Part 1
advertisement

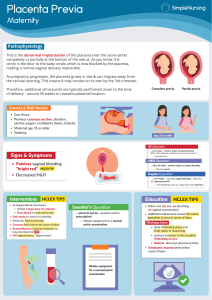
Part 1 (1) -The problem is vesicular mole (molar pregnancy) -Definition: It is a benign tumor during pregnancy in the trophoblastic tissues (2) Management plane : A- INVESTIGATIONS : Pregnancy test in urine ( positive in high dilutions ) B- h C G in serum ( very high levels ) U/S ( snow storm appearance in uterus / theca lutein cysts in ovaries ) Chest x – ray ( canon ball appearance if metastasis occurs ) Lab . investigations ( CBC. PT.PTT, ALT,…….) B- Once vesicular mole is diagnosed, immediate evacuation is mandatory. Surgical suction evacuation is considered the method of choice in all cases. Methods of evacuation: 1-vaginal evacuation: by suction apparatus ,ovum forceps, ring forceps or digital evacuation. During vaginal evacuation : I.V Pitocin drip , blood transfusion( IF NEEDED) After evacuation : I.V or I.M ergometrie, curettage which is immediatly or 1-2 weeks later. Complication of vaginal evacuation: 1- incomplete evacuation 2- excessive bleeding 3- perforation 2-Medical evacuation: by a) Pitocin drip: start by 10-20 units increased gradually up to 50 units + 500 glucose 5% or saline. b) Prostaglandins: are more effective for ripening of cervix PGE2, PGF2α. Medical evactuation is usually completed by vaginal evacuation and vaginal evacuation may be preceded by medical induction. 3- Abdominal hysterotomy: Indications: 1- severe bleeding, the uterus is > 14 weeks and the Os is closed. 2- Failed medical induction (the uterus > 14 weeks). 4-abdominal hysterectomy: Indications: 1- Age of PT> 40 y (high risk of choriocarcinoma) 2- Women completing her family (3) Follow up: weekly β-hCG untile –ve for 3 consecutive weeks then monthly untile –ve for 6 monthes. Methods of follow up: 1-History: irregular OR persistent vaginal bleeding. 2-Clinical examination : uterus and ovaries. 3- Special investigations: x-ray chest, liver function, U/S ,….. Contraception during period of follow up is essential to exclude positive pregnancy test due to pregnancy. Methods of contraception: 1-if undetectable βhCG : combined oral pills. 2-if high βhCG : use local methods such as condom. 3- IUCD contraindicated due to risk of perforation Part 2 (1) Definition of obstructed labor :failure of delivery of the fetus due to mechanical obstruction in the process of delivery of the fetus through the passages. Causes of obstructed labour: (A) Fetal: 1- fetal macrosomia 2- Congenital anomalies: hydrocephalus. 3- mal presentation and malposition: shoulder, impacted Frank breech, persistent occipito transverse. (B) Maternal: 1- Contracted pelvis and tumour of pelvic bones 2- Pelvic tumours : such as cervical fibroid, pedunculated low Subserous fibroid. 3-cervical dystocia. 4- constriction ring opposite the fetal neck. 5- tumours of the vagina. 6- vaginal stenosis. (2) Tyeps of eclampsia: 1-antepartum eclampsia: before onset of labour . 2-intrapartum eclampsia: during labour . 3-postpartum eclampsia: after labour . Complication of eclampsia: (A) Immediate: 1- maternal: - Haemorrhage: accidental, cerebral, DIC. -Failure: renal, heart, liver, suprarenal. -aspiration pneumonia and maternal hypoxia. - Bone fracture - Hyperpyrexia 2- Fetal: - fetal hypoxia. -intrauterine growth retardation. -intrauterine fetal death. -prematurity. (B) Remote: 1- Residual hypertension 2- Recurrence of pregnancy induced hypertension in future Pregnancies. (3) Definition of placenta previa: situation of the placenta partially or completely in the lower uterine segment. Types: -placenta previa lateralis:the lower margin of the placenta reach the Lower segment but does not reach the in. os. -placenta previa marginalis:the lower margin of the placenta reach the In. os but does not cover it. -placenta previa incomplete centralis:the lower margin of the placenta Partially cover the in. os. -placenta previa complete centralis: the lower margin of the placenta Completely cover the in. os. Clinical presentation: (A)symptoms: 1- vaginal bleeding: - painless due to Braxton hicks contraction and There is no retention of blood inside uterus. -causless: as the cause of separation is Placenta physiologic Process as the lower segment enlarged more than the upper segment. -recurrent: as the enlargement of the lower segments Progressive. 2- Symptoms of anemia: sweating, easy fatigue, palpitation, dyspnea. (B) Signs: 1- General examination: with severe vag. Bleeding the patient signs of Shock (rapid weak pulse, low blood pressure, subnormal temp) . Pallor will appear with recurrent bleeding with small amount of blood or with severe attack 2- Abd. Examination: -fundal level equals amenorrhea period - NO abdominal Tenderness or rigidity -fetal heart sounds - Abdomen is lax - Fetal parts can be easy felt 3-Vag. Examination: not done except with presence of certain precautions: In the operating theatre, complete aseptic condition, blood transfusion is ready and C.S equipment are ready.