File
advertisement

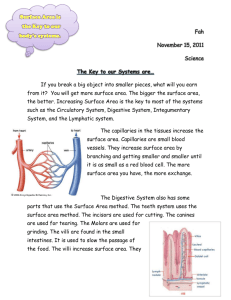
1. You are effected with a mutation that distorts your body’s ability to produce villi. Explain the effect of this mutation on your digestive system. 2. The molar concentration of a sugar solution in an open beaker has been determine to be 0.3M. Calculate the solution potential at 27 degrees Celsius. Round your answer to the nearest tenths. 3. Distinguish between DNA and RNA with regard to chemical composition, nucleotides included in each, location in the cell, and function. 1. You are effected with a mutation that distorts your body’s ability to produce villi. Explain the effect of this mutation on your digestive system. If your villi is absent, your small intestine would be inefficient at absorbing nutrients. 2. The molar concentration of a sugar solution in an open beaker has been determine to be 0.3M. Calculate the solution potential at 27 degrees Celsius. Round your answer to the nearest tenths. 3. Distinguish between DNA and RNA with regard to chemical composition, nucleotides included in each, location in the cell, and function. DNA RNA Double stranded Single stranded A,T,C, and G A,U,C, and G Deoxyribose sugar Ribose sugar Nucleus Nucleus and cytoplasm Genetic information mRNA, tRNA, and rRNA Homeostatic control systems in species of microbes, plants, and animals support common ancestry. Page 101 Circulatory System Recap: Every organism must exchange material with its environment AQUEOUS o Organisms exist in an _____________ environment o What are we exchanging??? (hint: materials) • CO2, O2, waste, and nutrients 1. The interstitial fluid of vertebrates: a. is the internal environment within cells b. bathes cells and provides for the exchange of nutrients and wastes c. makes up the plasma of blood d. surrounds unicellular and flat, thin animals For example: o The gills of a salmon (structure relating to function) o Capillaries lie close to the surface to allow for effective diffusion • External structure • Issue?? Diffusion: o The movement of molecules from high to low concentration • Passive transport o Only works across small distances like across the cell membrane o For longer distances (across the body), diffusion is ineffective o The complex human body relies on structures (organs) for transport Key Point #1: The circulatory system functionally connects the aqueous environment of the body cells to the organs that exchange gases, absorb nutrients and dispose of wastes o Remember respiratory system?? Lack a “true” circulatory system Gastrovascular cavity serves as digestive AND circulation system To overcome the diffusion limitation, organisms consist of either open or closed circulation systems. Key Point #2: Both open and closed systems share the following characteristics: blood, blood vessels, and a heart. Key Point #3: Open Systemo Blood and Interstitial fluid is NOT separated o Common in: insects, arthropods, and mollusks Key Point #4: Closed systemo Blood is confined to vessels and IS separated from the interstitial fluid Heart pumps blood through vessels then materials are exchange AT organs o Common in: vertebrates, earthworms, squids, and octopuses OPEN Decrease cost (energy) to support body CLOSED More effective at transport in large and active organisms The need for O2 increases Key players: o Heart: 2 atrium and 2 ventricles o Blood vessels: arteries, veins, and capillaries • Function of capillaries: • EXCHANGE! Keeping it all straight: o To heart or away from heart o Arteries carry blood AWAY from heart INs carry blood INTO heart o Ve Slight differences in closed systems of different organisms are evidence of natural selection o Complex animals= complex systems Blood trace: Ventricle->artery->capillaries (exchange)->body->capillaries>veins->atrium Key Point #5: Fisho The double capillaries slow down the O2 delivery throughout the body o Single circulation- low pressure Blood trace: Ventricle->lungs & skin capillaries->left atrium->body->right atrium Key Point #6: Amphibianso 3 chambered heart o Double circulation- vigorous flow of blood Key Point #7: Mammalso 4 chambered heart o Left side: O2 rich o Right side: O2 poor o Prevents mixing of oxygenated blood and deoxygenated blood Endotherms require A LOT of energy! This means A LOT of O2 delivery The heart is an essential muscle to pump blood throughout the blood The blood carries the O2, CO2, and nutrients throughout the body *This is an example of convergent evolution* James, Joe, and Paul: o Watch the following video on the circulatory system o http://www.bozemanscience.com/circulatory-system o Watch this video on a potential lab on the circulatory system. As you watch the video, take notes on the lab and how you will be able to use the information as a potential essay topic. Show me the notes on the lab for your daily grade. o http://www.bozemanscience.com/ap-bio-lab-10-physiology-of-thecirculatory-system Homework: read and outline page 869, 870,and 871 Tuesday HW: read and outline page 922 and 939 on osmoregulation