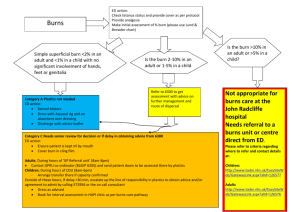
Rehabilitation of Hand Burns
advertisement

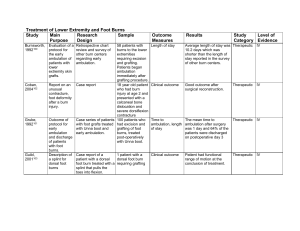
Rehabilitation of Hand Burns Study Main Research Purpose Design Ause-Ellias, 199484 Barillo, 199781 Chung, 199980 Evaluate the effectiveness of mechanical compression in decreasing hand edema. Evaluation of hand volume before and after treatment with a Jobst Intermittent Compression Pump. Treatment was an average of 5.6 treatments over 2 weeks. Evaluation of Case series. results of a Standard treatment surgical and protocol with goal of rehabilitative wound closure within treatment 14 days, range of protocol for motion therapy, burned hands. static splinting, continuous passive motion. Assess the Case series. sensitivity of the Michigan Outcome Questionnaire (MHQ) to clinical change in patient status. Sample Outcome Measures Results 9 chronically edematous hands of 5 patients. Hand volume, hand range of motion Mean pretreatment hand Therapeutic volume was 628.47 ml and post treatment volume was 619.02. This difference was not statistically significant. No statistical change in hand range of motion. IV Average of 220.6 degrees of total active motion at discharge and 229.9 degrees at 3 months after injury. Mean grip strength of 60.8 pounds at discharge and 66 pounds at 3 months. IV 43 patients with 82 hands with severe burns. Average TBSA 19.4%. 89% had hand autografting procedure by day 16. Total active motion (TAM) of the hand and grip strength at the time of hospital discharge. Normal TAM is 270 degrees and greater than 220 degrees is considered functional. A grip strength of greater than 65 pounds is considered functional. 187 patients with MHQ questionnaire and chronic hand patients self-assessment disorders of clinical change. completed a baseline MHQ and a second MHQ 6-18 months later (follow-up 49%) Study Level of Category Evidence Therapeutic The MHQ demonstrated Prognostic good correlation with the patients assessment of clinical change. IV Gulati, 200491 Evaluation of the Joshi External Stabilizing System (JESS). Harvey, 199682 Evaluation of a Case series computer assisted impairment evaluation system for upper extremity function. Evaluation of Case series the use of an external fixator in the treatment of fixed joint contractures. Ilhami, 200392 Retrospective chart review 218 patients with severe burns treated with JESS from 1982-2002 with burns 4 months to 20 years before treatment. 80 upper extremities evaluated with the system. Clinical outcome Complete correction of Prognostic the deformity in the large majority of patients and increased number of patients with new independence with ADL’s after the surgery. IV Time to complete examination and correlation of computer and conventional examination. Computer system demonstrated good correlation coefficients and took less time to complete. Prognostic IV 6 hands in 5 patients previous failed reconstructive surgeries. Clinical outcome Improved hand function and motion after treatment. Therapeutic IV Lowell, 200386 Evaluation of Case study the use of Coban wrap to decrease hand edema Madhuri, 199893 Report of the use of the Ilizarov method for treatment of burn contracture. Manigandan Description of 200388 need to splint the wrist in axillary burns. Case report Description of splinting technique to extend the axillary splint to include the wrist. One subject with a 46% TBSA burn. After surgery one hand was wrapped in Coban and the other in standard gauze dressing. Random selection was used and right hand was wrapped in Coban. Patient was right hand dominant. 44-year-old man with a history of burn at age of 6 months with severe wrist/hand contracture. Treated with Iliazrov device. No subjects Measurement of circumferential measurements of the hand/fingers, active ROM, grip strength, and hand function up to 17 days post-op. There was a larger decrease in circumferential measurement in hand wrapped with Coban. Therapeutic IV Clinical outcome Deformity was corrected Therapeutic over a period of 6 weeks. IV None None IV Therapeutic Maslauskas, Describe the 200473 epidemiology of patients with severe hand burns Case series A total of 246 cases admitted to Kaunas University of Medicine Hospital (Lithuania) during 4 selected years (1985, 1995, 2001, 2002) Clinical outcome Nuchtern, 199579 Description of the treatment of 4th degree hand burns. Case series 25 patients (35 hands) with 4th degree burns treated over a 10 year period Clinical outcome Richard, 199489 Description of Descriptive the fabrication of hand splints. None None 74.4% were male, Prognostic average age 40, median TBSA 12%, early skin grafting in 29.4% and delayed skin grafting (primarily in 1985, 1995) in 70.6%. There was a significant decrease in median hospital length of stay from 35 days in 1985 to 19 days in 2002. 11 hands were treated Prognostic with K-wire immobilization and grafting. 