Land and Water Study Guide
advertisement

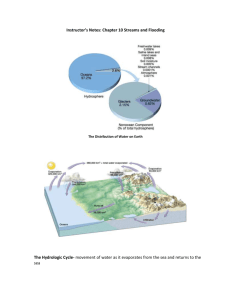
Land and Water Study Guide 1. Water Cycle: the continuous process by which water is used and re-used on earth a. Evaporation: when a liquid (water) is changed to a gas (water vapor) because it has been heated by the sun b. Condensation: when a gas (water vapor) changes to a liquid (water droplets) because it has been cooled c. Precipitation: rain, sleet, snow, or ice that falls from the sky to earth d. Runoff: water that flows over the surface of earth and re-enters oceans, lakes, rivers, and streams e. Groundwater: water that soaks into the ground and flows beneath the earth’s surface 2. Weathering: the breaking down and wearing away of rock a. Caused by 4 main forces: water, wind, ice, and gravity 3. Erosion: when sediment materials (soil, rock, etc.) are picked up and moved to another location a. Also caused by 4 main forces: water, wind, ice, and gravity b. More erosion happens at the beginning of a stream or river (head) because the water is moving faster 4. Deposition: when sediment that has been eroded is deposited (dropped off) in a new location a. More deposition occurs at the end of a stream or river (mouth) because the water is moving slower 5. Sediment: rock, soil, and other earth materials that have been eroded or deposited by moving water 6. Landforms: physical features of earth’s surface a. Examples include mountains, valleys, canyons, plains, plateaus, etc. 7. Aerial view: a view from above; also called a “birds-eye view” 8. Model: a smaller version of something that is too large or too complicated for scientists to study in real life a. Example: stream tables; globe; model car; dollhouse 9. Tributary: a small stream that feeds into a larger river or stream 10. Flood: a large amount of water in a given place at one time a. Flood increases the amount of erosion in an area because there is a larger volume of water flowing through the area 11. Floodplain: the flat land surrounding the banks of a river that is likely to flood; formed by deposition of sediment a. Increased deposition occurs in floodplains, which means that lots of nutrients are deposited in the area; as a result, floodplains are very fertile. 12. Meander: a curvy river or stream that changes directions many times a. Meanders occur in slow-moving streams; fast-moving streams are very straight instead of curvy. 13. Channel: the path or course a river or stream follows 14. Head: beginning of stream or river 15. Mouth: end of a stream or river 16. Slope: a change in height a. A greater slope will cause an increase in erosion, because the force of gravity pulling downward is increased. 17. Delta: a triangle-shaped area of sediment that is formed by increased deposition at the mouth of a stream or river a. Also called an alluvial fan 18. Valley: a U-shaped cut in the Earth’s surface bounded by areas of higher land on both sides a. Usually contains a river or stream. b. Not as deep or steep as a canyon. 19. Canyon: a deep, V-shaped cut in the Earth’s surface with steep sides a. Usually does not contain a river or stream b. Deeper and steeper than a valley c. Typically formed by the constant wearing away of rock and soil by moving water over hundreds or thousands of years 20. Glacier: a slow-moving river of ice a. Glaciers are typically found on steep mountains b. Glaciers are always moving, but at an extremely slow rate—only an inch or so over a long period of time. 21. Dam: a barrier to the flow of water in a river a. Dams may be natural or man-made b. Dams cause increased erosion upstream and decreased erosion downstream 22. Clear-cutting: clearing an area of all its trees and plants a. Clear-cutting causes erosion to increase because there are no plants to hold down the soil with their roots Additional information: About 70-75% of earth’s surface is covered by water. Moving water creates many landforms because this constant movement of water wears away rock and soil. Erosion is increased by flood (increased volume of water), fast-moving water, and the downward pull of gravity. Humans also increase erosion by clear-cutting. Humans slow down erosion by planting vegetation, because the roots of plants act like arms to hold down soil and other earth materials.