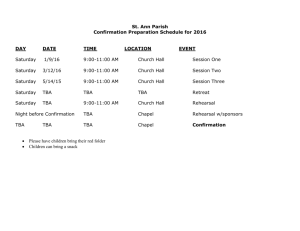
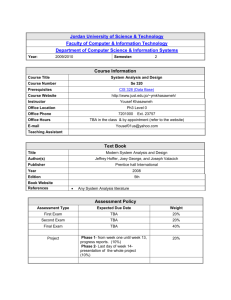
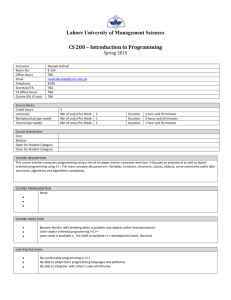
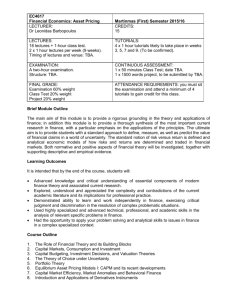
I. EDUC 7782 Applied Linguistics for the ESOL
advertisement

I. ENGL 3035 Introduction to Language and Linguistics Department of English Kennesaw State University Summer 2009 II. Instructor: David Johnson, Ph.D. Office: EB 224 Office Hours: 12:00 – 1:00 M-F Phone: 770-423-6208 e-mail: djohnson@kennesaw.edu homepage: http://ksumail.kennesaw.edu/~djohnson I will also post the syllabus on WebCT III. Class Sessions: MTWTHR 1:00 – 5:30 EB 168 IV. Texts: Bauer, L. and Trudgill, P. (Eds.) (1998). Language myths. London: Penguin Books. Fromkin, V., Hymes, N., and Rodman, R. (2007). An introduction to language. Boston: Thomson and Wadsworth. Rodriguez, R. (1982). Hunger of memory: The education of Richard Rodriquez. New York: Bantam. Valdes, G. (2001). Learning and not learning English: Latino students in American schools. New York: Teachers College Press. V. Catalogue Description: This course will analyze the nature of human language. It will include an introduction to speech sounds, morphology, syntax, and semantics. A heavy emphasis will be placed on the social and pedagogical implications of modern linguistic theory which will include an examination of issues such as language acquisition, dialect variation, historical linguistics, and English as a Second Language. VI. Purpose/Rationale: The purpose of this course is for students to increase their understanding of what language is, how it functions as a system, and how it functions in society. Conceptual Framework – see webpage VII. Goals and Objectives: Course Goals/Objectives: The KSU teacher preparation faculty is strongly committed to the concept of teacher preparation as a developmental and collaborative process. Research for the past 25 years has described this process in increasingly complex terms. Universities and schools must work together to successfully prepare teachers who are capable of developing successful learners in today’s schools and who choose to continue their professional development. (in process – from Conceptual Framework, Draft 17) All of the learning activities (readings, class discussions, lectures, projects, homework) are designed to help you achieve interrelated objectives and goals drawn from the Kennesaw Secondary Education Program Committee's objectives modeled from NCTE's Standards for the Preparations of Teachers of English/LA. 2 These objectives and goals also reflect the function of the course as a bridge between discipline-centered and professional education courses that introduce concepts and practices early in the program and the student teaching experience at its close. Objective Unit Proficiency NCATE/NCTE Assignments and Assessment 1. Explain how and why language varies 1.1, 1.2, 2.2 3.1.5 textbook readings and changes across regions, cultural view videos on dialects groups, and time periods. memorize timeline for English language quizzes/reflective essays 2. Explain general linguistic principles 1.1, 1.2 3.1.7 textbook readings and terminology (e.g., semantics, syntax, homework exercises on morphology, and phonology). phonetics, morphology, and syntax homework assignments quizzes 3. Analyze common language 1.1, 1.2 3.1.4 analyze popular misconceptions myths/realities. in popular media language surveys homework participation 4. Discuss the evolving nature and 1.1, 1.2 3.1.5 textbook readings historical development of the English view videos on dialects language and influences on its forms. memorize timeline for English 5. Analyze leading theories of first and 1.1, 1.2 3.1.1 read articles on SLA second language acquisition classroom discussions on role of “critical period” 6. Articulate principles of teaching of 1.1, 1.2 4.4 read case studies of ELL English as a second or other language. students in K-12 settings reflective essay VIII. Course Requirements: Explanation of Assignments: Quizzes and Tests will be a combination of multiple choice, short answer, and short essay. The final exam will be cumulative. Homework will be assigned on occasion. Please come to class with it already completed and typed. Participation is expected. You should participate with engaging and constructive comments/questions. We will be discussing complex and sometimes controversial issues. Your input is greatly valued IX. Evaluation and Grading: Assignment Points Assessed Final exam 30% Mid-term Exam 30% Quizzes (announced & unnan.) 