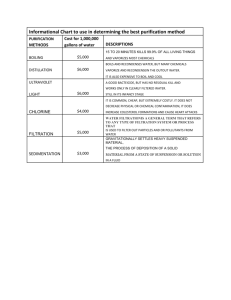
Iron oxide nanoparticles with potential applications in the purification
advertisement

Iron oxide nanoparticles with potential applications in the purification of nucleic acids José R. Sosa-Acostaa, Leunam Fernández-Izquierdob, Judith CastilloRodríguezb, Linnavel Jiménez-Hernándezc, Alicia M. Díaz-Garcíaa a Department of Inorganic Chemistry - Bioinorganic Laboratory, Faculty of Chemistry, University of Havana, Cuba b Center c for Advanced Studies of Cuba, Ministry of Science Technology and Environment Institute of Material Sciences and Technology (IMRE), University of Havana, Cuba jrsosa@fq.uh.cu Nucleic acids purification is considered a critical step in detecting both viral and genomic diseases. The quality of the purification will determine the sensitivity and specificity of the diagnostic assay. Appropriate modification of magnetic nanoparticles (MNP) with stabilizers that contain certain groups capable of forming hydrogen bond, allow a quickly and easily nucleic acids purification. [1] This research is intended to obtain MNP by coprecipitation method followed by the modification with hydroxyl groups as stabilizers and silicate and 3-aminopropyl trietoxysilane. [2] The unmodified and modified MNP were characterized by FT-IR spectroscopy, XRD and SEM. A characteristic band, around 575 cm-1, assignable to Fe-O valence vibration of magnetite was observed in the IR spectrum. From XRD pattern analysis, it appears that the obtained materials correspond to magnetite phase (JCPDS 19-629). Spherical morphology of MNP was observed by SEM. Preliminary extraction tests of oligomer were studied by UV-Vis spectroscopy at 260 nm. [1] Z. M. Saiyed; J. Phys. Condens. Matter, 2008,20(20), 204153. [2].W. U.Neng-Biao; Chinese Journal of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 2009, 25(10), 958-962.