Chapter 25
advertisement

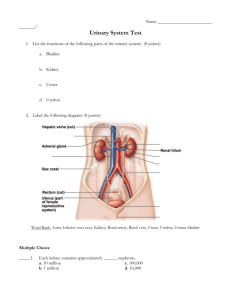
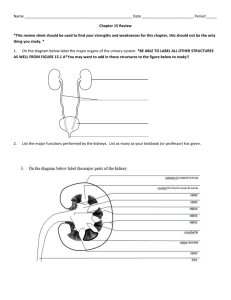
Chapter 25 Approximately how many liters of blood filter through the kidneys each day? ~200L What types of substances do the kidneys take from the blood and put into urine? Any substance small enough to get through the filtration membrane, but only water, salts, metabolic waste (urea, uric acid and creatinine) and secreted substances such as antibiotics. Other than urine formation, what are the functions of the kidneys (renal system)? Regulation of blood pressure, blood pH, water and salt balance, Vit D metabolism and RBC production. Can you list all of the structures of the urinary system and give a brief description of their function? Kidneys (right and left)- functions above; ureter- convey urine from kidney to bladder; urinary bladder- store urine; urethra- convey urine to the external environment. Can you describe the location of the kidneys? Which one sits lower than the other and why? Kidneys are retroperitoneal, along the lumbar region and the right sits lower than the left (crowded by the liver). Can you describe the shape of the kidney? Bean-shaped. Concave medially, convex laterally. What is the portion of the kidney called where blood vessels, nerves and the ureter enter/leave the kidney? Hilus/hilum Can you describe the three layers of tissue that support the kidney? Fibrous capsule, adipose (perirenal fat) and renal fascia. Can you describe the internal anatomy of the kidney using the following terms, and can you provide a function for these terms? Can you diagram them? o Renal pyramids – triangle shaped medulla tissue that conveys urine from the cortex to the pelvis o Medulla – inner renal tissue, arranged into pyramids o Cortex- outer renal tissue. Contains nephron and is responsible for urine production o Renal columns – cortex tissue that divides the kidney into functional units called lobes o Renal pelvis- collects the urine from the papilla and conveys it to the ureter o Papilla- tip of each renal pyramid that allows urine to be guided into the pelvis o Renal calyx (calyces) Major- major branch of the pelvis, collects urine from each minor calyx and guides it to the ureter Minor- minor branch of the pelvis that collects urine from the papilla o Lobe- functional unit of the kidney o Renal sinus- pockets within the renal tissue Can you describe the blood supply to the kidney? – aorta branches into the renal artery and blood enters kidney, renal vein joins the vena cava to drain blood from the kidney To the nephron? Afferent arteriole into the glomerulus and efferent arteriole out of the glomerulus What is the structural and functional unit of the kidney? nephron Can you describe the anatomy of the nephron using the following terms, and can you provide a function for these terms? Can you diagram it? o Glomerulus- capillary bed that allows blood to be filtered for the formation of urine o Bowman’s (renal) capsule- simple squamous structure that surrounds the glomerulus and guides filtrate (filtered blood) into the nephron tubular system o Renal corpuscle- glomerulus + Bowman’s capsule o Afferent arteriole- leads blood into glomerulus o Efferent arteriole –leads blood away from glomerulus o Peritubular capillaries arises from efferent arteriole and surrounds the tubular system for reabsorption and secretion o Proximal convoluted tubule- tubular section after Bowman’s capsulemostly reabsorption of substances such as glucose, amino acids, vitamins), also some secretion o Distal convoluted tubule – tubular section after Loop- mostly secretion, some water/salt reabsorption o Loop of Henle- descending then ascending limbs. Descending is after prox. Conv. Tubule and is responsible for reabsorption of water. Ascending limb after descending limb and is responsible for reabsorption of sodium o Collecting duct- leads urine out of cortex and through medulla. Can you describe the glomerular endothelium? Glomerulus Capillaries. These vessels are only made of simple squamous walls, so they are also glomerular endothelium What is filtrate? Filtered blood Where is it produced? Comes out of the glomerulus and into the renal tubules Do you know what podocytes are and what their function is? Specialized cell found on the glomerular capillaries and forms filtration slits Can you