Respiratory System
advertisement

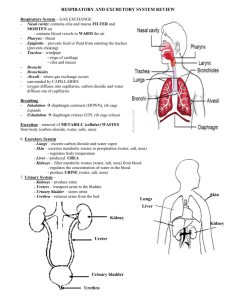
Name: _____________________________________ Unit 12: Respiratory & Excretory Systems Part A: Respiratory System mitochondria oxygen ATP energy Respiratory System nostrils/mouth nasal passages to throat o cilia o pharynx o epiglottis trachea bronchial tubes (bronchi) bronchioles alveoli o gas exchange lungs Breathing inhalation exhalation diaphragm factors affecting breathing rate: o foreign particles o oxygen o carbon dioxide Disorders bronchitis asthma emphysema lung cancer penumonia Per. ________ Part B: Excretory System removing cellular waste Excretory skin o liver o o o System sweat glands urea poisons glycogen -Urinary System kidneys o filteration o nephrons o glomerulus o Bowman’s capsule ureters urinary bladder urethra Metabolic Wastes carbon dioxide water urea mineral salts Disorders kidney stones gout uremia cirrhosis of the liver 1 Part A: Respiratory System Why do we need a respiratory system? To take in oxygen for cellular respiration to create ATP. To take out carbon dioxide as a waste product. Respiratory System nostrils and mouth- air enters nasal passages to the throat lined with mucous membranes- moisten and warm the air cilia- hair-like structures that filter air pharynx- back of the throat o glottis- opening of the windpipe o epiglottis- flap of tissue covering glottis prevent food from entering the glottis and trachea trachea- windpipe kept open by rings of cartilage lined with cilia that beat constantly in one direction moving foreign material out (dust, pollen, and smoke) bronchial tubes (bronchi) bronchioles alveoli moist thin membrane surrounded by capillaries respiratory gases exchanged o blood in capillaries absorb oxygen o blood in capillaries release respiratory wastes, carbon dioxide, and water vapor lungs lined with pleural membrane that secretes moisture; allows smooth movements Breathing movement of respiratory gases between the outside environment and the lunges o inhalation- movement of air into the lungs o exhalation- movement of air out of the lungs lungs have no muscle tissues to help with the movement diaphragm- dome-shaped muscle at the bottom of chest cavity o inhalation- diaphragm moves down, rib muscles move upward and outward englarges the chest cavity force air into lungs o exhalation- diaphragm moves up to original curved position, ribs move in chest cavity smaller force air out of lungs 2 breathing rate affected by: o foreign particles from smoking or air pollution o oxygen o carbon dioxide (most important) increase in carbon dioxide increases breathing rate decrease in carbon dioxide decreases breathing rate Disorders Bronchitis o inflammation of the lining of the bronchial tubes o bronchioles secrete too much mucus and become small and irritated o respiratory cilia cannot clear the passages of the mucus & particles that clog them Asthma o caused by unknown substances or by allergic reactions o bronchial tubes narrow preventing oxygen from entering the lungs o feeling of suffocation o made worse by air pollution, including pollution by nearby smokers Emphysema o lung disease where alveoli become large and break down o lungs become less elastic o amount of air they can hold decreases o shortness of breath with the slightest activity o no cure, but life can be prolonged with proper treatment o smoking thought to be one of the causes Lung Cancer o uncontrollable growth of tumors in the lungs o proven relationship between lung cancer and cigarette smoking Pneumonia o infection of the lungs caused by bacteria or virus o alveoli fill with fluid preventing proper exchange of gases o difficulty breathing Practice: 1. Humans breathe more rapidly during exercise than before it because during exercise the blood contains 1. an increased level of oxygen 3. an increased level of carbon dioxide 2. a decreased number of red blood cells 4. a decreased amount of hemoglobin 2. Smoking may damage the respiratory system because deposits from the smoke can 1. interfere with ciliary action in the trachea 2. trigger the release of antigens by the alveoli 3. block the transmission of impulses that regulate breathing 4. lower blood pressure in the mucous membranes of the bronchioles 3. The human trachea is a passageway that remains open due to the presence of 1. bones 2. ligaments 3. skeletal muscles 4. cartilaginous rings 4. Which statement best describes the human respiratory system? 1. It is composed of a network of moist passageways that permit air to flow from the external environment to the lungs. 2. Each cell of the human body is in direct contact with the external environment, and gas exchange occurs by diffusion 3. The external body surface is kept moist to allow for gas exchange. 4. Gases diffuse across membranes on both the external and internal surfaces of the body. 3 Part B: Excretory System removes cellular wastes from the body Excretory System skin sweat glands excrete perspiration through skin pores perspiration made up nitrogenous wastes (urea), salts, and water controls body temperature liver largest internal organ in the body produces urea (nitrogenous waste) by breaking down excess amino acids removal of poisons ( ex. alcohol) from the blood stores extra sugar as glycogen (animal starch) o converts it into glucose and secretes it into the blood stream whenever your body needs energy -Urinary Systemkidneys bean-shaped organs that lie along the back wall of the abdomen filters in the removal of urea and excess water and salts from the blood regulate concentrations of substances in body fluids o useful substances diffuse out of blood into kidneys and returned to blood before leaving kidneys made up of masses of microscopic subunits called nephrons o artery divided into smaller arteries o glomerulus- ball of capillaries Bowman’s capsule- surrounds glomerulus