Y8-Physics-Keyword
advertisement

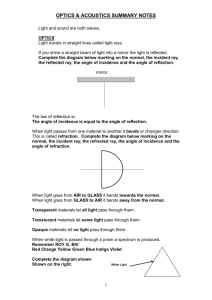
Y8 Physics Keyword List Autumn Term – Forces Word force contact force non-contact force force meter newton meter newton (N) mass gram (g) kilogram (kg) weight gravity magnetism static electricity Definition A push or a pull A force that needs to touch an object before it can affect it (e.g. friction) A force that can affect something from a distance (e.g. gravity) A piece of equipment containing a spring that is used to measure forces Another name for force meter The unit of force The amount of matter that something is made of. Your mass does not change if you go into space or to another planet A unit for measuring mass A unit for measuring mass. 1 kg = 1000 g The amount of force with which gravity pulls something towards the Earth The force of attraction between any two objects. The Earth has a large mass, so it has a strong force of gravity that pulls objects down towards it A non-contact force that attracts objects made out of certain materials A non-contact force that attracts things. It is caused when some materials rub together Word friction lubricant lubricating Definition A force that slows things down when they rub against something A substance used to reduce friction Adding a lubricant to something Word air resistance water resistance drag streamlined balanced forces Definition A force that acts to slow things down as they move through air A force that acts to slow things down as they move through water Another name for air resistance and water resistance Something that has a smooth shape to reduce drag Two forces that are the same strength and working in opposite directions Word upthrust float sink volume density displace Word prediction method apparatus independent variable dependent variable control variable Definition A force that pushes things up in liquids and gases When an object stays on the surface of a liquid When an object falls to the bottom of a liquid The space that an object takes up. Measured in m3 or cm3 A measure of mass per unit volume of a substance. Measured in kg/m3 or g/cm3 To push out of the way Definition What you think will happen in an experiment A detailed explanation of how to carry out an experiment The equipment used in an experiment The thing you change in an experiment The thing you measure in an experiment. It depends on the independent variable The things you keep the same in an experiment to achieve a fair test Word Definition conclusion A summary of what you have learnt from your results continuous data Results that can take any numerical value. These are plotted in a line graph categoric data Results that can be grouped into categories. These are plotted in a bar chart Word permanent magnet bar magnet attract repel north pole south pole electromagnet core magnetic material iron steel nickel cobalt Definition A magnet that keeps its magnetism – it does not depend on electricity A straight magnet shaped like a small bar Pull towards Push away One end of a magnet. It is attracted to a south pole One end of a magnet. It is attracted to a north pole A coil of wire with electricity flowing in it A solid bar inside an electromagnet, usually made of iron Material that is attracted to a magnet A metal that is a magnetic material A mixture of metals mostly made of iron. It is a magnetic material A metal that is a magnetic material A metal that is a magnetic material Word magnetic field compass plotting compass north seeking pole south seeking pole Word lever effort pivot load biceps muscle distance multiplier force multiplier fulcrum Definition The space around a magnet where it can affect magnetic materials or other magnets A magnetised piece of metal that can swing around – it points north A small compass used for finding the direction of a magnetic field The end of a magnet that points north if the magnet can move freely The end of a magnet that points south if the magnet can move freely Definition A simple machine that can increase the size of a force, or increase the distance the force moves A force put on something, especially a lever a point about which something turns The weight or force on something The muscle on the front of the upper arm that makes the arm bend A lever where the load moves further than the effort A lever where the load is bigger than the effort Another name for a pivot Spring Term – Sound Word vibrations sound waves intensity volume pitch cycles per second longitudinal transverse Definition Movement backwards and forwards Sound energy carried from one place to another in the form of waves The loudness or volume of a sound The loudness of a sound How high or low a note sounds The number of complete forward and backward vibrations made in one second A wave in which the vibrations are parallel (in the same direction) as the transfer of energy A wave in which the vibrations are perpendicular (at right angles) to the direction of transfer of energy Word amplitude frequency Hertz (Hz) wavelength microphone Definition Half the height of a complete wave. The sound wave for a loud sound has a large amplitude The number of waves passing a point each second The unit of frequency. 