Solubility Rules & Electrolytes Reference Sheet
advertisement

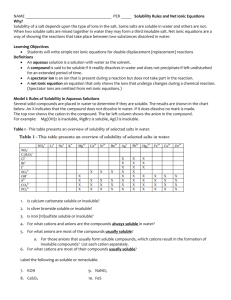
SOLUBILITY RULES A SUMMARY OF SOLUBILITIES RULE 1. Nitrates and acetates are generally soluble. 2. compounds of the alkali metals and the ammonium ion are generally soluble. 3. Chlorides, bromides, and iodides are generally soluble. 4. Sulfates are generally soluble. 5. Carbonates, chromates, phosphates, and sulfites are generally insoluble. 6. Sulfides are generally insoluble. 7. Hydroxides are generally insoluble. EXCEPTIONS No common ones. Silver acetate, mercurous acetate, and lead acetate are moderately soluble. No common ones. The halides of Ag1+, Hg22+, and Pb2+; also HgI2, BiOCl, and SbOCl. PbSO4, SrSO4, and BaSO4 are insoluble. CaSO4, Hg2SO4, and Ag2SO4 are moderately soluble. The corresponding bisulfates are more soluble. Those of the alkali metals and ammonium ion are soluble. Many acid phosphates are soluble, i.e., Mg(H2PO4)2 and Ca(H2PO4)2. Those of the alkali metals and ammonium ion are soluble. The alkaline earth metals are soluble. Cr2S3 and Al2S3 decompose and precipitate as hydroxides. Those of the alkali metals and ammonium ion are soluble. The hydroxides of Ba, Sr, and Ca are moderately soluble, i.e., Ca(OH)2 @20C = 0.02M (Consider theses strong electrolytes in water.) The hydroxide of Mg is only very lightly soluble, i.e. Mg(OH)2 @20C = 0.0002M (Consider this an insoluble substance.) 8. Almost all ionic compounds containing NO2-, ClO4-, ClO3-, ClO2-, and ClO- are soluble. 9. All inorganic acids are soluble. Solubility of organic acids is variable. SOLUTIONS MADE FROM THE ABOVE SPECIES, WHEN SOLUBLE, ARE FOUND TO EXIST AS CHARGED PARTICLES AND THUS CONDUCT ELECTRIC CURRENT. SUMMARY OF STRONG AND WEAK ELECTROLYTES RULE 1. Most acids are weak electrolytes 2. Most bases are weak electrolytes 3. Most soluble salts are strong electrolytes. EXCEPTIONS Common strong acids (strong electrolytes) are HCl, HBr, HI, HNO3, H2SO4, HClO3, and HClO4 Strong base hydroxides (strong electrolytes) are those of Li, Na, K, Rb, Ca, Sr, and Ba. Important weakly ionized salts are HgCl2, Hg(CN)2, CdCl2, CdBr2, CdI2, and Pb(C2H3O2)2. WHEN A SPECIES IS LISTED AS A STRONG ELECTROLYTE, WRITE IT IN IONIZED FORM IN AQUEOUS SOLUTIONS. WEAK ELECTROLYTES ARE WRITTEN IN MOLECULAR FORM IN AQUEOUS SOLUTIONS.