Ch01TBQues - UK Ag Weather Center
advertisement

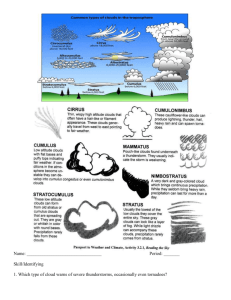
CHAPTER 1 MONITORING WEATHER __________________________________________________________ MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. Depending on local topography, the maximum range of broadcasts of the NOAA weather radar is about ____________ kilometers. a. 10 b. 100 c. 20 d. 65 2. High pressure systems are usually accompanied by __________ weather and low pressure systems are usually accompanied by __________ weather. a. fair……………stormy b. stormy……………fair 3. Viewed from above in the Northern Hemisphere, surface winds blow ___________ about the center of a low pressure system. a. clockwise and outward b. clockwise and inward c. counterclockwise and outward d. counterclockwise and inward 4. Air temperatures tend to be relatively low to the ___________ of a low pressure system. a. east and south b. north and west 5. a. b. c. d. Weather systems usually cross the United States in one day. several days. twenty or so days. one month. 6. a. b. c. d. Weather systems in the middle latitudes of the Earth generally move in the direction towards the east. south. west. north. 7. Air pressure can be thought of as a. air temperature. b. wind speed. c. weight of the overlying air. d. weight of the underlying air. 8. a. b. c. A front is a narrow zone of transition between air masses that contrast in temperature. humidity. Either or both of the above are correct. 9. a. b. c. Tornadoes are most common on the U.S. East Coast. on the U.S. Pacific Coast. in the central United States. 10. The National Weather Service issues a weather __________ when hazardous weather is imminent or actually taking place. a. watch b. warning 11. Scattered cumulus clouds usually indicate ___________ weather. a. stormy b. fair 12. Weather radar monitors the movement of a. cloud particles. b. precipitation. 13. A(n) __________ satellite image is especially useful at night. a. visible b. infrared 14. A horizontal wind is named for the direction ___________ the wind blows. a. toward which b. from which 15. A cloud that is in contact with Earth’s surface is known as ____________. a. a cumuliform cloud b. a stratiform cloud c. fog 16. Viewed from above in the Northern Hemisphere, surface winds in a high pressure system blow a. clockwise and inward. b. clockwise and outward. c. counterclockwise and inward. d. counterclockwise and outward. 17. An air mass is a huge volume of air that is relatively uniform horizontally in a. temperature. b. humidity. c. Both of the above are correct. 18. As a general rule, lows that track from west to east across southern Canada produce ___________ precipitation compared to lows that track along the Gulf of Mexico coast. a. more b. less c. about the same amount of 19. Usually, the day’s minimum temperature occurs a. around midnight. b. around sunrise. c. near sunset. 20. A geostationary satellite orbits Earth at a _________ altitude than a polar-orbiting satellite. a. lower b. higher 21. Meteorologists use water vapor satellite imagery to a. determine the humidity in the air next to Earth’s surface. b. monitor the temperature of the tops of clouds. c. track the movement of water vapor at higher altitudes of the atmosphere. d. measure the surface wind speed in a hurricane. 22. A cloud in contact with the Earth’s surface is known as a. a cumuliform cloud. b. fog. c. a cirrus cloud. d. a thunderstorm. 23. Wispy-appearing clouds that occur at high altitudes are composed of mostly a. tiny liquid water droplets. b. tiny ice crystals. c. methane. d. solid carbon dioxide. 24. Cumulus clouds that exhibit essentially no vertical growth are ___________ to produce precipitation. a. likely b. unlikely 25. A thunderstorm cloud: a. cumulus b. cirrus c. cumulonimbus d. stratiform