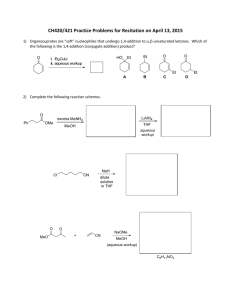
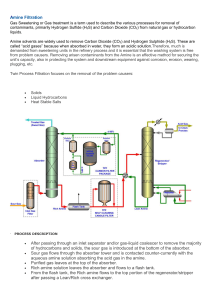
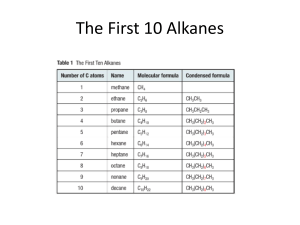
Glossary of Key Terms in Chapter Two
advertisement

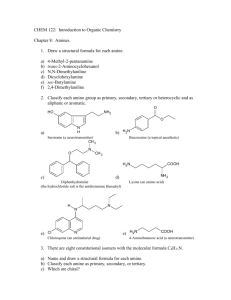
Denniston, 7e Glossary of Key Terms in Chapter Fifteen acyl group (15.3) the functional group found in the carboxylic acid derivatives that contains the carbonyl group attached to one alkyl or aryl group. alkaloid (15.2) a class of naturally occurring compounds that contain one or more nitrogen heterocyclic rings; many of the alkaloids have medicinal and other physiological effects. alkylammonium ion (15.1) the ion formed when the lone pair of electrons of the nitrogen atom of an amine is shared with a proton from a water molecule. amide (15.3) the family of organic compounds formed by the reaction between a carboxylic acid derivative and an amine. amide bond (15.3) the bond between the carbonyl carbon of a carboxylic acid and the amino nitrogen of an amine. amine (15.1) the family of organic molecules with the general formula R-NH2 , R2NH, or R3N (R- can equal R- or Ar-); they may be viewed as substituted ammonia molecules in which one or more of the ammonia hydrogens has been substituted by a more complex organic moiety. aminoacyl group (15.4) the functional group that is characteristic of an amino acid: O + H3N CH C R anesthetic (15.2) any drug that causes lack of sensation in any part of the body (local) or causes unconsciousness (general); there is generally an analgesic effect also associated with these compounds. analgesic (15.2) any drug that acts as a painkiller. heterocyclic amine (15.2) a heterocyclic compound that contains nitrogen in at least one position in the ring skeleton. neurotransmitter (15.5) a chemical that carries a message, or signal, from a nerve cell to a target cell. peptide bond (15.4) the amide bond between two amino acids in a peptide chain. primary (1˚) amine (15.1) an amine with the general formula RNH2. quaternary ammonium salt (15.1) an amine salt with the general formula R4N+ A– (in which R– can be an alkyl or aryl group or a hydrogen atom and A– can be any anion. secondary (2˚) amine (15.1) an amine with the general formula R2-NH. tertiary (3˚) amine (15.1) an amine with the general formula R3-N. transfer RNA (tRNA) (15.4) a small RNA that binds to a specific amino acid at the 3’ end and mediates its addition at the appropriate site in a growing peptide chain. This is accomplished by recognition of the correct codon on the mRNA by the complementary anticodon on the tRNA.