Name - Mr. Spechts world of Science
advertisement

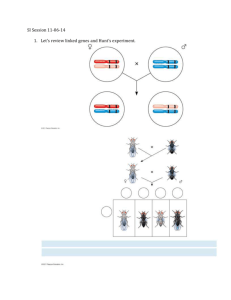
NAME___________________________ 1. The production of certain human hormones by genetically engineered bacteria results from: (1) inserting a specific group of amino acids into the bacteria (2) combining a portion of human DNA with bacterial DNA and inserting this into bacteria (3) crossing two different species of bacteria (4) deleting a specific amino acid from human DNA and inserting it into bacterial DNA 2. A mutation occurs in a cell. Which sequence best represents the correct order of the events involved for this mutation to affect the traits expressed by this cell? (1) a change in the sequence of DNA bases joining amino acids in sequence appearance of characteristic (2) joining amino acids in sequence a change in the sequence of DNA bases appearance of characteristic (3) appearance of characteristic joining amino acids in sequence a change in the sequence of DNA bases (4) a change in the sequence of DNA bases appearance of characteristic joining amino acids in sequence 3. Recently, scientists noted that stained chromosomes from rapidly dividing cells, such as human cancer cells, contain numerous dark, dotlike structures. Chromosomes from older human cells that have stopped dividing have very few, if any, dotlike structures. The best generalization regarding these dotlike structures is that they (1) will always be present in cells that are dividing (2) may increase the rate of mitosis in human cells (3) definitely affect the rate of division in all cells (4) can cure all genetic disorders Period 5a/6 Date_______________________ 4. Fruit flies with the curly-wing trait will develop straight wings if kept at a temperature of 16°C during development and curly wings if kept at 25°C. The best explanation for this change in the shape of wings is that the: (1) genes for curly wings and genes for straight wings are found on different chromosomes (2) type of genes present in the fruit fly is dependent on environmental temperature (3) environment affects the expression of the genes for this trait (4) higher temperature produces a gene mutation 5. The genetic code of a DNA molecule is determined by a specific sequence of (1) ATP molecules (3) chemical bonds (2) sugar molecules (4) molecular bases 6. To produce large tomatoes that are resistant to cracking and splitting, some seed companies use the pollen from one variety of tomato plant tofertilize a different variety of tomato plant. This process is an example of (1) selective breeding (3) direct harvesting (2) DNA sequencing (4) cloning 7. If a set of instructions that determines all of the characteristics of an organism is compared to a book, and a chromosome is compared to a chapter in the book, then what might be compared to a paragraph in the book? (1) a starch molecule (3) an amino acid (2) an egg (4) a DNA molecule 8. What determines the kind of genes an organism possesses? (1) type of amino acids in the cells of the organism (2) sequence of the subunits A, T, C, and G in the DNA of the organism (3) size of simple sugar molecules in the organs of the organism (4) shape of the protein molecules in the organelles of the organism 9. People with cystic fibrosis inherit defective genetic information and cannot produce normal CFTR proteins. Scientists have used gene therapy to insert normal DNA segments that code for the missing CFTR protein into the lung cells of people with cystic fibrosis. Which statement does not describe a result of this therapy? (1) Altered lung cells can produce the normal CFTR protein. (2) Altered lung cells can divide to produce other lung cells with the normal CFTR gene. (3) The normal CFTR gene may be expressed in altered lung cells. (4) Offspring of someone with altered lung cells will inherit the normal CFTR gene. 10. A portion of a molecule is shown in the diagram below. Which statement best describes the main function of this type of molecule? (1) It is a structural part of the cell wall. (2) It stores energy for metabolic processes. (3) It determines what traits may be inherited. (4) It transports 11. When DNA separates into two strands, the DNA would most likely be directly involved in (1) replication (3) differentiation (2) fertilization (4) evolution 12. Which statement is true regarding an alteration or change in DNA? (1) It is always known as a mutation. (2) It is always advantageous to an individual. (3) It is always passed on to offspring. (4) It is always detected by the process of chromatography. 