From Single Cells to Body Systems Notes
advertisement

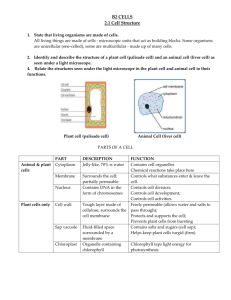
Unit 1 From Single Cells to Body Systems Review 1. Cell Basic unit of structure and function of all living things. 2. Cell Membrane Thin cell covering that holds the parts of the cell together. 3. Nucleus Organelle that controls a cell’s activities. 4. Cytoplasm Jellylike substance that contains many chemicals to keep a cell functioning. 5. Diffusion Process by which particles of a substance move from an area where there are many particles of the substance to an area where are fewer particles of substance. 6. Osmosis Movement of water and dissolved materials through the cell membrane. 7. Tissue Cells that work together to perform a specific function. 8. Organ Tissues that work together. 9. System Organs that work together to perform a function. 10. Capillaries The circulatory system transports blood through various-sized tubes called arteries, veins, and capillaries. 11. Alveoli The smallest of these tubes are blood vessels so tiny that blood cells have to move through them in single file. In the respiratory system, air travels into and out of the lungs through tubes. The smallest tubes in tiny sacs called alveoli, which are surrounded by capillaries. 12. villi Nutrients move from the digestive system into the blood by traveling through villi, tiny tubes sticking out of the wall of the small intestine. 13. nephrons In the body’s excretory system, urea and water travel from the blood into the kidneys and diffuse into nephrons. 14. bone marrow Bones have a hard outer membrane and a soft center that contains bone marrow. 15. joints This soft material is connective tissue that produces red and white blood cells. Bones are attached to each other in places called joints. 16. tendons Tough bands of tissue called tendons attach bones to muscles. 17. ligaments Other bands of tissue called ligaments attach bones to each other. 18. neurons To move, a muscle must receive a signal from the nervous system. Specialized cells called neurons, detect conditions in the body’s environment. 19. Osmosis Allows water to flow into the roots of plants. 20. Diffusion Osmosis is one kind of diffusion. 21. Reproduce Plants and animals grow when cells reproduce. 22. Epithelial tissue An animal’s skin is an example of epithelial tissue. 23. Respiratory system Oxygen enters the body through the respiratory system. 24. Circulatory system Oxygen travels to every cell in the body through the circulatory system. 25. Digestive The system that breaks down food into nutrients is the digestive system. 26. Heart The heart is a muscle. 27. Hip The hip is a ball-and-socket joint. 28. Signals The nervous system carries signals to and from the brain.