Introduction to Biology
advertisement

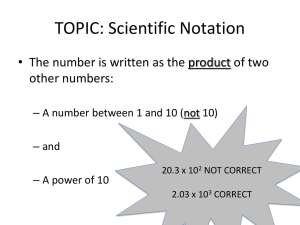
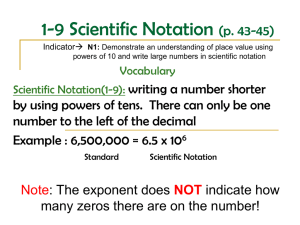
Introduction to Biology Measurement Conversion between units Kilo (k) 103 1,000 Hecto (h) 102 100 Metric Prefixes Deca (da) Base Unit Deci (d) 1 10 Meter 10-1 10 Gram 0.1 Liter Centi (c) 10-2 0.01 Milli (m) 10-3 0.001 When moving from one unit to the other, remember this: - when you move to the right, the numbers get bigger because you multiply - when you move to the left, the numbers get smaller because you divide Example: How many centimeters is 3.5 hectometers? Moving from hectometer to centimeters is to the right 4 times (104 = 10,000). So multiply 3.5 x 104 or 3.5 x 10,000 = 35,000 Answer: 3.5 hm = 35,000 cm Example: How many kilometers is 4.15 decimeters? Moving from decimeters to kilometers is to the left 4 times (104 = 10,000). So divide 4.15 / 10,000 = .000415 Answer: 4.15 dm = .000415 km Mean, Median, Mode Mean = the average of a set of numbers Median = the middle value when the values are ranked in numerical order Mode = the value that occurs most often in a set of numbers Example: An experiment has the following data collected: 5, 7, 3, 7, 7, 5, 9 Mean = 43 / 7 = 6.1428 Median = 7 (3, 5, 5, 7, 7, 7, 9) Mode = 7 (the number 7 occurs the most often, 3 times) Significant Figures Addition and Subtraction When measurements are added or subtracted, the number of decimal places in the answer is equal to the number of decimal places in the measurement with the smallest number of decimal places. Example: If you add 1.23 and 4.567, you get an answer of 5.797. However, 1.23 and 4.567 have different number of decimal places. Answer: Since there is no third decimal place in 1.23, the answer of 5.80 only has two decimal places and thus three significant figures. (Rounding up or down rules apply) Multiplying or Dividing When multiplying or dividing measurements, the answer should have only as many significant figures as the value with the fewest significant figures. Example: A density calculation is made in which a mass of 5.31 g is divided by a volume of 22 ml. The calculator output is 0.241363636 g/ml. Answer: There are three significant figures in the mass but only two significant figures in the volume measurement. Therefore, the density should have two significant figures = 0.24 g/ml Scientific Notation = a shorthand way to write very large or very small numbers as a product of a number times a power of 10 Example: To convert from standard form to scientific notation Standard Form Scientific Notation 720, 000 7.2 X 105 5 decimals to the left Exponent is 5 0.000291 4 decimals to the right 2.91 X - 4 Exponent is -4 To convert from scientific notation to standard form Scientific Notation Standard Form 7 4.63 X 10 46, 300, 000 Exponent is 7 7 decimals to the right 1.08 X 10 – 6 Exponent is – 6 0.00000108 6 decimal places left Characteristics of Living Things 1) Cells - all living things are composed of cells 2) Organization - highly organized at molecular and cellular levels 3) Energy Use - use energy in a process called metabolism 4) Homeostasis - all living things maintain stable internal conditions 5) Response to Environment - all organisms must respond to environment to survive 6) Growth - all living things grow and develop 7) Reproduction - essential for the continuation of a species Steps to Scientific Thinking Observing Forming Hypothesis Testing Hypothesis Analyzing Data Evaluation Results Independent Variable = a condition in a experiment that is changed or manipulated Dependent Variable = observed or measured changes during an experiment Qualitative Data = descriptions of the dependent variable example: colors, sounds, yes or no Quantitative Data = numerical measurements of the dependent variable example: size, mass, frequency, temperature, rate