Organic Chemistry
advertisement

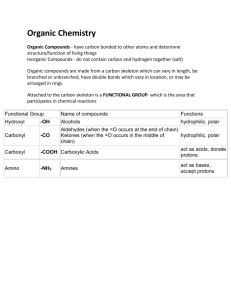
Organic Chemistry Organic Compounds - compounds synthesized by cells and contain carbon Organic compounds are made from a carbon skeleton which can vary in length, be branched or unbranched, have double bonds which vary in location, or may be arranged in rings. Attached to the carbon skeleton is a FUNCTIONAL GROUP - which is the area that participates in chemical reactions Functional Group Name of compounds Functions -OH Alcohols hydrophilic and polar Carbonyl -CO Aldehydes (when the =O occurs at the end of chain) hydrophilic and polar Ketones (when the =O occurs in the middle of chain) Carboxyl -COOH Carboxylic Acids act as acids, donate protons Amino -NH2 Amines Act as bases, pick up protons from acids Hydroxyl What type of compounds are the following? Reaction Types Hydrolysis - break down compounds by adding water Dehydration - two components brought together, produces H2O Endergonic - requires the input of energy Exergonic - releases energy Redox - electron transfer reactions MACROMOLECULES important to life 1. 2. 3. 4. Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic Acids 1. CARBOHYDRATES monosaccharides - simple ring sugars, glucose and fructose disaccharides - two monosaccharides combined, sucrose and lactose polysaccharides - polymers (long chains of repeating units) of monosaccharides, starch and glycogen 2. Lipids Hydrophobic waxes, oils, fats, steroids (cholesterol & sex hormones) important structural component of the cell membrane (phospholipid) Saturated fats contain no double bonds *Saturated fats solidy at room temperature, unsaturated fats are liquid at room temperature 3. Proteins Polymers made of amino acids Amino acids are joined by peptide bonds Amino acids form a wide variety of structures, building blocks for living tissue The chain of amino acids coil into a 3D structure Proteins can be denatured, heat causes it to lose its shape, and its functionality (More on enzymes later) Proteins have four shapes 1. 2. or 3. 4. Primary Structure - sequence of amino acids that form the polypeptide chain Secondary Structure - Parts of the polypeptide fold into local patterns (alpha helix pleated sheet) Tertiary Structure - the overall 3D shape (globular or fibrous) Quaternary Structure - consits of two or more polypetide chains or subunits 4. Nucleic Acids Informational polymers DNA & RNA