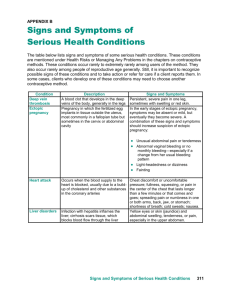
Holy Angel University School of Nursing and Allied Medical Sciences (SNAMS) Department of Nursing Name: John Alexis M. Parras Study Buddy: Dannielle S. Erni Section: NU-201 Date: January 26, 2022 With your study buddy, read Module 2 to answer the cases below. Submit individually. The patient is an 18-year-old G1P0 female with a past medical history of pelvic inflammatory disease. She was brought to the emergency department by a friend because of severe low abdominal pain and vaginal spotting. 1. What is the tentative medical diagnosis? 1pt Ectopic pregnancy – The patient has a history of pelvic inflammatory disease and a severe low abdominal pain and vaginal spotting 2. Discuss the possible cause of the condition. Relate it to pelvic inflammatory disease. (2pts) Scarring in the Fallopian tube caused by PID (Pelvic inflammatory disease) is a major cause of a Tubal/Ectopic pregnancy; an untreated PID would cause scar tissue to develop in the fallopian tubes. Preventing the fertilized egg to be implanted in the uterus. Instead, the egg implants in the fallopian tube. 3. Discuss the possible complications. 2pts Possible Complications Description Hemorrhage - Blood loss due to the scarring of fallopian tube that could lead to hypovolemic shock Potential hemodynamic instability - Abnormal or inconsistent blood flow leading to an insufficient blood flow if a dilation and curettage are performed. - Inability of Intrauterine Pregnancy - Women who present early in pregnancy and have testing suggestive of an ectopic pregnancy would jeopardize the viability of an intrauterine pregnancy if given Methotrexate 4. What are the appropriate interventions 2pts Treatment Administration of intramuscular methotrexate Description - Laparoscopic procedures 1) Salpingostomy 2) salpingectomy - Single-dose methotrexate regimen would assist patients with low hCG levels. Patients with elevated hCG levels may require a two-dose treatment. A small incision is made near or in the navel of the abdomen. The tubal area is then seen by the doctor using a narrow tube fitted with a camera lens and light (laparoscope). 1) The ectopic pregnancy is removed and the tube left to heal on its own 2) The ectopic pregnancy and the tube are both removed. - The procedure that would be performed depends on the amount of bleeding and damage and if the tube has ruptured. The other fallopian tube would also be taken into account if there are any signs of prior damage. The patient is a 26-year-old G3P1A1 who has arrived at the emergency department complaining of vaginal bleeding. She states, “My bleeding scares me, however I feel fine”. She is 35 weeks pregnant 1. What is the possible medical diagnosis? 2pts ● Placenta previa- The patient has an incident of bleeding which occurs in his third trimester, adding up the subjective data which is “I feel fine” means painless. 2. Discuss the possible complications especially to the fetus. (2pts) Complication Description (Maternal Complication) -Risk of Hemorrhage -The greater the amount of placenta that covers the cervix opening, the greater the risk of bleeding. -Hypovolemic shock -Occur when 10% of blood volume, or approximately 2 units of blood, have been lost. -Emergency cesarean delivery (if bleeding is not control) -Women with placenta previa require a C-section because vaginal delivery can result in severe bleeding if the placenta covers all or part of the cervix. This can be fatal to both the mother and the child. -Death -Placenta accreta spectrum -The risk of placenta accreta spectrum is dramatically increased in the presence of a placenta previa and one or more previous cesarean deliveries. (Cahill et al.,2018) (Fetal Complication) -Fetal distress- because of lacking oxygen - Occurs when 25% of blood volume is lost. -Premature -Premature babies are those born before 37 weeks of pregnancy. The earlier a baby is born, the greater the risk of death or serious disability. -Low Birthweight Placenta previa may prevent the fetus from developing normal polarity, resulting in abnormal fetal lying, -Abnormal Fetal position 3. Describe the possible causes of this condition (2Pts) Possible Causes Description -Intercourse post-bleeding - Sexual activity can also result in placental previa bleeding. -Smoking, several instances of gestation and high altitude - It disrupts the quality and quantity of oxygen supplied by the placenta. The placenta will then have to compensate causing elongation and an increase in surface area. Finally, this causes the dreaded placenta previa. -Abortion - Uterine tissue lining stretches, which increases the risk of a woman having placenta previa. 4. Discuss the appropriate interventions. (2pts) Intervention Description -Monitor maternal vital signs, fetal heart rate, and fetal activity. The fetal heart rate is continuously monitored for patterns that indicate hypoxemia or anemia. -Prepare for an ultrasound to confirm the diagnosis. To be able to distinguish other medical conditions that may be imposed on the baby. Furthermore, to be able conduct an early cesarean earlier if the baby life is in stake. -Monitor Bleeding. A placenta previa is more likely to result in heavy, painless bleeding with bright red blood. -Maintain bed rest(Pelvic rest) or side lying position. -(Intravenous therapy) Blood transfusion for hemorrhage. Avoidance of activities that could cause bleeding, Blood transfusion for patients with an active bleeding should be closely monitored such as the amount of blood loss over time; changes in hemodynamic parameters should also be monitored (eg, Blood pressure, maternal and fetal heart rates, peripheral perfusion, and urine output) and hemoglobin level. Reference: ● Bleeding in Pregnancy/Placenta Previa/Placental Abruption | Children's Hospital of Philadelphia. Chop.edu. (2022). Retrieved 25 January 2022, from https://www.chop.edu/conditions-diseases/bleeding-pregnancyplacenta-previaplacentalabruption#:~:text=The%20greatest%20risk%20of%20placenta,over%20the%20cervix%2 0to%20bleed. ● ● Obstetric care consensus No. 7: Placenta Accreta spectrum. (2018). Obstetrics & Gynecology, 132(6), e259-e275. https://doi.org/10.1097/aog.0000000000002983 ● Placenta previa. (2014). Better Health Channel. https://www.betterhealth.vic.gov.au/health/healthyliving/placenta-previa ● UpToDate. (n.d.). https://www.uptodate.com/contents/placenta-previa-management/print ● Prematurity - Health encyclopedia - University of Rochester Medical Center. (n.d.). Welcome to URMC - Rochester, NY - University of Rochester Medical Center. https://www.urmc.rochester.edu/encyclopedia/content.aspx?contenttypeid=90&contentid =p02401 Placenta Previa and placenta Abruptio | Article | GLOWM. (2021). The Global Library of Women's Medicine. https://www.glowm.com/article/heading/vol-10--common-obstetricconditions--placenta-previa-and-placenta-abruption/id/413763# Placenta Previa causes: Genetic or other reasons. (2020, July 9). What Is Placenta Previa?. https://www.placentaprevia.com/placenta-previa-causes/ · Mayoclinic. (2020, April 23). Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID). https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/pelvic-inflammatory-disease/symptomscauses/syc20352594#:~:text=PID%20is%20a%20major%20cause%20of%20tubal%20%28ectopic %29,the%20fallopian%20tube%20to%20implant%20in%20the%20uterus. · Ncbi. (2020, November 20). Ectopic pregnancy - StatPearls - NCBI bookshelf. National Center for Biotechnology Information. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK539860/ · Ectopic pregnancy - Diagnosis and treatment - Mayo Clinic. (2020, December 18). Mayo Clinic - Mayo Clinic. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/ectopicpregnancy/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20372093 ● ● ● ● ●