P11-7A) - JustAnswer

BE11-1 Cardinal Company has the following obligations at December 31: (a) a note payable for $100,000 due in 2 years, (b) a 10-year mortgage payable of $300,000 payable in ten $30,000 annual payments, (c) interest payable of $15,000 on the mortgage, and (d) accounts payable of $60,000. For each obligation, indicate whether it should be classified as a current liability.(Assume an operating cycle of less than one year.)
(a) A note payable due in two years is a long-term liability, not a current liability.
(b) $30,000 of the mortgage payable is a current maturity of long-term debt.
This amount should be reported as a current liability.
(c) Interest payable is a current liability because it will be paid out of current assets in the near future.
(d) Accounts payable is a current liability because it will be paid out of current assets in the near future.
E11-1 On June 1, Padillio Company borrows $70,000 from First Bank on a 6-month,
$70,000, 12% note.
Instructions
(a) Prepare the entry on June 1.
(b) Prepare the adjusting entry on June 30.
(c) Prepare the entry at maturity (December 1), assuming monthly adjusting entries have been made through November 30.
(d) What was the total financing cost (interest expense)?
Instructions
Prepare the entry to record the sales transactions and related taxes for each client.
(a) June 1 Cash .................................................................. 70,000
Notes Payable ......................................................
700 (b) June 30 Interest Expense ...........................................................
Interest Payable ...................................................
[($70,000 X 12%) X 1/12]
(c) Dec. 1 Notes Payable ...............................................................
Interest Payable ............................................................
(d) $4,200
($70,000 X 12% X 6/12)
Cash ......................................................................
70,000
4,200
70,000
700
74,200
E11-3 Nevin Company publishes a monthly sports magazine, Fishing Preview .
Subscriptions to the magazine cost $20 per year. During November 2006, Nevin sells
9,000 subscriptions beginning with the December issue. Nevin prepares financial statements quarterly and recognizes subscription revenue earned at the end of the quarter.The company uses the accounts Unearned Subscriptions and Subscription
Revenue.
Instructions
(a) Prepare the entry in November for the receipt of the subscriptions.
(b) Prepare the adjusting entry at December 31, 2006, to record subscription revenue earned in December 2006.
(c) Prepare the adjusting entry at March 31, 2007, to record subscription revenue earned in the first quarter of 2007.
(a) Nov. 30 Cash ...................................................................180,000
Unearned Subscriptions ......................................
(9,000 X $20)
180,000
(b) Dec. 31 Unearned Subscriptions ................................................ 15,000
Subscription Revenue .......................................... 15,000
($180,000 X 1/12)
(c) Mar. 31 Unearned Subscriptions .................................................
Subscription Revenue ...........................................
45,000
($180,000 X 3/12)
P11-1A On January 1, 2006, the ledger of Shumway Software Company contains the following liability accounts.
Accounts Payable $42,500
Sales Taxes Payable 5,800
Unearned Service Revenue 15,000
During January the following selected transactions occurred.
Jan. 1 Borrowed $15,000 in cash from Amsterdam Bank on a 4-month, 8%, $15,000 note.
5 Sold merchandise for cash totaling $10,400, which includes 4% sales taxes.
12 Provided services for customers who had made advance payments of $9,000. (Credit
Service Revenue.)
14 Paid state treasurer's department for sales taxes collected in December 2005, $5,800.
20 Sold 700 units of a new product on credit at $52 per unit, plus 4% sales tax.
25 Sold merchandise for cash totaling $12,480, which includes 4% sales taxes.
Instructions
(a) Journalize the January transactions.
(b) Journalize the adjusting entry at January 31 for the outstanding notes payable.
45,000
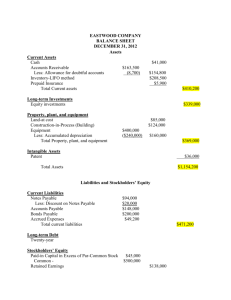
(c) Prepare the current liabilities section of the balance sheet at January 31, 2006. Assume no change in accounts payable.
Please see the attached excel sheet
*P11-6A On July 1, 2006, Kingston Satellites issued $3,600,000 face value, 9%, 10-year bonds at $3,375,680. This price resulted in an effective-interest rate of 10% on the bonds.
Kingston uses the effective-interest method to amortize bond premium or discount. The bonds pay semiannual interest July 1 and January 1.
Instructions
(Round all computations to the nearest dollar.)
(a) Prepare the journal entry to record the issuance of the bonds on July 1, 2006.
(b) Prepare the journal entry to record the accrual of interest and the amortization of the discount on December 31, 2006.
(c) Prepare the journal entry to record the payment of interest and the amortization of the discount on July 1, 2007, assuming that interest was not accrued on June 30.
(d) Prepare the journal entry to record the accrual of interest and the amortization of the discount on December 31, 2007.
(e) Prepare an amortization table through December 31, 2007 (3 interest periods) for this bond issue.
