from the donor organism to the recipient organism. State the ethics, risks and control of the risks when using microorganisms © PJS@JOAT2014 Page 4 of 4