Mendelian Inheritance (PowerPoint) Northeast 2011
advertisement

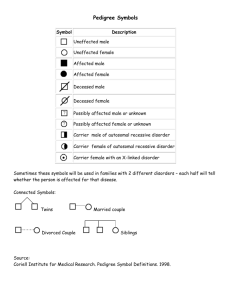
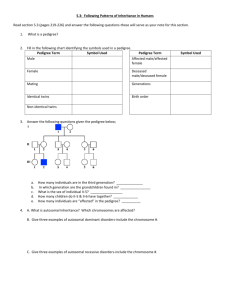
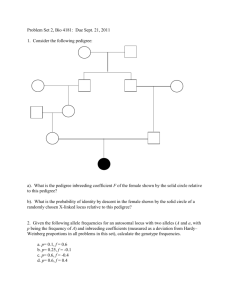
Heredity Teachable Unit: Mendelian Inheritance Group 6: HHMI SI, 2011, Yale University Bob O’Donnell and Kevin Militello (SUNY Geneseo) Cintia Hongay and Jim Schulte (Clarkson) Anne Dranginis and Chris Bazinet (St. John’s, New York) Facilitator Pete Mirabito (University of Kentucky) Goals: Students will understand That segregation of chromosomes gives rise to Mendelian ratios The relationship between genotype and phenotype The principle of a test cross Mendel’s two laws and linkage That most mutations are recessive Inheritance in humans (pedigree analysis) Outcomes: Students will be able to Distinguish sex-linked from autosomal inheritance Predict distribution of gamete genotypes given parental genotype Define the following terms: haploid, diploid, allele, gene, homologs, dominant, recessive, sex-linked, autosomal, genotype, phenotype, wild-type, mutants, hemizygous, homozygous, heterozygous Determine the relationship between genotype and phenotype Solve genetic problems: monohybrid cross, dihybrid cross, sexlinked Solve genetic problems: sum rule, product rule (basic probability) Teachable Tidbit: Case-Study in Human Genetics Recently completed experiments with peas and flies (Mendel’s two laws) How can we learn about human genes when we cannot do controlled crosses? A Case Study in Human Genetics Goal: apply principles of Mendelian genetics to human inheritance Learning Outcomes: You will be able to determine the mode of inheritance from pedigrees. You will be able to apply rules of probability to pedigrees. In the following video, you might observe an important feature of the disease. In the video, what observations did you make? Please brainstorm. Pedigree Symbols Carrier female Royal Family Pedigree Victoria Princess of Saxe-Coberg 1786-1861 Edward Duke of Kent 1767-1820 Victoria Queen of England 1819-1901 Albert 1819-1861 Edward VII Of England Victoria Frederick Wilhelm Sophia of Greece Alexandra George V George VI Princess Margaret Queen Elizabeth Prince Phillip Alice Louis of Hesse Alfred Irene Henry Fred Alix Helena Louise Nikolas of Russia Arthur Lady May Abel Smith Waldemar Prince Henry Olga Tatiana Marie Anastasia Alexie Sigmund of Prussia Leopold Helen Beatrice Henry Alice of Athelon Alfonso XIII of Spain Eugenic Leopold Maurice Rupert Alfonso (adapted from a case study by Yelena Aronova-Tiuntseva and Clyde Freeman Herreid University at Buffalo, State University of New York) Gonzalo Juan Carlos What type of inheritance does the pedigree suggest? A. B. C. D. E. X X-linked dominant X-linked recessive Y-linked autosomal recessive autosomal dominant X X Who are the carriers? XhY I. XhXH XhXH XhXH XH Y II. XH Y XH Y XhY XhY XH Y XH Y XH Y XHY XH Y XhY V. XH Y Xh Y III. IV. XH Y X hY XH Y XH Y Royal Family Pedigree with carrier females revealed If a hemophilic male marries an unaffected female (non-carrier), what is the probability that they have an affected child? A. B. C. D. E. 0 0.25 0.50 0.75 1.00 Thus, the correct answer is 0 If a hemophilic male marries an unaffected female (non-carrier) and they have a daughter, what is the probability that she will be a carrier? A. B. C. D. E. 0 0.25 0.50 0.75 1.00 Thus, the correct answer is 1 Summary 1. Hemophilia is an X-linked recessive disorder 2. Hemophilia is typically expressed in males and carried by females 3. Hemophilia affects all races and ethnic groups equally HW Assignment: Construct a pedigree of a different X-linked disease: SCID by going to homework 3 at course management site http://ghr.nlm.nih.gov/condition/x-linked-severecombined-immunodeficiency Assignment: Construct a pedigree of a different X-linked disease: SCID Draw a pedigree and identify: carriers, affected individuals, informative individuals , and individuals of unknown genotype. Calculate the probability that a female of unknown genotype is a carrier. The mating pair is a carrier woman and an unaffected male. They have 5 daughters and 3 sons: Daughter 1 gets married and has 3 girls and one boy who dies in infancy. Daughters 2 and 3 get married and have two boys each that go on to marry and have one boy each that lives to be an adult. Daughter 4 gets married and has 4 daughters and no sons. Daughter 5 has three sons and two daughters. One of the sons dies in infancy.