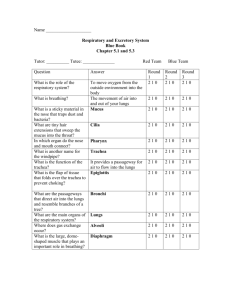
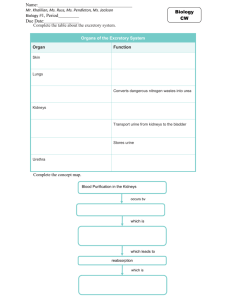
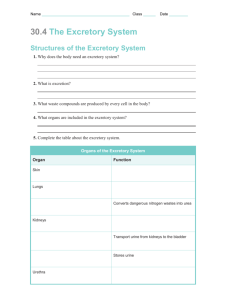
Res/Exc Vocabulary
advertisement
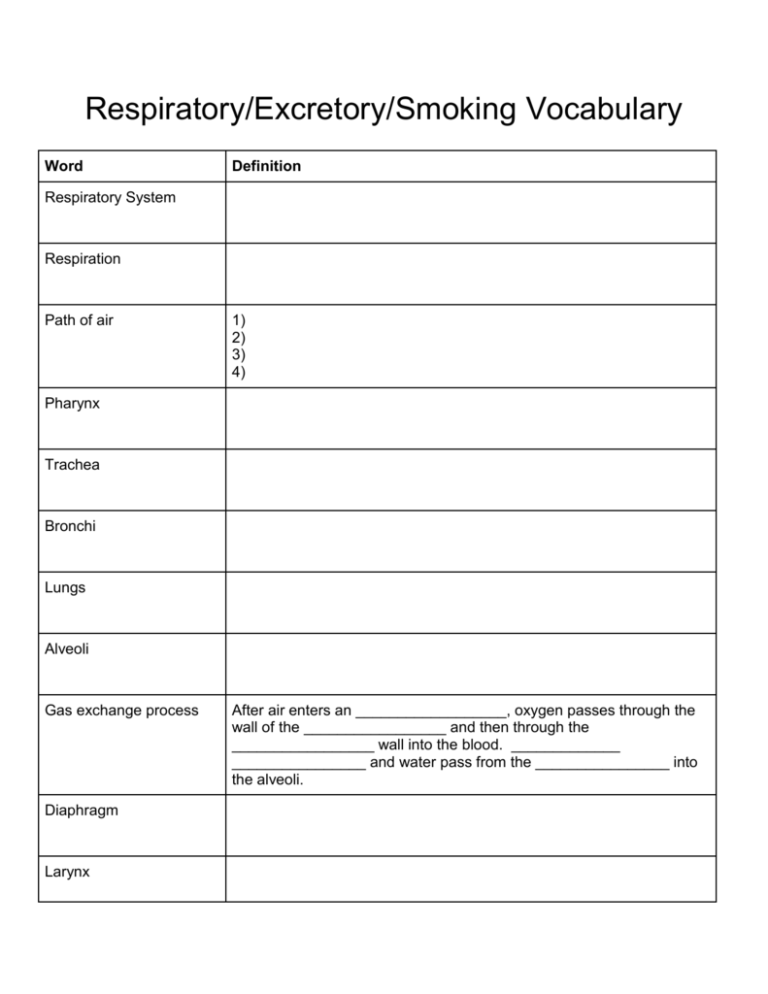
Respiratory/Excretory/Smoking Vocabulary Word Definition Respiratory System Respiration Path of air 1) 2) 3) 4) Pharynx Trachea Bronchi Lungs Alveoli Gas exchange process Diaphragm Larynx After air enters an __________________, oxygen passes through the wall of the _________________ and then through the _________________ wall into the blood. _____________ ________________ and water pass from the ________________ into the alveoli. Vocal cords Tar Carbon monoxide Nicotine Addiction Bronchitis Emphysema Lung cancer Cancerous growths, or ______________, take away space in the _____________ that should be used for _________ ___________. Smoking and heart attacks Compared with nonsmokers, smokers are more than ______________ as likely to have heart attacks. Passive smoking People _______________________ inhale smoke from other people’s cigarettes, cigars, or pipes. Excretory system Excretion Urea Kidneys Urine Ureters Urinary bladder Urethra Nephrons Stages of urine formation 1) 2) Other organs of excretion 1) 2) 3) Respiratory/Excretory/Smoking Vocabulary Word Definition Respiratory System Moves oxygen from the outside environment into the body. It also removes carbon dioxide and water from the body. Respiration Process in which oxygen and glucose undergo a complex series of chemical reactions inside cells. Respiration produces carbon dioxide and water. Path of air 1) Nose 2) Pharynx 3) Trachea 4) Bronchi Pharynx The THROAT, it is the only part of the respiratory system that is shared with another system-----the digestive system. Trachea It is lined with cilia and mucus and is also known as the WINDPIPE. Bronchi The passages that direct air into the lungs. Lungs The main organ of the respiratory system. Alveoli Tiny sacs of lung tissue whose structure is specialized for movement of gases between air and blood. Where GAS EXCHANGE takes place. Gas exchange process After air enters an alveolus, oxygen passes through the wall of the alveolus and then through the capillary wall into the blood. Carbon dioxide and water pass from the blood into the alveoli. Diaphragm Located at the base of the lungs, its a dome shaped muscle that plays an important role in breathing. Larynx Also known as the VOICE BOX, located in the top part of the trachea underneath the epiglottis. Vocal cords The folds of connective tissue that produce your voice, stretch across the opening of the larynx. Tar The dark sticky substance that forms when tobacco burns. Carbon monoxide A colorless, odorless gas that is produced when substances burn like tobacco. It is harmful to inhale because its molecules bind to hemoglobin in red blood cells and take up space needed for oxygen. Nicotine Chemical found in tobacco, it is a drug that speeds up the activities of the nervous system, heart, and other organs. Addiction A physical or psychological dependence on a substance or something. Bronchitis Irritation of the breathing passages in which the small passages become narrower than normal and may be clogged with mucus. Emphysema Disease that destroys lung tissue and causes difficulty breathing. Lung cancer Cancerous growths, or tumors, take away space in the lungs that should be used for gas exchange. Smoking and heart attacks Compared with nonsmokers, smokers are more than twice as likely to have heart attacks. Passive smoking People involuntarily inhale smoke from other people’s cigarettes, cigars, or pipes. Excretory system The system in the body that collects wastes produced by cells and removes the wastes from the body. Excretion The process of removal. Urea A chemical that comes from the breakdown of proteins, its a waste product that is removed by the kidneys. Kidneys Major organs of the excretory system, they eliminate urea, excess water, and other waste materials. Urine Watery fluid produced by the kidneys. Ureters Two narrow tubes that transports urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder. Urinary bladder A sacklike muscular organ that stores urine. Urethra A small tube where urine exits the body. Nephrons The tiny structures that remove wastes from blood and produce urine Stages of urine formation 1) Both wastes and needed materials, such as glucose, are removed from the blood. 2) Much of the needed material is returned to the blood. Other organs of excretion 1) Lungs 2) Skin 3) Liver