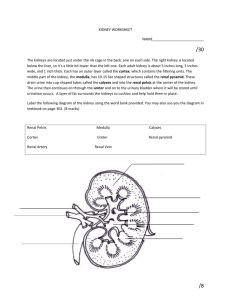
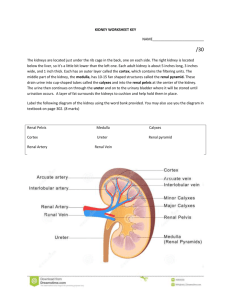
FUNCTION OF KIDNEY
advertisement

DVT 1102 TITLE : KIDNEY NURUL ALIYA BT ROSLAN (D11A030) HASNA NADIA BT HASAN SAZALLI (D11A009) JOSEPHIN SUZANA AK JOHN ASIN LOW (D11B013) NORZUFIKAL BT ZULKIFLY (D11A022) SYAFFIQ BIN OTHMAN (D11B039) ANATOMY OF KIDNEY The Kidney and the Nephron A. Renal Vein B. Renal Artery C. Ureter D. Medulla E. Renal Pelvis F. Cortex 1. Ascending loop of Henle 2. Descending loop of Henle 3. Peritubular capillaries 4. Proximal tubule 5. Glomerulus 6. Distal tubule Efferent Arteriole Proximal Tubule Afferent Arteriole Distal Tubule Glomerulus Bowman’s Capsule Collecting Duct Loop of Henle peritubular capillaries Structure of kidney • Renal artery -takes blood into the kidney • Renal vein -this has a large diameter and a thin wall. It carries blood away from the kidney and back to the right hand side of the heart. • Ureter -it is the tube that carries urine from kidney to the bladder. It orignates from the base of the kidney and terminates in the base of the bladder. Consists of three layers which are the mucosal, muscular and fibrous. • Pelvis -this is the region of the kidney where urine collects. • Medulla -the medulla is the inside part of the kidney. This is where the amount of salt and water in your urine is controlled. It consists of billions of loops of Henlé. • Cortex -the cortex is the outer part of the kidney. This is where blood is filtered. Billions of glomeruli are found in the cortex. • Glomerulus and Bowman's Capsule -a glomerulus is a tiny ball of capillaries. Each glomerulus is surrounded by a "Bowman's Capsule“. This is where ultra-filtration takes place. • Collecting Duct -collecting ducts run through the medulla and are surrounded by loops of Henlé. • Proximal Convoluted Tubules -is the coiled up tube near to the Bowman's capsule. This is the place where all that useful glucose is re-absorbed from the ultra-filtrate and put back into the blood. • Loop of Henlé -this part of the nephron is where water is reabsorbed. • Distal Convoluted Tubules -end of the nephron from the Bowman's capsule. This is where most of the salts in the ultra-filtrate are re-absorbed. HISTOLOGY OF KIDNEY Capsule of the Kidney • A dense collagenous connective tissue envelope. *Masson’s stain 2 regions of the kidney H&E (100x) Renal Corpuscle: Glomerulus • Made up of many parallel capillaries • Blood flows into these capillaries through a wide afferent arteriole and leaves through a narrower efferent arteriole • The blood entering the afferent arteriole is at very high pressure already as it from the renal artery • The pressure actually forces molecules through the glomerular filtration barrier which is responsible for selectively filtering the blood, forming the glomerular filtrate. • The other component of the glomerulus are the mesangial cells: – These give support to the glomerulus – Maintain glomerular basal lamina H&E (400x) • 1. Capsular epithelium 2. Urinary space 3. Glomerulus 4. Macula densa 5. Distal convoluted tubule 6. Proximal convoluted tubule Renal Corpuscle: Bowmans Capsule • Surrounds the capillaries of the glomerulus • Has two layers – Inner visceral layer - Podocytes – Outer parietal layer • It is here where the filtrate is collected before entering the proximal tubule H&E 400x Fenestrated wall of the capillary Proximal Convoluted Tubule • This is the piece of nephron which starts at the Bowmans capsule and ends in the loop of Henle • Has a wall of simple cuboidal epithelium • Has a brush border of densely packed microvilli to increase surface area • Only the proximal convoluted tubules has such a brush border. The other kidney tubules don't • Here at least 99% of what is present in the filtrate as it leaves Bowman's space is recovered Stain: H&E microvilli Transmission Electron Micrograph Loop of Henle • The loop of Henle is made of simple squamous epithelium. • The loop of Henle basically consists of two parallel limbs which descend from the cortex into the medulla. • They are joined at the bottom and as such the flow moves down one limb and up the other in opposite directions. • This sets up a counter current exchange and allows the loop of Henle to be the major site of water reabsorption along the nephron. H&E (240x) H&E (400x) Loop of Henle Blood capillaries Distal Convoluted Tubule • Made of simple cuboidal epithelium • Consists of two parts – Straight part - connects the ascending limb of the loop of Henle to the distal convoluted tubule – Convoluted part - connects the straight part to the connecting duct • No brush border, very few microvilli (difficult to see through light microscope) • Characterized by large open lumen with presence of urine. • The straight portion of the distal tubule contacts the glomerulus forming the macula densa. • Its role is to pump sodium ions out of its lumen into the surrounding intracellular space. It does this by active transport. Convoluted part Macula densa Straight part H&E (400x) Collecting Duct • This structure links the distal tubule to the area cribosa of the papilla into the renal pelvis • Collecting tubules are quite large, with walls formed of cuboidal epithelium. • The epithelium of the collecting ducts is sensitive to antidiuretic hormone (ADH). When ADH levels are high, the walls become very permeable to water. When ADH levels are low, the opposite occurs; duct walls are impermeable to water. Hormonal control of duct permeability adjusts the final volume and concentration of urine voided. H&E Vasa recta (blood capillary) PCT CD Loop of Henle H&E THANK YOU Difference of kidney among the animals Location of the kidney • Other than pig, right kidney is located further cranial than the left and its cranial extremity lies in contact with caudate process of the liver and right hepatic lobe. • Lies in a fossa of the liver which helps to limit its movement. • Left kidney not present in the liver. • In ruminants, considerable size of the rumen pushes the left kidney towards the right half of the abdomen where it is suspended by the long and mobile mesonephros caudal to the right kidney. Shape of the kidney • In cat, dog, sheep and dog, the shape of kidney is bean-shape • Pig-more flatttened • Horse-right kidney has a valentine heart shape while left kidney has a bean to pyramidal shape. • bovine-irregular oval shape and its surface is fissured to divide the organ into many lobes. • Other animals kidney has a smooth surface except bovine. Structure of the kidney • Ox and pig, medulla and its associated cortex are divided into pyramidal shaped lobes. • Ox has multilobar organization of the kidneys is revealed by the fissure that penetrate the organ between the different lobes from the surface. • In dog, horse and sheep, all the lobes fuse finally to form a single medullary mass with a continuous cortical shell surrounding it. Nephron Segment Renal Corpuscle: •Glomerulus •Bowman's Capsule U-Shaped Tubule Collecting Duct Function Filtration: Glomerulus filters proteins and cells from the blood. All other blood components pass into Bowman's capsule, then into the tubule. Reabsorption and Secretion: Semipermeable membranes surrounding the tubule allow selective passage of particles back into the blood (reabsorption), or from the blood into the tubule (secretion). Collection: Collects all material that has not returned to the blood through the tubular membranes. This material exits the kidney as urine.