5th Grade Science
advertisement

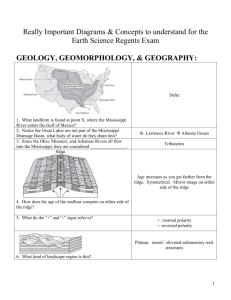
Mrs. Gomez 5th Grade Science Unit: Earth and Space Science Bonus: Flash cards by day of vocabulary test will earn a bonus 50 points in the grade book. Flash cards should have the word on the front, a picture and definition on the back. Cards should be handwritten and neat. Vocabulary – 1. Sedimentary Rocks: rocks that form when sediments (dead plants and animals) are pressed together into layers by heat and pressure. 2. Fossil Fuels: a fuel that is formed from the decayed remains of ancient plants and animals. A non-renewable energy resource. 3. Landform: a natural structure on Earth’s surface. 4. Weathering: the breaking down of rock. 5. Erosion: the movement of weathered materials by water, wind or ice. 6. Deposition: the process by which materials eroded by water, wind or ice are dropped to a new place. 7. Sediment: bits of rock, soil, sand, shells and the remains of organisms. 8. Non-Renewable Resources: resources that nature cannot replace quickly enough to meet people’s needs. We will eventually run out. 9. Renewable Resources: resources that nature produces again and again. 10. Inexhaustible Resources: resources we will never run out of. (wind, solar) 11. Weather: the condition of the atmosphere at a place for a short period of time. 12. Climate: the general weather of an area over a long period of time. 13. Rotation: the spinning of a planet or moon on its own axis. 14. Revolution: one complete trip of a planet around the sun. What you need to know: 1. How are sedimentary rocks formed? Layers of broken rock, sand (or sediment) are piled on top of each other. After millions of years, the pressure of all of the layers solidifies (makes solid) the small pieces into a sedimentary rock. 2. Describe how each of the following landforms is made. (Be sure to include if the change is from moving wind, water or ice) Delta: formed when moving water slows down at the mouth of a river and deposits sediment. As the sediment builds up, a delta is formed when the water must find a new path to the ocean. Canyon: formed when running water weathers and erodes small pieces of rock over millions of years creating a U shaped valley. Sand Dunes: formed when wind blows small sand (sediment) particles and they pile up. Formed fairly quickly in comparison to canyons and deltas. Glacial Valley: formed when large chunks of ice slide over the land. The ice moves everything in its path (trees, rocks, boulders) and creates a “V” shape valley. 3. List the five types of renewable energy and describe each one. a. Solar-energy from the sun. It can be collected in a solar panel and stored in batteries. It is free and causes no pollution. Solar panels can be expensive to purchase. b.Wind-energy from the blowing wind. It can be collected by a wind turbine in which the blades spin and convert wind to electrical energy. The energy is free, but the turbine is expensive to build. Does not cause pollution. c.Geothermal-energy from the heat of the Earth. Can be converted to electricity in power plants. It is free to use, but power plants are expensive to build and maintain. Free and will not run out and does not cause pollution. However, very few places have geothermal energy where we can build power plants. d.Hydroelectric-water turns a generator which converts the movement of water into electricity. Running water is free to use, but it is expensive to build dams. Does not cause pollution. e.Biofuels-energy converted from wood, manure, garbage or waste. It is cheap and created from things we might throw away. Greenhouse gases are produced when biofuels are burned. 4. How can you use fossils to help you describe an area’s past environment? Fossils are evidence of past living organisms. Based on the organism’s features, you can determine the environment (such as ponds, lakes, desert) or what type of plants grew in the environment. 5. What is the difference between weather and climate? Weather is the current conditions of the atmosphere while climate is the average conditions (rainfall and temperature) of a specific area over an extended period of time. 6. Write two statements about our weather. It rained yesterday. The temperature is going to be about 70 degrees today. 7. Write two statements about our climate: The summers in Texas are very hot. Texas is in a temperate climate. 8. Draw a diagram and label the four parts of the water cycle. Evaporation Condensation Precipitation Run-off 9. Draw an example that shows Earth’s ROTATION. What do we get from the Earth’s rotation? The Earth rotates on its axis. This rotation causes our day/night cycle. The Earth rotates every 24 hours. 10. Draw an example that shows earth’s REVOLUTION. What do we get from the Earth’s revolution? The Earth revolves around the sun. The Earth’s revolution causes (and tilt of the Earth on its axis) is what causes seasons. The Earth completes one revolution every 365 days (1 year) 11. Fill in the following Venn Diagram. SUN EARTH MOON Sun: made of gases, hot Center of our solar system Provides heat and light to Earth, Sphere, largest celestial body, rotates Earth:Sustains life, medium size celestial body, 75% water, rocky crust, rotates every 24 hours, revolves around sun every 365 days, sphere, 3 phases of water (solid, liquid, gas), has an atmosphere, few craters Moon:Rocky crust, sphere, ice at the poles, reflects the sun’s light, small celestial body, has many craters, no atmosphere (no weathering), less gravity than Earth What are the moon phases? Full moon > less light> less light>less light > New moon> more light > more light> more light>full moon How often does each phase of the moon occur? Each phase occurs every 28 days.