OPTICS AND ACOUSTICS SUMMARY
advertisement

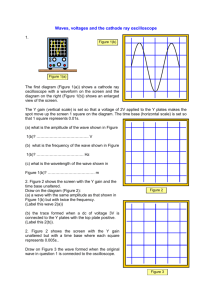
OPTICS & ACOUSTICS SUMMARY NOTES Light and sound are both waves. OPTICS Light travels in straight lines called light rays. If you shine a straight beam of light into a mirror the light is reflected. Complete the diagram below marking on the normal, the incident ray, the reflected ray, the angle of incidence and the angle of reflection. mirror The law of reflection is: The angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection. When light passes from one material to another it bends or changes direction. This is called refraction. Complete the diagram below marking on the normal, the incident ray, the refracted ray, the angle of incidence and the angle of refraction. When light goes from AIR to GLASS it bends towards the normal. When light goes from GLASS to AIR it bends away from the normal. Transparent materials let all light pass through them. Translucent materials let some light pass through them. Opaque materials let no light pass through them. When white light is passed through a prism a spectrum is produced. Remember ROY G. BIV Red Orange Yellow Green Blue Indigo Violet Complete the diagram shown Shown on the right. White Light 1 OPTICS & ACOUSTICS SUMMARY NOTES When white light is passed through a filter only light the same colour as the filter passes through the filter. All other colours are absorbed. E.g. a red filter lets only the red part of white light through. Orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo and violet are absorbed. Some uses of filters include: traffic lights, photography and disco lights. The three primary colours are red, blue, and green. All of the colours we see are made from these three colours. They mix to give the Red following colours RED + GREEN = YELLOW Magenta Yellow Blue Green RED + BLUE = MAGENTA (PINK) BLUE + GREEN = CYAN (LIGHT BLUE) Cyan RED + BLUE + GREEN = WHITE The colours we see objects depend on two things: the colour of the object and the colour of the light shining on the object. ACOUSTICS Sound is caused by vibrations. In order for sound to travel we need solids, liquids or gases. Sound cannot travel through a vacuum. Space is a vacuum. Bell Connect to battery Connect to pump When air is pumped out of the bell jar the sound gets quieter. When there is no air left (a vacuum) you will hear no sound because there are no particles to vibrate. A sound meter is used to measure the loudness of sound; this is also called sound level. Sound level is measured in decibels, dB. If you are exposed to loud sounds for a long period of time your hearing can be damaged. Soundproofing can be used to reduce the harmful effects of sound 2 OPTICS & ACOUSTICS SUMMARY NOTES Wave diagrams ‘Starter sound wave’ Another word for pitch is frequency. The frequency of a wave is the number of waves produced in a second and is measured in Hertz, Hz. The higher the pitch the higher the frequency. You would see more waves on the screen of an oscilloscope. Sketch what you would see on an oscilloscope if the pitch of the ‘starter sound wave’: a) was higher b) was lower HIGH PITCH LOW PITCH When the loudness of a sound increases the amplitude of the wave increases. The frequency does not change. Sketch what you would see on an oscilloscope if the ‘starter sound wave’ a) was quieter b) was louder LOUD QUIET Ultrasound Humans can hear sounds between the frequencies of 20Hz and 20,000Hz. Some animals can hear or communicate in frequencies above 20,000Hz called ultrasounds. Some examples are dogs, bats and dolphins 3