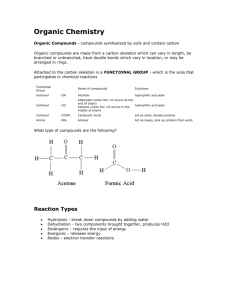
have carbon bonded to other atoms and
advertisement

Organic Chemistry Organic Compounds - have carbon bonded to other atoms and determine structure/function of living things Inorganic Compounds - do not contain carbon and hydrogen together (salt) Organic compounds are made from a carbon skeleton which can vary in length, be branched or unbranched, have double bonds which vary in location, or may be arranged in rings. Attached to the carbon skeleton is a FUNCTIONAL GROUP- which is the area that participates in chemical reactions Functional Group Name of compounds Functions Hydroxyl -OH Alcohols hydrophilic, polar Carbonyl -CO Aldehydes (when the =O occurs at the end of chain) Ketones (when the =O occurs in the middle of hydrophilic, polar chain) Carboxyl -COOH Carboxylic Acids act as acids, donate protons Amino -NH2 act as bases, accept protons Amines What type of compounds are the following? Isomers – molecules with the same molecular formula, but different arrangement of atoms Reaction Types Hydrolysis - break down compounds by adding water Dehydration - two components brought together, produces H2O Endergonic - requires the input of energy Exergonic - releases energy Redox - electron transfer reactions - Remember OIL RIG Monomers link together to form polymers Dehydration reaction – water is removed, joins monomers together Hydrolysis – water attaches to a polymer and breaks it into smaller units MACROMOLECULES fall into four major groups 1. Carbohydrates 2. Lipids 3. Proteins 4. Nucleic Acids 1. CARBOHYDRATES monosaccharides - simple ring sugars, glucose and fructose disaccharides - two monosaccharides combined, sucrose and lactose (dehydration synthesis) polysaccharides - polymers (long chains of repeating units) of monosaccharides, starch (plant energy storage) and glycogen (animal energy storage) pentoses - five carbon sugars; deoxyribose & ribose (DNA) Polysaccharides as Structural Molecules Cellulose - glucose bonded to form "fibers", composes cell walls (cotten is almost pure cellulose); not easily digested Chitin - polymer of glucose, makes up exoskeletons of arthropods Glucose is a molecule that can be combined to make lactose and sucrose. 2. Lipids Hydrophobic (insoluble in water) Used for insulation and long term energy storage (fat)* Fats* & Oils are made of subunits – glycerol and fatty acids Waxes – mainly used for covering and protection Phospholipids - Important structural component of the cell membrane Steroids - cholesterol & sex hormones (estrogen & testosterone) – made of 4 fused rings *Saturated fats contain no double bonds, unsaturated have double bonds that “kink” the molecule *Saturated fats solidify at room temperature; unsaturated fats are liquid at room temperature 3. Proteins Polymers made of amino acids, which are joined by peptide bonds - proteins are also called polypeptides Amino acids form a wide variety of structures, mainly building blocks for living tissue Support | Enzymes | Transport | Defense | Hormones | Motion Proteins can be denatured, heat causes it to lose its shape, and its functionality (More on enzymes later) There are 20 known amino acids Proteins have four shapes 1. Primary Structure - sequence of amino acids that form the polypeptide chain 2. Secondary Structure - Parts of the polypeptide fold into local patterns (alpha helix or pleated sheet) 3. Tertiary Structure - the overall 3D shape (globular or fibrous) 4. Quaternary Structure consists of two or more polypeptide chains or subunits 4. Nucleic Acids Informational polymers made of individual nucleotides DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) & RNA (ribonucleic acid) Each nucleotide consists of: 1. A sugar (deoxyribose or ribose) 2. A phosphate 3. A nitrogen base - adenine - thymine (in DNA) - guanine - cytosine - uracil (in RNA) ATP (adenosine triphosphate) - high energy molecule that contains two phosphate bonds that are easily broken to release energy (this energy drives the reactions in our bodies) Molecule of ATP stores energy Dehydration reaction releases this energy QUIZ YOURSELF! a. carbohydrate 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. b. lipids contains adenine and thymine lactose chains of amino acids long term energy storage cholesterol chains of fatty acids and glycerol plant cell walls c. protein d. nucleic acids