(a)
July 1
2006
Cash ...................................................3,375,680
Discount on Bonds Payable ..............................
Bonds Payable ..........................................
(b) Dec. 31 Bond Interest Expense ......................................
224,320
168,784
($3,375,680 X 5%)
Discount on Bonds Payable ....................
Bond Interest Payable .............................
($3,600,000 X 9% X 1/2)
(c) 2007
July 1 Bond Interest Expense ......................................
[($3,375,680 + $6,784) X 5%]
Discount on Bonds Payable ....................
Cash ..........................................................
(d) Dec. 31 Bond Interest Expense ......................................
[($3,382,464 + $7,123) X 5%]
169,123
169,479
3,600,000
6,784
162,000
7,123
162,000
Discount on Bonds Payable ....................
Bond Interest Payable .............................
7,479
162,000
(e) KINGSTON SATELLITES
Bond Discount Amortization
Effective-Interest Method—Semiannual Interest Payments
9% Bonds Issued at 10%
Semi-
(A) (B)
Interest
(C)
Discount
(D)
Unamor-
(E)
Bond annual
Interest
Periods
Issue date
Interest to Be
Paid
Expense to Be
Recorded
Amor- tization
(B) – (A) tized
Discount
(D) – (C)
$224,320
Carrying
Value
($3,600,000 – D)
$3,375,680
1
2
$162,000
162,000
$168,784
169,123
$6,784
7,123
217,536
210,413
3,382,464
3,389,587
3 162,000 169,479 7,479 202,934 3,397,066
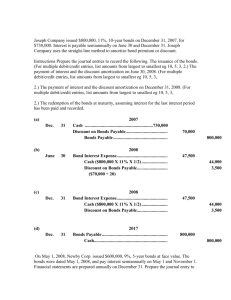
*P11-7A On July 1, 2006, S. Strigel Chemical Company issued $5,000,000 face value,
10%, 10-year bonds at $5,679,533. This price resulted in an 8% effective-interest rate on the bonds.
Strigel uses the effective-interest method to amortize bond premium or discount. The bonds pay semiannual interest on each July 1 and January 1.
Instructions
(Round all computations to the nearest dollar.)
(a) Prepare the journal entries to record the following transactions.
(1) The issuance of the bonds on July 1, 2006.
(2) The accrual of interest and the amortization of the premium on December 31, 2006.
(3) The payment of interest and the amortization of the premium on July 1, 2007, assuming no accrual of interest on June 30.
(4) The accrual of interest and the amortization of the premium on December 31, 2007.
(b) Show the proper balance sheet presentation for the liability for bonds payable on the
December 31, 2007, balance sheet.
(c) Provide the answers to the following questions in letter form.
(1) What amount of interest expense is reported for 2007?
(2) Would the bond interest expense reported in 2007 be the same as, greater than, or less than the amount that would be reported if the straight-line method of amortization were used?
(3) Determine the total cost of borrowing over the life of the bond.
(4) Would the total bond interest expense be greater than, the same as, or less than the total interest expense if the straight-line method of amortization were used?
P11-7A)
(a) (1) 2006
July 1 Cash .........................................5,679,533
Bonds Payable ................................
Premium on Bonds
Payable .......................................
(2) Dec. 31 Bond Interest Expense ............................
($5,679,533 X 4%)
Premium on Bonds
Payable .................................................
Bond Interest Payable ...................
($5,000,000 X 5%)
(3) 2007
July 1 Bond Interest Expense ............................
[($5,679,533 – $22,819) X 4%]
Premium on Bonds
Payable ...................................................
Cash ................................................
(4) Dec. 31 Bond Interest Expense ............................
[($5,656,714 – $23,731) X 4%]
Premium on Bonds
Payable ...................................................
Bond Interest Payable ...................
(b) Bonds payable...................................................................
Add: Premium on bonds payable ..................................
*($679,533 – $22,819 – $23,731 – $24,681)
227,181
22,819
226,269
23,731
225,319
24,681
5,000,000 *
608,302*
5,000,000
679,533
250,000
250,000
250,000
5,608,302
(c) Dear :
Thank you for asking me to clarify some points about the bonds i ssued by
Strigel Chemical Company.
(1) The amount of interest expense reported for 2007 related to these bonds is $451,588 ($226,269 + $225,319).
(2) When the bonds are sold at a premium, the effective-interest method will result in more interest expense reported than the straight-line method in 2007. Straight-line interest expense for 2007 is $432,046
[$250,000 + $250,000 – ($33,977 + *$33,977)].
(3)
(4)
*$679,533 ÷ 20
The total cost of borrowing is as shown below:
Semiannual interest payments
($5,000,000 X 10% X 1/2) = $250,000 X 20 ......................................
Less: Bond premium ($5,679,533 – $5,000,000) .................................
Total cost of borrowing ...............................................................
The total bond interest expense over the life of the bonds is the same under either method of amortization.
$5,000,000
679,533
$4,320,467
If you have other questions, please contact me.
Sincerely,