o water, salts, urea, glucose, and amino acids diffuse in from blood (filteration) o glucose, water, amino acids, and some salts reabsorbed into blood by active transport ureters tube where kidneys send excretions (urine) urine- made of urea and water urinary bladder stores urine temporarily urethra single tube coming from bladder where urine leaves the body Metabolic Wastes wastes produced by metabolic processes o carbon dioxide formed during aerobic respiration o water produced by aerobic respiration and other cellular activities o urea nitrogen waste from the breakdown of amino acids during protein digestion o mineral salts formed from the breakdown of various compounds in the cell wastes leave body cells and are secreted into intercellular fluid then into blood plasma through diffusion blood plasma transports excretions to excretory organs 4 Disorders Kidney Stones o collections of solid material that may block the kidneys, ureters, or bladders Gout o production and deposition of uric acid crystals in joints o painful condition produces symptoms similar to arthritis Uremia o urea and other wastes not filtered out of the blood o body cells become poisoned and there is urine in the blood Cirrhosis of the Liver o damage to liver cells o leads to a type of high blood pressure which can cause serious complications o most common cause- drinking large amounts of alcoholic beverages o hepatitis (inflammation of the liver) can lead to this disease Practice: 1. The nephron is the structural unit of the human 1. lung 2. liver 3. kidney 2. In humans, gout is caused by excess production and deposition of 1. lactic acid 2. uric acid 3. fatty acids 4. intestine 4. amino acids 3. In the diagram, which structure is indicated by letter X? 1. ureter 2. urinary bladder 3. artery 4. urethra 4. In humans, urea is synthesized in the 1. liver 2. alveolus 3. large intestine 4. small intestine Base your answers to 5 and 6 on the diagram which represents the pathway of the blood throughout the body. 5. Within which structure does reabsorption of sodium and chlorine ions occur? 1. 6 2. 8 3. 3 4. 9 6. Within which structure are red blood cells broken down? 1. 1 2. 6 3. 7 4. 9 5 Unit Review: 1. Deposits from cigarette smoke are most likely to interfere with the ciliated mucous membranes located in both the 1. trachea and esophagus 3. nasal cavity and trachea 2. alveoli and liver 4. epiglottis and esophagus 2. Choking on food is most likely caused by an interference with the proper functioning of the 1. diaphragm 2. nasal cavity 3. bronchial tubes 4. epiglottis 3. Diagrams A and B represent structures found in the human body. Diagram B represents the functional unit of which structure represented in diagram A? 1. structure 1 2. structure 2 3. structure 3 4. structure 4 4. Which disease is linked to smoking and results in a reduction in the number and elasticity of alveoli? 1. emphysema 2. asthma 3. bronchitis 4. meningitis 5. In the human respiratory system, bronchioles directly connect the 1. trachea and pharynx 3. nasal cavity and trachea 2. bronchi and alveoli 4. epiglottis and larynx 6. The diagram represents part of a capillary in a specific region of the human body. The region labeled X represents part of 1. a glomerulus 2. an alveolus 3. a villus 4. the liver 7. Which disease is best described by the following statement: A change in the structure of the lung resulting in reduced lung capacity 1. Emphysema 2. Leukemia 3. Angina pectoris 4. Meningitis 6 8. The graph shows the number of push-ups a student completed in each of four 2-minute trials (A-D) during a 15minute exercise period. The concentration of lactic acid in the student’s muscle tissue was most likely greatest during trial 1. A 2. B 3. C 4. D Base your answers to 9 and 10 on the diagram that represents a microscopic view of a functional unit of a kidney. 9. In a kidney, which blood component would not usually pass through the membranes from region A to region B? 1. red blood cells 2. mineral salts 3. urea 4. water 10. The structure indicated by A is known as the 1. cyton 2. glomerulus 3. Bowman’s capsule 4. urinary bladder 11. In the human urinary system which substance is normally present in glomerular fluid and is not reabsorbed into capillaries surrounding kidney tubules? 1. urea 2. water 3. glucose 4. salts 12. In humans, the organ that most directly regulates the concentration of water in the blood is the 1. heart 2. liver 3. pancreas 4. kidney 13. As urine is excreted, muscle contractions of the urinary bladder will cause the urine to pass into the 1. ureter 2. glomerulus 3. urethra 4. Bowman’s capsule 14. During a long-distance run on a hot day, an athlete produces large quantities of sweat. As a result, the kidneys change the rate of urine production. Why is this change important? 1. Decreased urine production increases the amino acids in the blood. 2. Increased urine production removes amino acids produced as a result of running. 3. Decreased urine production allows the body to conserve water. 4. Increased urine production allows more water to remain in the bloodstream. 7 Base your answers to 15 and 16 on the diagram of a portion of the human urinary and circulatory systems. 15. Nephrons are contained within the structure represented by 1. A 3. C 2. B 4. D 16. The structure represented by D would connect directly to the 1. urethra 3. large intestine 2. liver 4. urinary bladder Use the following diagram for questions 16 and 17. 16. Letter A in the diagram indicates a structure known as 1. the ureter 2. a glomerulus 3. an artery 4. a Bowman’s capsule 17. Letter B in the diagram indicates structures that function in the 1. filtration of plasma leaving the blood 2. transport of urine to the ureter 3. reabsorption of water, minerals, and digestive end products 4. transport of blood directly to the glomerulus of a kidney 8