1 Hz = one wave per second The distance between two successive identical points on a wave A device that detects sound. It converts sound energy to electrical energy Word oscilloscope trace Definition An instrument that shows a picture of a wave on a screen The wave that is shown on an oscilloscope screen Word medium transferred vacuum Definition Any substance a wave travels through When energy, carried by waves, moves from one place to another A completely empty space that contains no particles Word incident absorbed transmitted reflected echo sound intensity meter decimeter decibel (dB) threshold of hearing noise Word ultrasound sonar eardrum cochlea impulses Definition Waves approaching an object Taken in Travels through a medium When a wave bounces back off a surface The reflection of a sound wave A meter that measures the loudness of a sound Another name for a sound intensity meter Unit for measuring the loudness of a sound The quietest sound that can be heard Unpleasant sound Definition Sound waves with frequencies above 20,000 Hz (the upper limit of human hearing) A machine for finding the depth of the sea or finding fish by sending sound waves and listening for echoes A thin membrane inside the ear that vibrates when sound reaches it The part of the ear that changes vibrations into electrical signals Electrical signals carried by a nerve cell Late Spring and Summer Term – Light Word source luminous source non-luminous source ray shadow image Word pinhole camera digital camera pupil retina Word transparent translucent opaque reflect absorb transmit sensor Word plane mirror ray diagram angle of incidence angle of reflection incident ray normal reflected ray scatter Definition An object that creates something Objects that create light Objects that do not create light A narrow beam of light. We draw arrows to represent rays and show the direction in which light is moving A place where light cannot get to, because an opaque object is blocking the light A picture that forms from the light from an object Definition Something that forms an image of an object on a screen when light rays travel through a tiny hole in the front A camera that uses electronics (instead of film) to record an image The hole in front of the eye that light can pass through The part at the back of the eye that converts light into electrical signals Definition Material that light can travel through Material through which a glow of light can be seen Material that does not let light through To bounce off something To take in. If something absorbs light it does not let it back out To send along or pass through An instrument that detects something. In a digital camera, the sensors detect light and convert it to electrical signals Definition A smooth, flat mirror A diagram showing the passage of light rays Angle between an incoming light ray and the normal The angle between the normal and the ray of light leaving a mirror A ray of light going towards the mirror or other object An imaginary line at right angles to the surface of a mirror or other object where a ray of light hits it A ray of light bouncing off a mirror Spread out in all directions Word refraction angle of refraction interface lens concave lens convex lens Word white light filter prism spectrum dispersion Word cone cells rod cells primary colours secondary colours cyan magenta Definition The change in direction when light goes from one transparent material another The angle between the normal and a ray of light that has been refracted The boundary between two materials A curved piece of glass or other transparent material that can change the direction of rays of light A lens which diverges (spreads out) rays of light. It is thinner in the middle than at the ends A lens which converges (focuses) rays of light. It is fatter in the middle than at the ends Definition Normal daylight, or the light from light bulbs Something that only lets certain colours of light through and absorbs the rest A block of clear, colourless glass or plastic, usually in a triangular shape The colours within white light separated out The separating of the colours in light, for example when white light passes through a prism Definition The cells in the retina that detect different colours of light The cells in the retina that detect low levels of light. They cannot detect different colours of light The three main colours which can make white light (red, green and blue) The colours made when two primary colours mix Secondary colour made by mixing green and blue light Secondary colour made by mixing red and blue light After Summer Exams – Static Electricity Word static electricity Van de Graaff generator nucleus electron neutron proton current electrical conductors electrical insulators discharging Definition A non-contact force that attracts things. It is caused when some materials rub together A device used to produce static electricity The small centre of the atom A particle with a negative charge which is found moving around the outside of the nucleus in an atom A particle with no charge which is found in the nucleus of an atom A particle with positive charge which is found in the nucleus of an atom A flow of charge. In an electric circuit, it is the flow of electrons around the circuit A material that allows a current to flow through it A material that does not allow a current to flow through it The process of removing charge from an object