Name - TeacherWeb

Name
Period
Chapter 1 Study Guide – The First Civilizations
Section 1 – Early Humans
When did history begin?
5,500 years ago
Peleolithic means what in Greek?
“old stone”
What kinds of things did people in the Paleolithic Era hunt and gather?
Animals, fish, insects, nuts, berries, fruits, grains, plants
How did Paleolithic people adapt to their environment?
Created shelters, tamed fire, cooked food, used animal hides for clothing
Explain what early humans used to make tools with? How were these tools used?
Animal bones, stones – tools were used as food choppers, meat scrapers, spear points, knives
Another name for the Paleolithic Era is the “____Old__________ ___Stone____ ____Age__”
Another name for the Neolithic Era is the “_____New_____ ______Stone______ _____Age___________”
What two major changes separated people in the Neolithic Era from people before them?
Farming and domestication
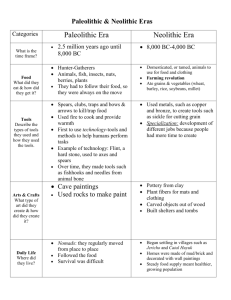
Compare the Neolithic and Paleolithic Ages using the chart on page 14.
Paleolithic cave paintings
Neolithic pottery, carved objects, shelters, tombs Arts & Crafts
Food hunted animals, gathered
Nuts, berries, grains farming, domestication
Adaptation made fire, created language
Simple tools, shelters mud-brick houses, places of worship specialization of jobs, copper/bronze tools
Work of Men hunted herded, farmed, protected the village
Work of Women gathered food, cared for children performed household tasks
1
VOCAB
Historians – people who study and write about the human past
Archaeologists – scientists who hunt for evidence of human past, artifacts
Artifacts – weapons, tools, and other man-made objects
Fossils – plants or animals preserved in rock
Anthropologists – scientists who study human development
Prehistory – time before the invention of writing
Nomads – people who move place to place
Bands – groups of 30 or so members who move together
2
Technology – tools and methods to help humans perform tasks easier
Domesticate – taming animals and plants for human use
Revolution – changes that greatly affect many areas of life
Specialization – development of different kinds of jobs
Section 2 – Mesopotamian Civilization
The earliest known civilizations developed between what two rivers?
Tigris and Euphrates
What are the two nicknames for this area? (You can find them in “quotations”)
“Land between the rivers” “Cradle of Civilization”
What present-day country is this area located?
Iraq
How and why did Sumerians control the twin rivers?
They built walls, waterways and ditches for irrigation in order to grow food and increase population
What material did Sumerians use to build their houses? Why was this material used?
Sun-dried mud brick was used because reeds and mud were easy to get from the rivers
What were the main rights of women?
They could buy and sell property and run businesses
How did men hold power in Sumerian families?
They were head of the household and only boys could attend school
Describe how the following people were influential in Mesopotamia.
Sargon I – King of the Akkadians, he setup the worlds first empire, ruled for over 200 years
Hammurabi of Babylon – Babylonian King, known for his law code or collection of laws
Gilgamesh – Sumerian king who traveled the world performing great deeds
List the contributions/achievements of the Mesopotamian people.
Wagon wheel, plow, sailboat, geometry, number system based on 60, calendar
Why did the first civilizations arise in river valleys?
Good farming conditions, rivers provided freshwater and trade routes
List the groups of people who were found in the classes listed below.
Upper Class Middle Class artisans, merchants, farmers, fishers Kings, priests, government officials
Lower Class enslaved people
VOCAB
Irrigation – a way of diverting water and to crops
City-state – a city and the land around it that had it’s own government
Ziggurat – “mountain of god” or “hill of heaven”
Artisans – skilled workers who made metal products, cloth, or pottery
Cuneiform – Sumerian writing made of hundreds of wedge-shaped marks
Scribes – people who learned the skill of writing and became record keepers
Empire – group of many different lands under one rule
Section 3 – The First Empires
How did the Assyrians organize their army and what weapons did they use?
They had foot soldier with spears and daggers and others with bows and arrows, others were chariot riders or fought on horseback
3
What technique did the Assyrians learn from the Hittites? Describe this process?
Iron making; iron ore was heated, hammered in shape and rapidly cooled
How did Assyrians attack cities and what did they do to people they conquered?
They tunneled walls or climbed them using ladders, used trees as battering rams and set buildings on fire. Conquered people and goods were carried away
How was the Assyrian government setup? What did they do to keep their lands safe?
Provinces were setup and they built roads and stations to protect traders from bandits
Where was the first library built? How many stories/songs did it have inside?
Ninevah, 25,000 tablets of stories and songs
Describe the city of Babylon by writing or drawing.
World’s largest and richest city at the time, surrounded by brick walls, watch towers, palaces, temples, ziggurat, hanging gardens
Why were the Hanging Gardens created? Describe the gardens and how they were maintained.
The gardens were created by Nebuchadnezzar to please his wife, who missed the mountains and plants of her homeland in the northwest
VOCAB
Provinces – political districts that divided empires
Nebuchadnezzar – Chaldean king who controlled Mesopotamia, built Hanging Gardens
Caravans – groups of traveling merchants
Astronomers – people who study the stars, planets, and moons
4