15% In-class work 15% Reflective Essay for Chalk/Wire 10% A 100 to 90 B 89 to 80 C 79 to 70 D 69 to 60 X. Course Objective 1-6 1-6 1-5 1-5 1-6 F 59 and below Academic Integrity Statement: Every KSU student is responsible for upholding the provisions of the Student Code of Conduct, as published in the Undergraduate and Graduate Catalogs. Section II of the Student Code of Conduct addresses the University's policy on academic honesty, including provisions regarding plagiarism and cheating, unauthorized access to University materials, misrepresentation/falsification of University records or academic work, malicious removal, retention, or destruction of library materials, malicious/intentional 3 misuse of computer facilities and/or services, and misuse of student identification cards. Incidents of alleged academic misconduct will be handled through the established procedures of the University Judiciary Program, which includes either an "informal" resolution by a faculty member, resulting in a grade adjustment, or a formal hearing procedure, which may subject a student to the Code of Conduct's minimum one semester suspension requirement. XI. Class Attendance Policy You may miss one full class with no penalty. After your first absence of a full class, your final grade will be reduced by 5% for each additional absence. Missing an hour of class will constitute and absence. After three hours of missed class time, your grade will be reduced by 5%. 4 IX Course Schedule BT = Bauer, L. and Trudgill, P. Language myths. FRH =. An introduction to language. Date May 11 May 12 May 13 May 14 May 15 May 18 May 19 May 20 May 21 May 22 XIII. Topics/Activities/Quizzes /Exam Introduction/Course Policies What is Language? The Brain and Language 1st Language Acquisition Morphology Syntax Semantics Phonetics Phonology Sociolinguistics Mid-term Exam Sociolinguistics History of English Second Language Acquisition Language Processing Writing Systems Final Exam Readings or Assign. Due TBA TBA TBA TBA TBA TBA TBA TBA Bibliography Conceptual Framework Summary References: Odell, S. J., Huling, L., & Sweeny, B. W. (2000). Conceptualizing quality mentoring, background information. In S. J. Odell & L. Huling (Eds.), Quality mentoring teachers (pp. 3-14). Indianapolis, IA: Kappa Delta Pi. Sternberg, R. J. (1996). Educational psychology has fallen, but it can get up. Educational psychology review, 8(2), 175-185. Sternberg, R. J. (1998). Metacognition, abilities, and developing expertise: What makes an expert student? Instructional Science, 26, 127-140. for novice Bibliography for this class: Asher, J. (1977). Learning another language through actions: The complete teacher's guidebook. Los Gatos: Sky Oaks Publications. Bialystyok, E. & Hakuta, K. (1994). In other words: The science and psychology of second-language acquisition. New York: Basic Books. Celce-Murcia, M. (2001). Teaching English as a second or foreign language. United States: Heinle & Heinle. Echevarria, J., Vogt, M., & Short, D. (2000). Making content comprehensible for English language learners. Boston: Allyn and Bacon. Ellis, R. (1994). The study of second language acquisition. Oxford: Oxford University Press. Fu, D. (1995). My problem is my English: Asian students and the American dream. Portsmith N.H.: Boyton/Cook Publishers. Graddol, D., Leith, D. & Swann, J. (1996). English: History, diversity and change. London: Routledge. Jannedy, S., Poletto, R. & Weldon, T. (eds). Language files: Materials for an introduction to language and linguistics. Columbus: Ohio State University Press. 5 Krashen, S. & Terrel, T. (1983). The natural approach: Language acquisition in the classroom. Oxford: Pergamon. Pinker, S. (1994). The language instinct: How the mind creates language. New York: HarperPerennial. Phillipson, R. (1992). Linguistic imperialism. Oxford: Oxford University Press. Tove Skutnabb-Kangas. (2000). Linguistic Genocide in Education - or Worldwide Diversity and Human Rights? Mahwah, New Jersey: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, 2000. Pp. v +785.