Phase Locked Loop
advertisement

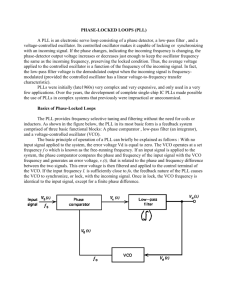
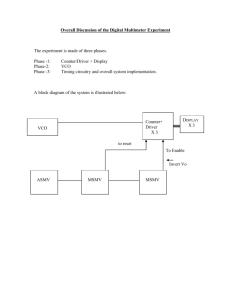
Humber Institute of Technology and Advanced Learning Wireless Telecommunication - WLS 611 Fundamentals of Electronics and Networking Project #3 Phase Locked Loop Objective: 1) To analyse some of the characteristics of a phase locked loop system. 2) To gain a deeper understanding of the various blocks of a PLL system. 3) To study the operational characteristics of the phase detector, low pass filter and Voltage Controlled Oscillator in a PLL system. 4) Identify the factor that can cause failures in a PLL circuit and learn the techniques to troubleshoot and correct the faults. The circuit you will be using is shown below: + 12 V 10 17 R3 2kΩ 4 100k 11 50% R6 150kΩ 9 TP5 R7 150kΩ + 5V 18 R1 10kΩ REF IN 12 Rx 1 TP1 2 8 14 TP2 3 1 Q1 2 7486N 33kΩ 3 6 TP3 Filter 7Output R 47kΩ C 100nF 7 2N2219 D1 D2 R2 33kΩ TP4 Q2 0 R5 2kΩ R4 2kΩ C1 15 500pF 14 13 Q3 0 Block A Block B Block C TP6 Equipments: DC Multimeter Scope 5 and 12V Power Supplies Audio Generator (Function Generator) 2 Scope Leads, 4 Power Supply leads Block D Q4 0 0 5 16 TP7 500pF 0 0 C2 VCO Output Block E Resistors (33k, 10k, 33k, 47k, 2k, 2k, 150k, 150k, 2k, ) 1 rectifier Diode and 1 zener diode. XOR gate 3 npn transistor and 1 pnp transistor Capacitors (100nf, 500pf, 500pf) 1 switch 1 potentiometer Procedure: A) 1. Connect the two power supplies of 5V and 12V. 2. Name the blocks of a PLL circuit and identify those blocks on the circuit schematic. 3. Once you have identified the blocks, label them on the schematic and show it to your teacher and let him initial your schematic. B) Free running frequency of the VCO:1) Connect the +12V supply voltage and measure the free running frequency of the VCO. C) Linear Range of VCO 1) Remove the jumper between point 1 and point 2 (if it is already removed, then proceed further) and apply a DC voltage of about 12V directly to point 2. Change the DC voltage in steps of 1V and record the frequency at the output of the VCO. Get enough readings to plot a suitable graph of DC voltage versus frequencies. 2) Determine the linear range of VCO output frequency versus DC voltage. Flow ………........................ and Fhigh......................................... 3) Plot the graph of your result. 4) Determine the gain of the VCO in Hz/V. The gain of the VCO is defined as ∆Hz/∆V. 5) Over the linear range, take any two voltages and the corresponding frequencies. ∆Hz/∆V= f2-f1/V2-V1. 6) What is the slope of your graph is Hz/V = ………………… 7) Why it is important to know the slope. D) Measuring the “Capture” and Tracking or Hold range or lock range. 1) Reconnect the jumper between point 1 and point 2. 2) Make sure that the 5V power supply is connected. 3) Connect the signal generator to the reference input, REF IN. Apply a sine wave with the amplitude set to 3-4 Vpp at a frequency of 6kHz. Connect one channel of the scope to each input lead of the phase detector. 4) Measure the “Capture Range” of the PLL. fimin:...............……………………. and fimax:………................………………….. 5) Measure the “Lock Range” or “Tracking Range” or “Hold Range”. fiL(min) : ……..........…………………… fiL(max)....................................................... 6) Which range is larger:……………….. and why:……………………. 7) Measure the “gain” of the phase detector and filter combination by measuring the change in DC output voltage of the filter to the change in phase at the phase detector input as the reference frequency is adjusted. Your gain will be in units of V/deg or V/Hz. Analysis: 1) Study the operation of the phase detector by adjusting the reference input over the tracking or lock range and watching the phase detector input and output on the scope. What did you observe? 2) Draw the waveform of input and output over the tracking range as well as when VCO is not in lock. 3) What happens to the filter output when VCO gets out of lock? 4) Observe the filter output as you adjust the reference frequency from a low (or high) value closer to the VCO free running frequency until it locks. Draw the sketch. 5) What happens to the filter output when VCO suddenly locks to the input frequency? 6) What determines the capture range, capture time and the lock range of the PLL? 7) Calculate the cut off frequency of the low pass filter and the time constant. Analyze and discuss the effects of the cut off frequency fc and the time constant Tc on the operation of the PLL. 8) Change the capacity value of the LPF and observe its effects on the operation of the PLL. What were the changes you observed? 9) Discuss the effects of the linear range of VCO on the PLL operation. How would it affect the system operation? Troubleshooting:Observe, measure and sketch the voltages and waveforms at TP1, TP2, TP3, TP4, TP5 TP6, TP7 using scope and multimeter as appropriate, while the system is in lock and out of lock. Record and sketch your results and answer the following questions. 1) What is the function of diode D1? 2) What will happen if diode D1 is accidently connected other way around i.e. if anode is at base of transistor Q1 and cathode is grounded. 3) What if diode D1 becomes shorted? 4) What is the function of block A? 5) What kind of waveform you are expecting at TP2 for normal operation? 6) What will be the effects on the PLL system, if Q1 becomes shorted. Sketch the output at pin 3 of the phase detector if Q1 becomes shorted. You can actually connect a jumper between the collector and ground to see the effects. 7) What is the function of Ex-OR gate? 8) What kind of waveform would you observe at TP3 and pin 3 if Ex-OR gate is defective (or the IC is defective)? 9) Sketch the waveform you are expecting at TP3 for normal operation. 10) What would you see at TP3, if C becomes shorted. 11) What will be the effect of an incorrect C value on system operation. 12) What is the purpose of Block D? 13) What is zener diode doing in the circuit. What is its purpose? 14) Sketch the expected waveform at TP5? 15) What will you see at TP5 if zener is accidentally reversed? Or becomes open? Or becomes shorted? 16) What will you see at TP4, TP5 if Q2’s emitter was grounded and collector was connected to the zener diode? 17) If Q2’s C-E junction becomes open? Or shorted? 18) What is the function of block E? 19) What determines the free running frequency of the VCO? 20) What determines the linear range of VCO? 21) What is the control voltage applied to the VCO? 22) Sketch the expected waveform at TP6 and TP7? 23) Discuss the effects of incorrect R6, R7 values? 24) What if R6 or R7 becomes shorted? or open? 25) What will be the effect of incorrect C1 or C2 value on TP6 and TP7? 26) What will be the effect of C1 or C2 becoming shorted on TP6 and TP7? 27) What will be the effect on TP6/TP7 of R6 or R7 becoming open.