Unit 4 – DNA Technology and Genomics Part II
advertisement

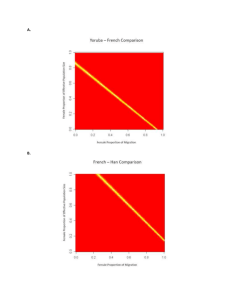
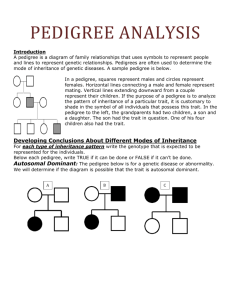
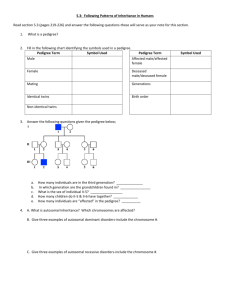
Unit 4 Biology Sex linkage and Pedigrees Guiding Questions 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Why are the X and Y chromosomes important in humans and some other organisms? What gene controls testis formation in humans? What does homogametic mean? What does heterogametic mean? What is a Barr body? 6. 7. 8. 9. What is the WZ chromosome system? What is the XO chromosome system? How does haplodiploidy determine sex? How does environment influence sex determination? 10. Where do males receive their X chromosome from? 11. How does this influence the phenotype of X-linked traits in males? 12. Why do heterozygous females express different alleles of X-linked genes in different cells? 13. What are the characteristics of inheritance of an X-linked recessive disorder? 14. What are the characteristics of inheritance of an X-linked dominant disorder? 15. 16. 17. 18. What is a reciprocal cross used for? How is a reciprocal cross carried out? What results do we expect if the gene is autosomal? What results do we expect if the gene is X-linked? 19. Why are there less Y-linked genetic disorders than X-linked disorders? 20. What is the pattern of transmission for Y-linked inheritance? 21. What is sex-limited inheritance? 22. What is an example of sex-limited inheritance? 23. How is a Barr body formed? 24. Does random inactivation of X chromosomes impact on phenotype? 25. Give an example where random inactivation does impact on appearance? 26. Why do we use pedigree analysis? 27. What modes of inheritance can be identified? 28. What is incomplete penetrance? 29. What are the symbols used in drawing pedigrees? 30. What features characterize a pedigree for an autosomal dominant disease? 31. What are two examples of autosomal dominant diseases? 32. What features characterize a pedigree for an autosomal recessive disease? 33. What are two examples of autosomal recessive diseases? 34. What features characterize a pedigree for an X-linked dominant disease? 35. What are two examples of X-linked dominant diseases? 36. What features characterize a pedigree for an X-linked recessive disease? 37. What are two examples of X-linked recessive diseases? 38. What steps can we use to analyse a pedigree?