describe filtration slits and how they are formed? Interlacing “feet” of the podocytes. The space between them is so small that only very small molecules can pass through. Can you list and describe the three layers of the filtration membrane? Glomerular endothelium, basement membrane and podocyte Can you give the epithelia type that makes up the following structures and explain what function the epithelia provides for that the structure? o Proximal convoluted tubule simple cuboidal with microvilli- increased surface area for reabsorption o Distal convoluted tubule – simple cuboidal epithelia- tubular secretion o Loop of Henle- squamous cells - reabsorption o Collecting duct- simple cuboidal with microvilli- secretion of bicarbonate ion for blood pH control; simple cuboidal w/o microvilli for water/sodium balance Can you describe the anatomy of the Loop of Henle?- descending limb with channels for water reabsorption, ascending limb with channels for sodium reabsorption Can you trace the flow of urine from the collecting duct to the external environment? Out a papilla minor calyx major calyx pelvis ureter urinary bladder urethra Can you describe the difference between the cortical and juxtamedullary nephrons? Cortical nephrons are completely contained in the cortex. Juxtamedullary nephrons have Loops that dip into the medulla tissue o Which is better at reabsorbing water? juxtamedullary What are the two capillary beds of the nephron? Glomerulus and peritubular capillaries Do you know what “vasa recta” are? The straight peritubular capillaries around the long Loops of the juxtamedullary nephrons How are they different from peritubular capillaries? Long and straight rather than convoluted Where are they located? Around juxtamedullary Loops Can you describe the location and components of the juxtamedullary apparatus? Composed of the granular (juxtamedullary) cells around the afferent arteriole and the macula densa cell around the end of the ascending limb of the Loop What type of cells secrete renin? Granular (juxtaglomerular) cells What is renin used for? Increase blood pressure What is erythropoietin and what secretes it? Hormone that acts on the kidney and causes increase of RBC production. Macula densa secretes Can you describe the structure, location and function of the ureters? Tri layered tube from the kidney to the urinary bladder. Conveys urine from kidney to the bladder Can you list and describe the layers of the ureter walls? Transitional mucosa, smooth muscle muscularis and fibrous adventitia from the lumen outwards. Can ureters actively propel urine towards the bladder?- yes, smooth muscle peristalsis Can you describe the structure, location and function of the urinary bladder? Hollow organ located in the pelvic cavity that stores urine. Can you list and describe the layers of the urinary bladder? Transitional mucosa, smooth muscle layer called “detrusor” muscle and fibrous adventitia from the lumen outwards Can you describe the trigone? Area of the urinary bladder where the openings to the two ureters and the urethra are What is its clinical importance? Area where bacteria tend to persist in bacterial infection of the bladder Where is the detrusor muscle located? Wall of the bladder What is its function? Bladder contractions to propel urine into the urethra About how much urine can the bladder hold before it will expel its contents? 800-1000mL Can you describe the structure, location and function of the urethra?trilayered tube in the pelvic cavity leaving the neck of the bladder. Conveys urine to the external environment. Can you list and describe the sphincters of the urethra? Internal urethral sphincter is a thickened portion of the detrusor that is under spinal reflex. External is part of the urogenital diaphragm that is skeletal muscle and voluntarily controlled. What is the approximate length of the male urethra? 20 cm Female urethra? 34 cm Can you list and describe the three regions of the male urethra? Prostatic urethra through the prostate, membranous urethra through the urogenital diaphragm and spongy urethra through the penis What is the name of the process of voiding urine from the body? micturition What is incontinence and what factors can lead to incontinence? Inability to retain urine voluntarily in the bladder. Causes include pregnancy, bacterial infection, etc.