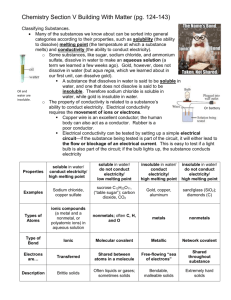
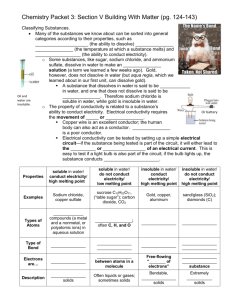
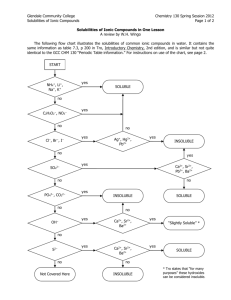
to dissolve in water
advertisement
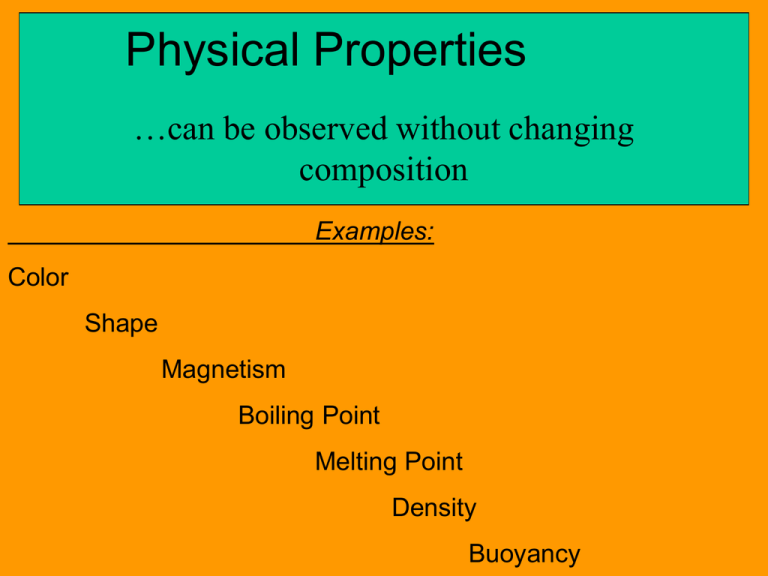
Physical Properties …can be observed without changing composition Examples: Color Shape Magnetism Boiling Point Melting Point Density Buoyancy Property = a characteristic or a quality Composition = the ingredients or make-up of a substance, often represented by a chemical formula Water is composed of Hydrogen and Oxygen Emeralds are composed of Al, Be, Si and O Diamonds are composed of Carbon only Shape and Form • Crystalline: solid with a repeating pattern. • Massive: shapeless, no pattern or order to shape. • Granular: made of grains or tiny crystals Color and Light • Transparent: clear, all light passes through (“see-through”) • Translucent: not clear, some light passes through (“light-through”) • Opaque: light cannot pass through; solid color. • Reflective: light bounces off; shiny • Dull: Non-reflective. Changes in Shape • Rigid: does not change shape • Brittle: rigid and fragile; breaks easily • Malleable: can change shape without breaking • Ductile: can be drawn out or stretched • Elastic: always returns to original shape (“shape memory”) Conductivity: the ability to conduct (carry) heat or electricity Conductors carry heat and electricity well. Insulators prevent or slow the flow of heat/electricity. Viscosity: a fluid’s resistance to flow (how slow it flows) Molasses is very viscous. Miscibility: the ability of two fluids to mix evenly. Juice and water are miscible. Oil and water are immiscible. Miscible vs. Immiscible These terms describe the ability of a liquid to form a solution in a given solvent. Alcohol is miscible in water. Oil is immiscible in water. Soluble vs. Insoluble These terms describe the ability of a solid to form a solution in a given solvent. Salt is highly soluble in water. Chalk is insoluble in water. CuCl2 is soluble in water. CuCl2 is insoluble in toluene. Solubility the ability to dissolve in water to dissolve in water : to form a homogeneous mixture with water Soluble : dissolves in water Insoluble : cannot dissolve in water Boiling Point The temperature at which evaporation or condensation occur. Melting Point The temperature at which melting or freezing occur.