Circulatory System (Human): Components
advertisement
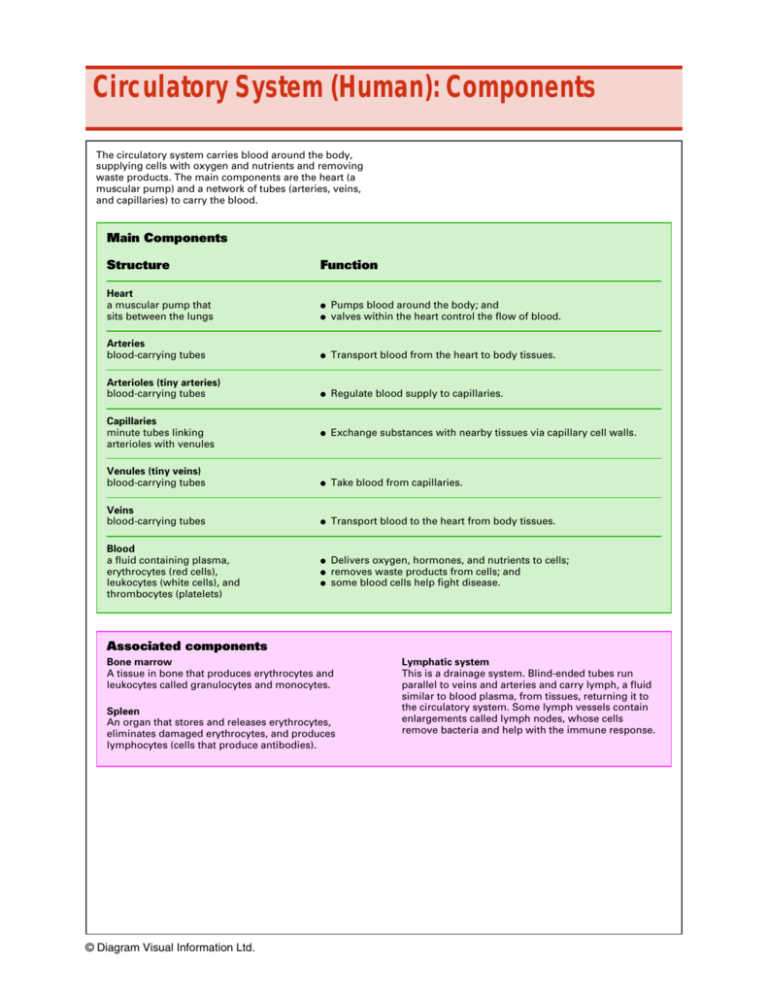
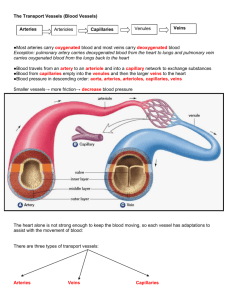
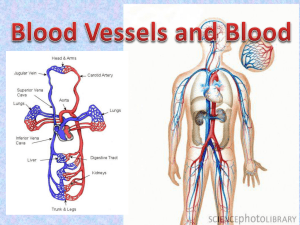
Circulatory System (Human): Components The circulatory system carries blood around the body, supplying cells with oxygen and nutrients and removing waste products. The main components are the heart (a muscular pump) and a network of tubes (arteries, veins, and capillaries) to carry the blood. Main Components Structure Function Heart a muscular pump that sits between the lungs ● ● Pumps blood around the body; and valves within the heart control the flow of blood. Arteries blood-carrying tubes ● Transport blood from the heart to body tissues. Arterioles (tiny arteries) blood-carrying tubes ● Regulate blood supply to capillaries. ● Exchange substances with nearby tissues via capillary cell walls. Venules (tiny veins) blood-carrying tubes ● Take blood from capillaries. Veins blood-carrying tubes ● Transport blood to the heart from body tissues. ● Delivers oxygen, hormones, and nutrients to cells; removes waste products from cells; and some blood cells help fight disease. Capillaries minute tubes linking arterioles with venules Blood a fluid containing plasma, erythrocytes (red cells), leukocytes (white cells), and thrombocytes (platelets) ● ● Associated components Bone marrow A tissue in bone that produces erythrocytes and leukocytes called granulocytes and monocytes. Spleen An organ that stores and releases erythrocytes, eliminates damaged erythrocytes, and produces lymphocytes (cells that produce antibodies). © Diagram Visual Information Ltd. Lymphatic system This is a drainage system. Blind-ended tubes run parallel to veins and arteries and carry lymph, a fluid similar to blood plasma, from tissues, returning it to the circulatory system. Some lymph vessels contain enlargements called lymph nodes, whose cells remove bacteria and help with the immune response.