Old endocrine and kidney quiz
advertisement

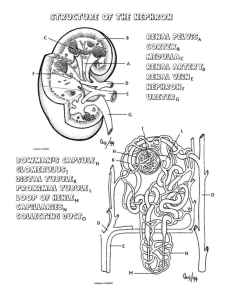
Old endocrine and kidney quiz. 1. A tropic hormone is one that influences another endocrine gland. A. T B. F 2. Hormones can work on cells that a. are inactive b. are already active c. next to them d. b and c e. a and c 3. Most endocrine cells are modifications of _______ tissue. a. connective b. nervous c. epithelial d. muscle 4. Prostaglandins are inflammatory and are inhibited by a. autocrines b. aspirin c. lipid membranes d. lack of receptors 5. Target cells are influenced by hormones because they ___________ a. are clones of hormones b. have receptors that chemically attract them c. have the same enzymatic reactions d. are the same histological origin 6. Which hormone is an antagonist to calcitonin? a. T3 or T4 b. PTH c. vitamin D d. TSH 7. Where is aldosterone secreted? a. adrenal glomerulosa b. adrenal medulla c. kidney d. hypothalamus 8. Which endocrine gland is really only a hormone repository? a. anterior pituitary b. adrenal medulla c. hypothalamus d. posterior pituitary 9. The major physical difference between a cortical nephron and a juxtamedullary one is a. the glomerulus of one is in the cortex and the other is in the medulla b. the cortical nephron has a very long loop of Henle, the other has a short one c. the juxtamedullary nephron has a very long loop of Henle, the other has a short one d. the cortical nephron has a much larger glomerulus 10. The renal capsule and the renal corpuscle differ in that the a. capsule is connective tissue and the corpuscle is part of the nephron b. they are the same thing c. corpuscle surrounds the kidney and the capsule immediately surrounds the glomerulus 11. Which sequence is correct? a. renal artery, interlobular artery, arcuate artery b. interlobular artery, efferent artery, afferent artery c. interlobular artery, efferent artery, vasa recta d. interlobar artery, peritubular capillaries, glomerulus 12. Which sequence is correct: a. Bowman’s capsule, distal convoluted tubule, proximal convoluted tubule b. proximal convoluted tubule, collecting duct, Bowman’s capsule c. glomerulus, proximal convoluted tubule, minor calyx d. glomerulus, proximal convoluted tubule, Bowman’s capsular space, renal pelvis 13. By which process is most material filtered in the glomerulus? a. diffusion b. osmosis c. pressure differences d. ATP pumps 14. What prevents all the components of the blood from being filtered into Bowman’s capsule? a. charge b. lipid solubility c. size d. water solubility 15. Which hormone is directly responsible for an increasing Na+ uptake from the filtrate in the collecting duct? a. ADH b. aldosterone c. renin 16. Where is ADH secreted? a. anterior pituitary b. kidney c. adrenal cortex d. posterior pituitary 17. The renin -angiotensin pathway is largely responsible for a. decreasing blood pressure in conjunction with ANP b. increasing blood pressure in conjunction with aldosterone c. passing kidney stones d. stimulating the hypothalamus to secret ADH 18. What is most likely excreted in the urine when someone drinks a six pack of coke a day? a. bicarbonate ion b. hydrogen ion c. ammonia d. bilirubin 19. What quantity of urine is considered a normal output? a. 500ml b. 1-2 liters c. 50-75 liters d. 180 liters 20. Insoluble crystals of salts in the urine are a. normal kidney functions b. kidney stones c. easy to pass d. a sign of good diet 21. What is the salt concentration of plasma? a. the same as the cells b. the same as urine c. the same as in the glomerular filtrate d. a and c e. a and b 22. What is AgNO3 used to test for? a. Na+ content b. hydrogen ion content c. pH d. specific gravity 23. The ________ is responsible for 65% of Na+ uptake from the nephron. a. glomerulus b. proximal convoluted tubule c. Loop of Henle d. distal convoluted tubule e. collecting duct 24. Osmolarity is a. the same as osmotic pressure b. the number of dissolved solute particles per 1000 ml water c. the number of dissolved particles in 100 ml of water d. the same as hypertonic e. the formula weight of a compound in 1 liter of water