33 amputations in 21 hands including one above elbow, 5 below elbow, 15 MCP level amputations. Evaluation of strength and ROM showed severe impairments in 7 hands and 7 with moderate effects, and 11 with minor sequelae. Described technique to Therapeutic compensate for bandage thickness in the fabrication of hand splints. IV IV IV Sheridan, 199577 Description of Case series the outcome of hand burns 659 patients with Clinical outcome 1047 burned hands admitted to burn center over 10 years. All treated in a uniform way with grafting, Kirschner wires, ROM 2x/day and splinting. 646 burned hands were followed for at least 6 months. Sheridan, 199978 Description of Case series the outcome of hand burns in children 495 children Clinical outcome admitted to burn center with 698 burned hands. Treatment was completed in a uniform way. In patients with deep Prognostic dermal or full-thickness injuries that required grafting, 80.9% were able to perform ADL’s independently without compensatory techniques or equipment and 18.4% were independent with ADL’s with compensatory techniques or equipment. In patients with burns that involved the underlying tendon, joint capsule, and bone 81% were able to perform ADL’s independently with compensatory techniques or equipment and 9.4% were unable to perform ADL’s. In subjects with deep Prognostic burns requiring surgery but not to bone, 85% had normal hand function, 9% had abnormal function but could complete ADL’s and 6% were unable to complete ADL’s. In subjects with burn involving bone requiring the use of K wires, 20% had normal function, 51% had abnormal function, and 25% were unable to complete ADL’s III IV Smith, 199875 Description of Descriptive management techniques for severe hand burns. Torres-Gray, Results of a Descriptive 199676 questionnaire distributed at a breakfast session at the 1993 American Burn Association Meeting. Umraw, 200474 Comparison of Case series 2 methods of hand function assessment. None No outcome 38 respondents Results of questionnaire to questionnaire to identify common post burn deformities and treatment obstacles. Description of treatment of hand burns. Therapeutic The most common N/A deformities were thumb web space contractures, PIP joint contractures, and 5th digit boutoniere deformities. Barriers to treatment included prolonged immobilization, lack of communication and support from physicians, noncompliance with garments and splints 20 patients with Results of evaluation Significant correlation of Prognostic hand burns. All with the Michigan Hand the total scores for the had surgery 2 or Outcomes Questionnaire MHQ and TEMPA. The 3 days after their (MHQ), a subjective self MHQ showed that 68% burn injury. report measure and the of patients reported Evaluation Test d’Evaluation des decreased hand function completed at Membres Superieurs and the level of disability least 3 months des Personnes Agees as measured by the after burn injury. (TEMPA), a Objective TEMPA was low. assessment of hand function. IV IV IV Van Straten, Description of 200090 a new hand splint technique. Case series Van Zuijlen, 199983 Description of Retrospective Case the outcome of Series hand burns. Ward, 199485 Description of Case report the use of Coban pressure wrap in the management of hand burns. The splint was Clinical outcome used on 15 patients and 20 hands. The splint is made of thermoplastic material with a dorsal outrigger that provides passive extension of the MCP joints and active resistive flexion. 88 patients (143 Jebsen hand function burned hands) test. admitted to burn center 2 subjects with hand burns treated with Coban wraps after surgery. Clinical outcome Specific data not reported, but the paper reported on decreased cost of splinting and reduction of therapy sessions while maintaining expected progress toward treatment goals. Therapeutic IV 29 hands had impaired Prognostic function and 114 hands did not have impaired function. Variables with significant predictive value for impaired hand function were finger amputation, age, impaired autograft take, percent full-thickness hand burn surface area, and full-thickness TBSA. There was no relationship between the timing of operation and long-term hand function. Good clinical results Therapeutic III IV WeinstockZlotnick, 200487 Compare the effect of pressure garment work gloves and standard pressure garment gloves on functional hand use. Repeated measures 2 subjects with 3 with the standard burned hands glove serving as the control and the work glove as the experimental condition. Each glove was worn for one week prior to testing and testing was separated by a period of 1-2 weeks. Grip strength, hand function, functional sensation, and functional task scores Decreased grip and Therapeutic pinch strength and functional sensation with work gloves. Better performance with work glove on functional tasks involving gross and static fine-motor movements and simple dynamic fin-motor movements. IV