13. Scientific studies show that identical twins who were separated at birth and raised in different homes may vary in height, weight, and intelligence. The most probable explanation for these differences is that (1) original genes of each twin increased in number as they developed (2) one twin received genes only from the mother while the other twin received genes only from the father (3) environments in which they were raised were different enough to affect the expression of their genes (4) environments in which they were raised were different enough to change the genetic makeup of both individuals 14. The diagram below shows a process that can occur during meiosis. The most likely result of this process is (1) a new combination of inheritable traits that can appear in the offspring (2) an inability to pass either of these chromosomes on to offspring (3) a loss of genetic information that will produce a genetic disorder in the offspring (4) an increase in the chromosome number of the organism in which this process occurs 15. A change in the order of DNA bases that code for a respiratory protein will most likely cause: (1) the production of a starch that has a similar function (2) the digestion of the altered gene by enzymes (3) a change in the sequence of amino acids determined by the gene (4) the release of antibodies by certain cells to correct the error 16. A sudden change in the DNA of a chromosome can usually be passed on to future generations if the change occurs in a (1) skin cell (3) sex cell (2) liver cell (4) brain cell 17. The diagrams below represent some steps in a procedure used in biotechnology. Letters X and Y represent the (1) hormones that stimulate the replication of bacterial DNA (2) biochemical catalysts involved in the insertion of genes into other organisms (3) hormones that trigger rapid mutation of genetic information (4) gases needed to produce the energy required for gene manipulation 19. In Siamese cats, the fur on the ears, paws, tail, and face is usually black or brown, while the rest of the body fur is almost white. If a Siamese cat is kept indoors where it is warm, it may grow fur that is almost white on the ears, paws, tail, and face, while a Siamese cat that stays outside where it is cold, will grow fur that is quite dark on these areas. The best explanation for these changes in fur color is that: (1) an environmental factor influences the expression of this inherited trait (2) the location of pigment-producing cells determines the DNA code of the genes (3) skin cells that produce pigments have a higher mutation rate than other cells (4) the gene for fur color is modified by interactions with the environment 20. The diagram below represents the organization of genetic information within a cell nucleus. 18. The letters in the diagram below represent genes on a particular chromosome. Gene B contains the code for an enzyme that cannot be synthesized unless gene A is also active. Which statement best explains why this can occur? (1) A hereditary trait can be determined by more than one gene. (2) Genes are made up of double-stranded segments of DNA. (3) All the genes on a chromosome act to produce a single trait. (4) The first gene on each chromosome controls all the other genes on the chromosome. The circle labeled Z most likely represents (1) amino acids (3) vacuoles (2) chromosomes (4) molecular bases 21. The chance of a XY chromosome combination occurring in humans under normal conditions is; (1) 0% (2) 50% (3) 75% (4) 100% 22. Molecule 1 represents a segment of hereditary information, and molecule 2 represents the portion of a molecule that is determined by information from molecule 1. What will most likely happen if there is a change in the first three subunits on the upper strand of molecule 1? (1) The remaining subunits in molecule 1 will also change. (2) A portion of molecule 2 may be different. (3) Molecule 1 will split apart, triggering an immune response. (4) Molecule 2 may form two strands rather than one. 26. Observe the following test cross: Using your knowledge of genetics, write the correct genotypes under each guinea pig for both the Parental and the offspring generations. What are the genotypes for the parent mice? (1) Ww (2) Bw (3) Bb (4) Wb 23. How could you determine the phenotype of Mr. Specht? (1) Examine his DNA (2) Look at him (3) Extract his genes (4) Blood test 27. Two individuals with a given trait, one pure dominant and one pure recessive, are mated. In the resulting offspring, what percentage would show the dominant phenotype? (1) 50% (2) 25% (3) 75% (4) 100% 24. If heterozygous black mice are with each other, what percentage of the offspring will be expected to have the same genotype for coat color as their parents? 28. The diagram below represents a process that occurs within a cell in the human pancreas. (1) 100% (3) 75% (2) 50% (4) 0% 25. A cross is made between two organisms, both of which have a genotype of Bb for a particular trait, and two offspring are produced. The first offspring exhibits the dominant trait. What is the probability that the second offspring will exhibit the recessive trait? (1) 1/2 (2) 1/4 (3) 3/4 (4) 0 This process is known as (1) digestion by enzymes (2) protein synthesis (3) energy production (4) replication of DNA